Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate factors associated with objective cognitive impairment in patients diagnosed with Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE). Subjective complaints of changes in cognition are common, being reported by up to 50% of patients with SLE.Previous studies have showed objective declines in immediate memory and total memory.
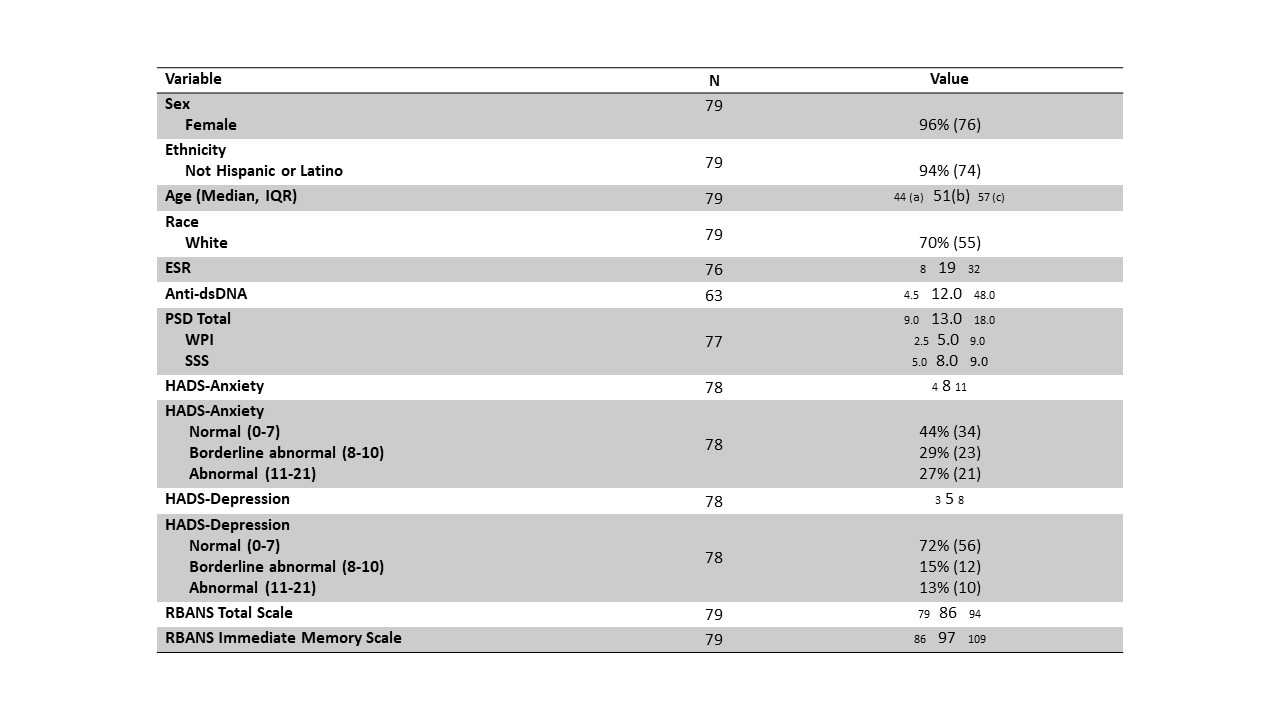
Methods: This study was conducted using baseline data from ClearMEMory (Clearing Lupus Fog with Memantine), an ongoing clinical trial. Seventy-nine participants who reported neuropsychiatric symptoms on pre-screen and came for in-person screening were included. The dependent variable was the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS), a brief, age-normalized, individually administered battery to measure cognitive decline or improvement. Potential predictive variables were sex, race, ethnicity, ESR, anti-dsDNA antibodies, the polysymptomatic distress scale (PSD) and the hospital anxiety and depression scales (HADS-A, HADS-D). Regression models were run to determine covariates that effect the RBANS total and the RBANS immediate memory. The models examined HADS-D scores between 6-12 to determine if there was a statistically significant difference when the scores went from normal to depressed. The models used PSD values 12-16 which are values that cross the threshold for diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
