Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previous studies have identified predictors of radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). In this post hoc analysis of the SURPASS study (NCT03259074), we evaluated baseline factors of radiographic spinal progression in patients with radiographic (r-) axSpA treated with secukinumab (SEC, an IL-17A inhibitor) or adalimumab biosimilar (SDZ-ADL, a TNF inhibitor) over 2 years.
Methods: SURPASS, a phase IIIb randomized controlled study included biologic-naïve patients with active r-axSpA at high risk for radiographic spinal progression (high-sensitivity CRP [hsCRP] ≥5 mg/L and/or ≥1 syndesmophyte(s) on spinal radiographs); randomized (1:1:1) to receive SEC (150 or 300 mg; dose blinded) or SDZ-ADL (40 mg; open label) for 2 years. Radiographic spinal progression was assessed by the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS). In this analysis, all patients with data available for radiographs and MRI of the spine at baseline and Week (W)104 were included. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to assess baseline factors associated with the formation of new syndesmophytes (dependent variable). Formation of a new syndesmophyte was defined as a change in mSASSS < 2 (0 or 1) at baseline to ≥2 (2 or 3) post baseline, at any vertebral corner, as determined by at least 2 of the 3 readers. The mean total spine bone marrow edema (BME) and fat lesion MRI scores in non to slow progressors (change in mSASSS < 2) vs moderate to fast progressors (change in mSASSS ≥2) was evaluated.
