Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: To examine and compare baseline predictors of improvement in HRQoL in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with disease onset occurring before age 24 (juvenile-onset SLE or jSLE) and at 24 or older (adult-onset SLE or aSLE) accounting for sociodemographic, comorbidities and disease-specific factors.
Methods: Patients with SLE enrolled in the LUMINA cohort were included. Sociodemographic, clinical, medications, behavioral/psychological and functioning data were obtained at baseline. Predictors of minimally important differences in the physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS) scores from baseline to last follow-up were examined and compared between the groups using logistic regression models. Covariates at baseline included gender, ethnicity, poverty, educational level, the Systemic Lupus Activity Measure (SLAM), the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology (SLICC/ACR) Damage Index (SDI), antimalarial use, proliferative lupus nephritis (Class III and IV lupus nephritis), arthritis, glucocorticoid (highest dose prior to baseline), cyclophosphamide, coping with illness with the Illness Behavior Questionnaire (IBQ), fibromyalgia, fatigue severity scale, and baseline PCS and MCS scores. For the definition of minimally important differences, a previously validated patient-reported anchor-based method was used where improvement was defined as any increase of at least 2.1 and 2.4 points for the PCS and MCS scores, respectively from baseline to last follow-up1. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
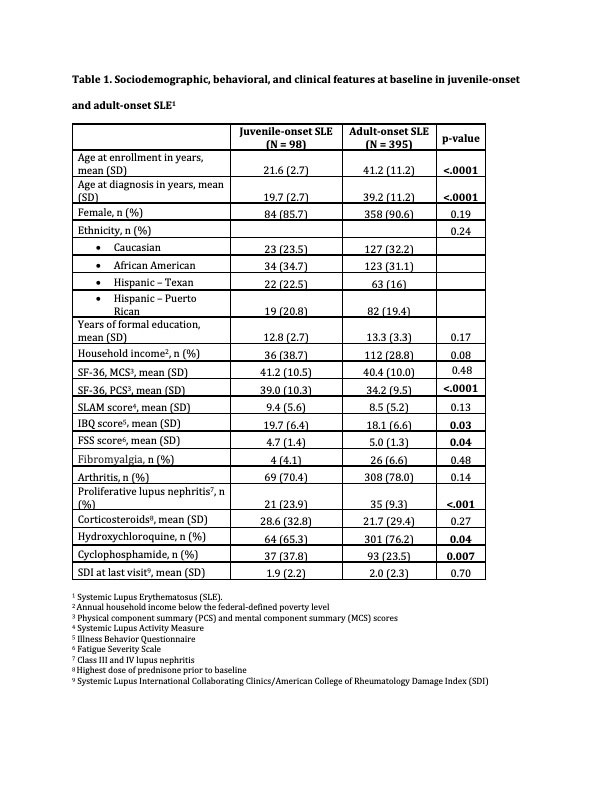
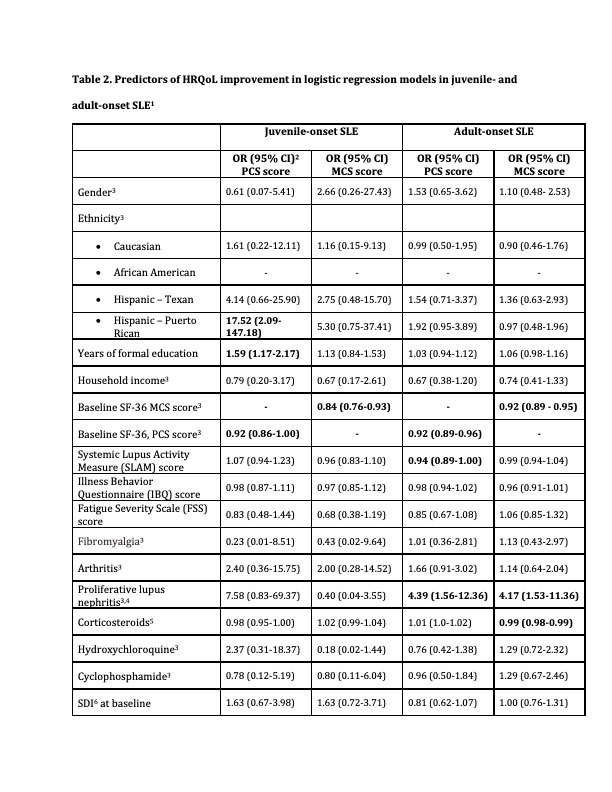
Results: 493 SLE patients were included (98 juvenile- and 395 adult-onset SLE) (Table 1). In both age groups, lower MCS and PCS scores at baseline were associated with clinically meaningful improvement in both scores from baseline to last follow-up. In aSLE, lower dose of corticosteroids prior to baseline and proliferative lupus nephritis were associated with improvement in MCS score whereas lower disease activity and proliferative lupus nephritis were associated with minimal clinically improvement in the PCS score. In jSLE, higher education level and being Hispanic from Puerto Rico, were associated with improvement in the PCS score (Table 2).
Conclusion: Worse HRQoL at baseline predicted subsequent clinically meaningful improvement in physical and mental functioning in both adults with jSLE and aSLE. This may be attributed to treatment effects or improvement in coping skills over time as HRQoL can be affected by different styles of coping. While disease-specific variables were associated with HRQoL improvement in aSLE, sociodemographic features such as education level and race/ethnicity had higher impact on HRQoL course in the juvenile group. The results of this study underscore the need for assessment of social determinants of health in clinical practice, specifically in young adults with jSLE, a vulnerable group transitioning to adult care.
1. Colangelo KJ, Pope JE, Peschken C. The minimally important difference for patient reported outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus including the HAQ-DI, pain, fatigue, and SF-36. J Rheumatol 2009; 36(10): 2231-7.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Borgia R, Ugarte-Gil M, Vilá L, Reveille J, McGwin G, Alarcón G. Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in Adults with Juvenile- and Adult-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results from a Multiethnic US Cohort (LUMINA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-in-adults-with-juvenile-and-adult-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-from-a-multiethnic-us-cohort-lumina/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-in-adults-with-juvenile-and-adult-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-from-a-multiethnic-us-cohort-lumina/