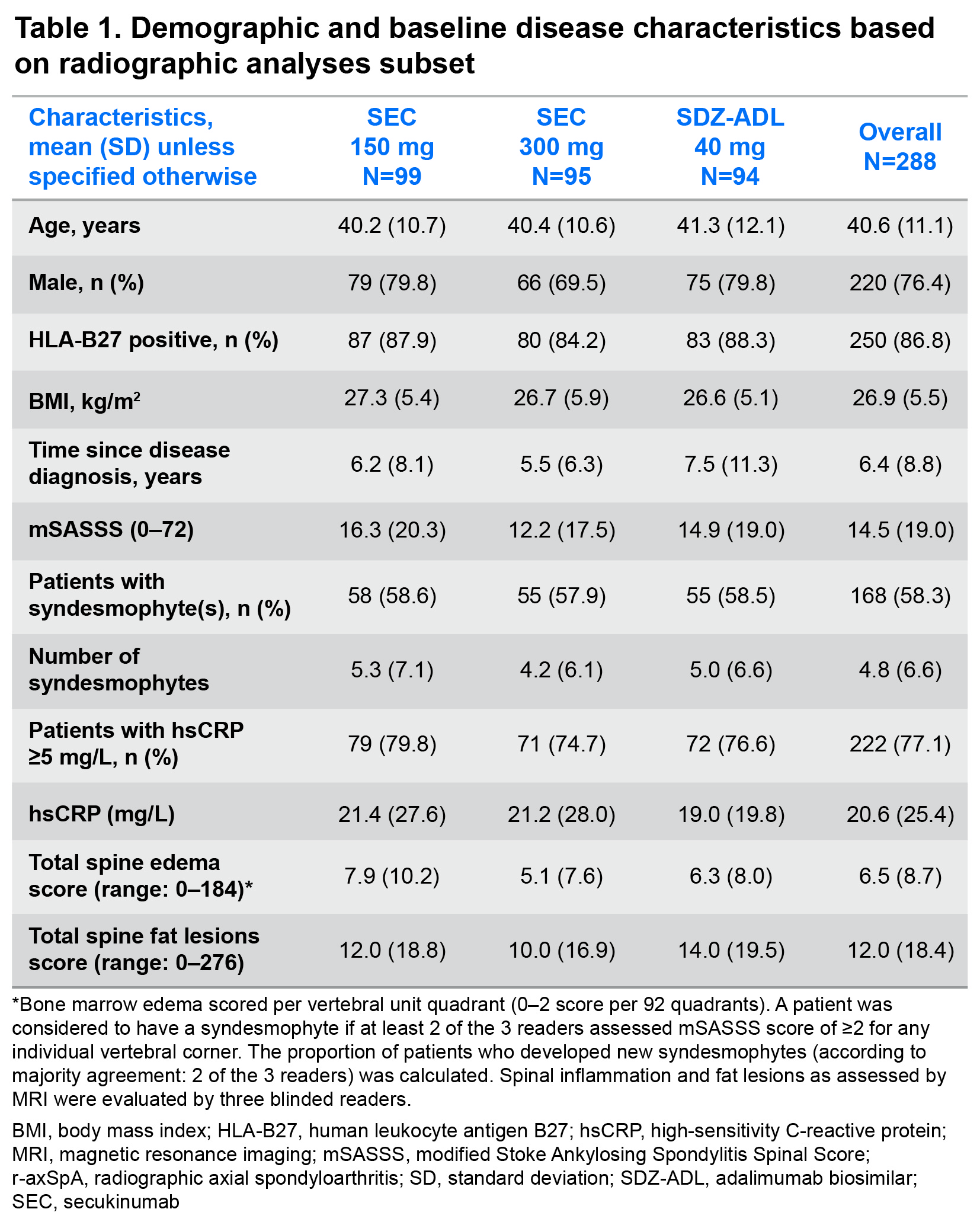
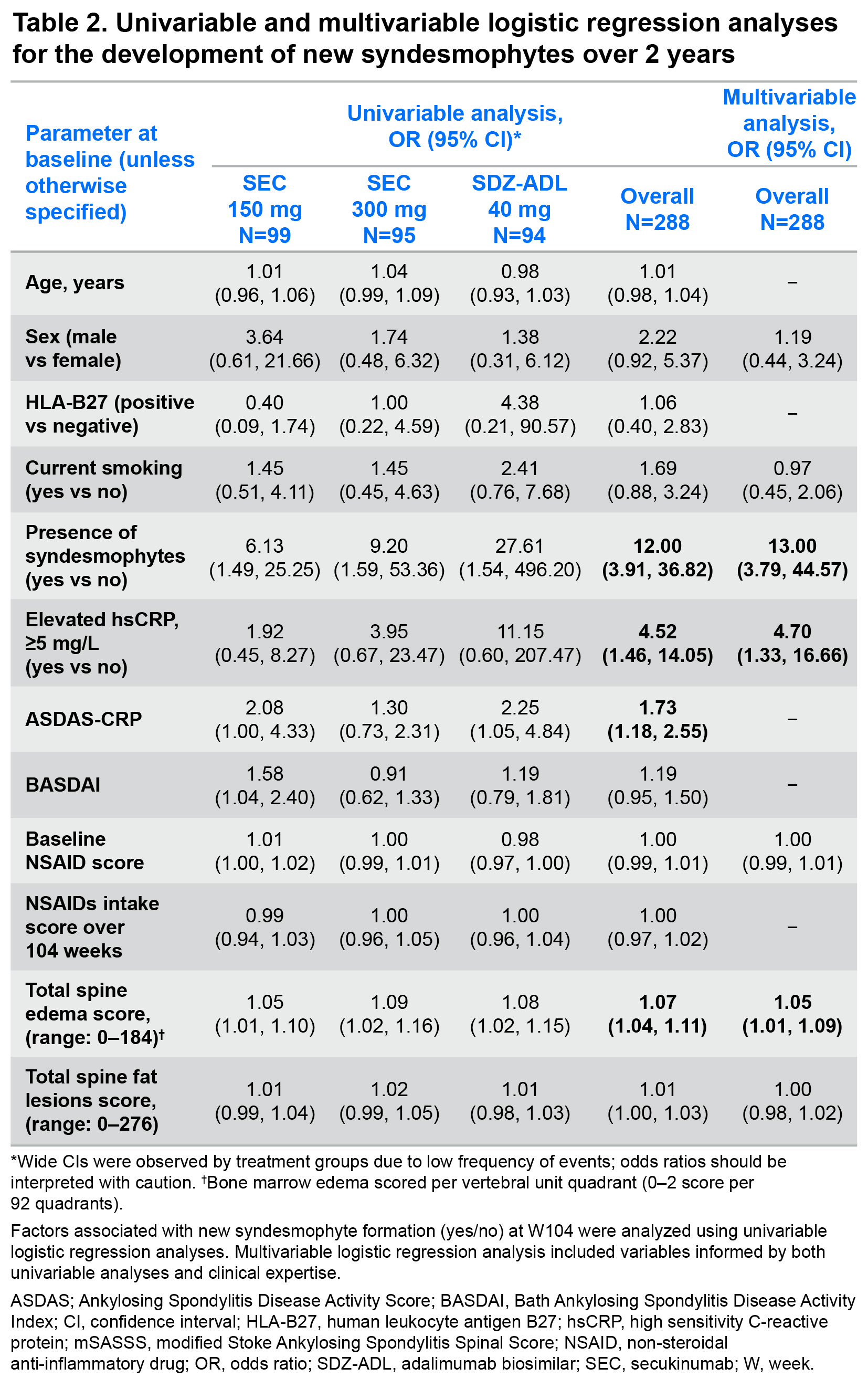
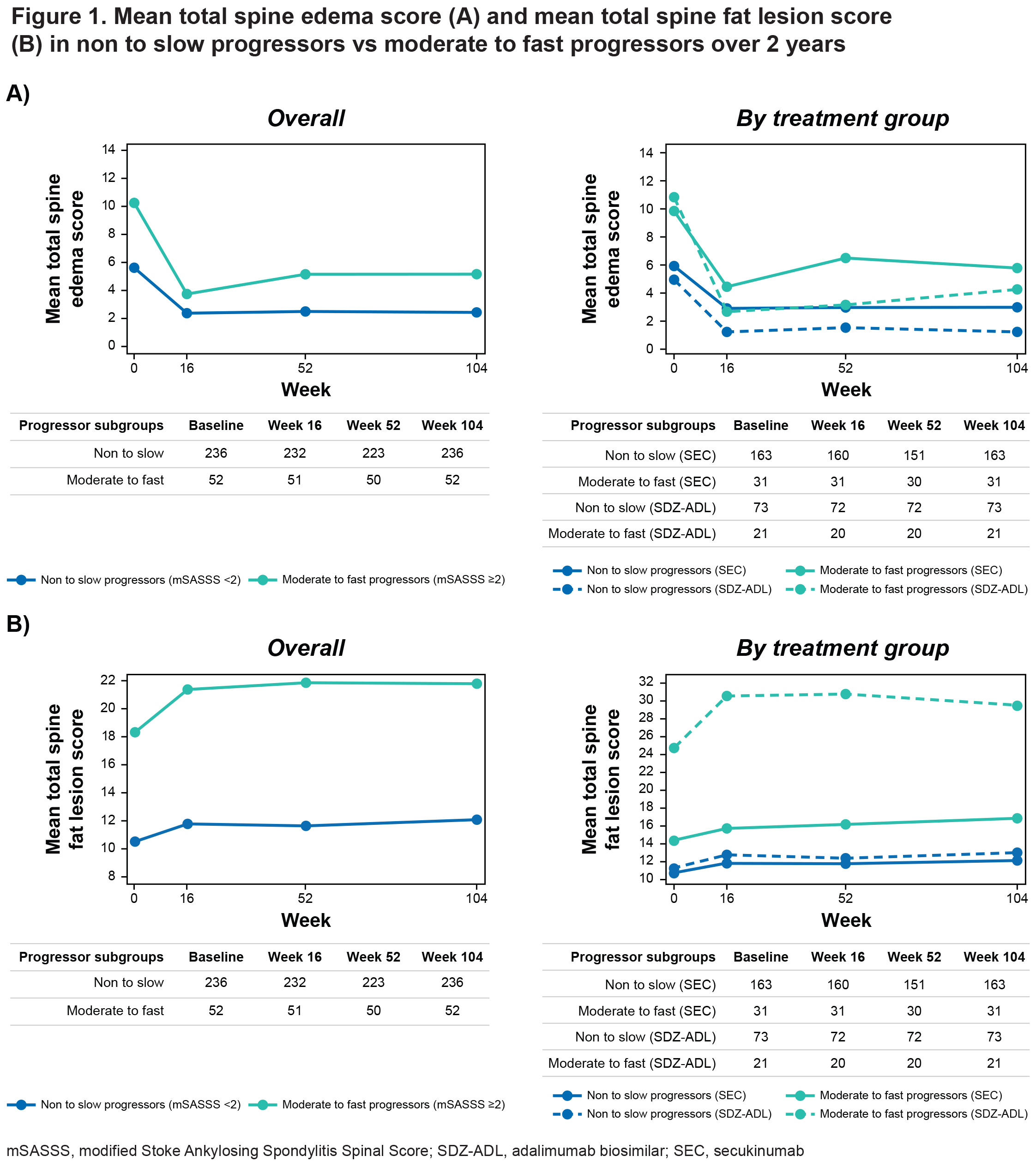
Results: Demographics and baseline disease characteristics are presented for each treatment group (SEC 150 mg: N=99; SEC 300 mg: N=95; SDZ-ADL: N=94) and overall, in Table 1. At W104, new syndesmophytes were observed in 18.2%, 15.8%, and 14.9% of the patients receiving SEC 150 mg, SEC 300 mg, and SDZ-ADL, respectively. In both univariable and multivariable analyses, the presence of syndesmophytes and higher level of inflammatory activity as reflected by elevated CRP, higher Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS), and higher spinal MRI BME scores at baseline were related to the development of new syndesmophytes after 2 years (Table 2). The mean total spine BME score at baseline was higher in moderate to fast progressors vs non to slow progressors. A decrease in BME from baseline to W16 was seen in both subgroups, which remained consistent thereafter up to W104, remaining higher in moderate to fast progressors. Mean total spine fat lesion score was higher at baseline in moderate to fast progressors vs non to slow progressors. An increase from baseline to W16 was seen in both subgroups, which remained consistent thereafter up to W104 with fat lesion score remaining higher in moderate to fast subgroups (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Pre-existing syndesmophytes and high inflammatory activity with objective signs of inflammation were the main drivers of radiographic spinal progression in patients with r-axSpA, irrespective of the treatment with IL-17A or TNF inhibitor over 2 years. Moderate to fast progressors had higher levels of BME and fat lesion scores not only at baseline but also over time vs non to slow progressors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Poddubnyy D, Braun J, Machado P, Navarro Compán V, Gensler L, Hermann K, Quebe-Fehling E, Pieterse C, Readie A, Gaillez C, Baraliakos X. Predictors of Radiographic Spinal Progression in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Receiving IL-17A Inhibitor or TNF Inhibitor Therapy over 2 Years: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase IIIb Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-receiving-il-17a-inhibitor-or-tnf-inhibitor-therapy-over-2-years-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-iiib-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-receiving-il-17a-inhibitor-or-tnf-inhibitor-therapy-over-2-years-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-iiib-study/