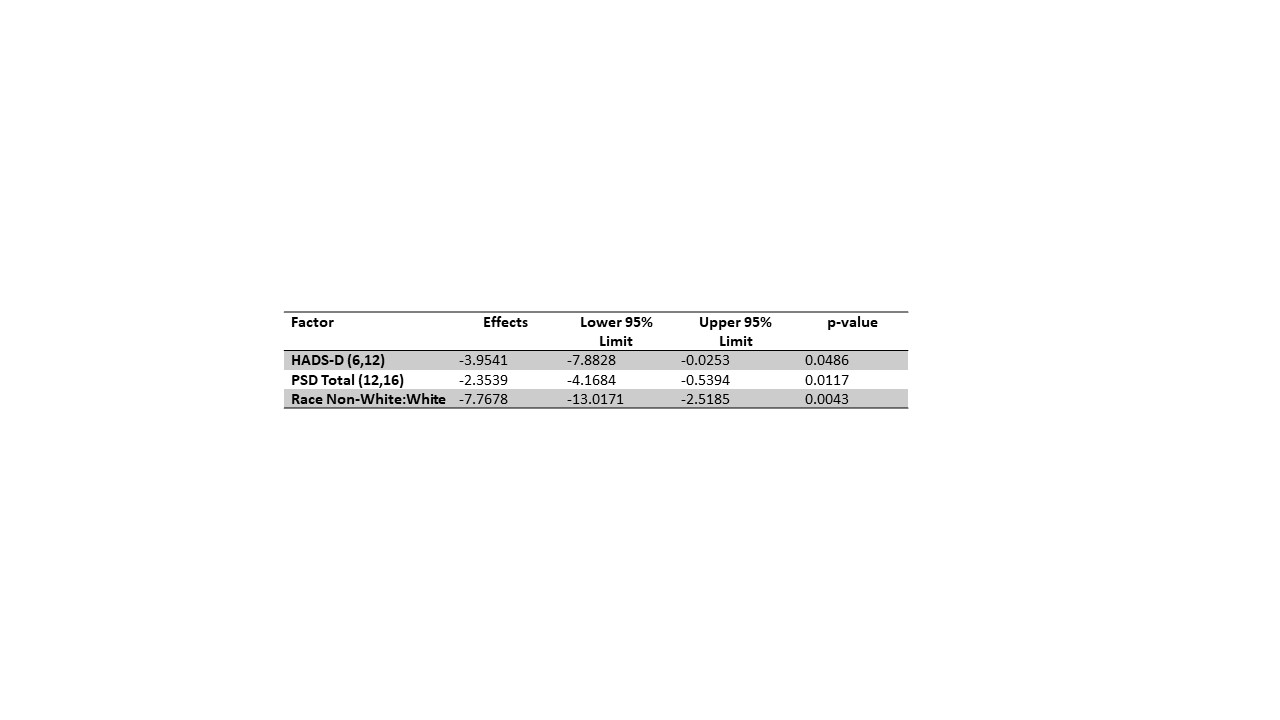
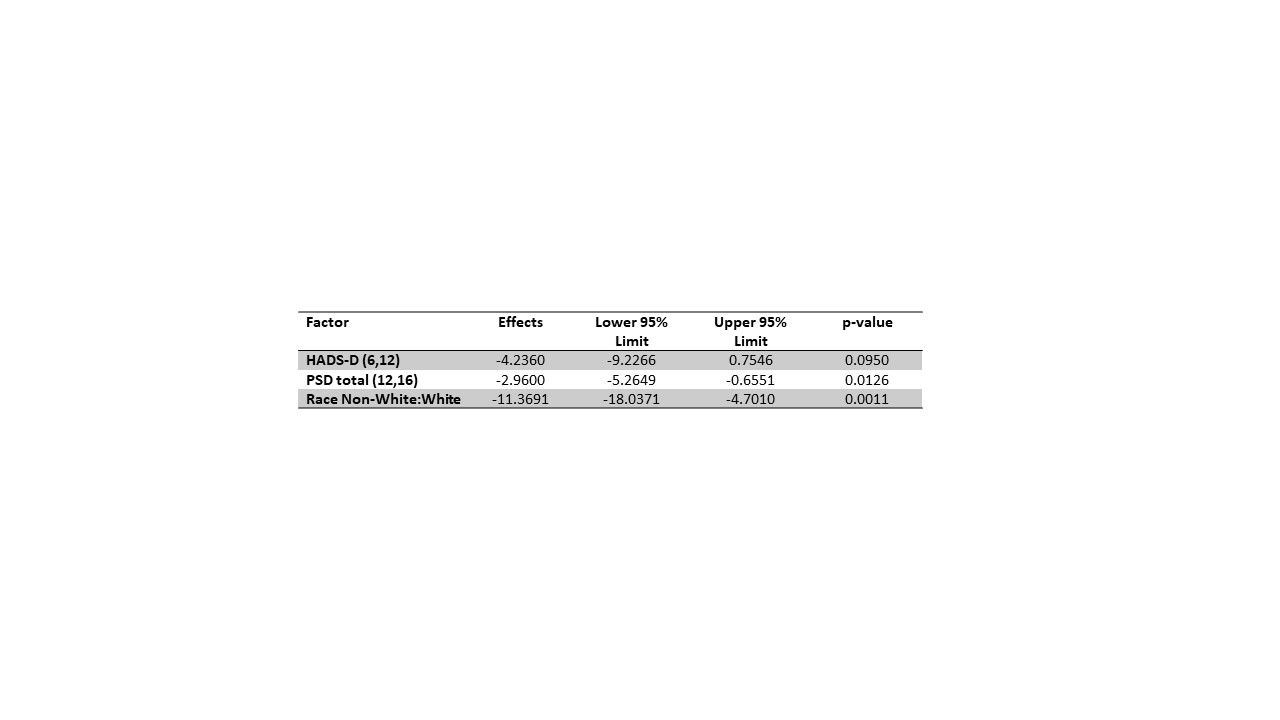
Results: Participant’s median age was 51 years, and they were predominantly female (96%), non-Hispanic (94%) and White (70%) (Table 1). We used linear regression to model the RBANS total score. A model including HADS-D, PSD, and race was the most significant (p = 0.0004) (Table 2). As the HADS-D score increased from 6 to 12, the RBANS total decreased by 3.95 points and as the PSD total increased from 12 to 16, the RBANS total decreased by 2.35 points on average. Non-Whites, when compared to Whites had a decrease in the RBANS total by 7.77 points. The most significant model for RBANS immediate memory included the same factors (p = 0.0004, Table 3).
Conclusion: Results support race, depression, and polysymptomatic distress as significant contributors to the risk of cognitive impairment in patients with SLE. Disease activity did not appreciably affect cognition in this participant sample. As participant scores crossed thresholds for depression or fibromyalgia diagnosis, measurable declines in cognition, particularly immediate memory, were observed. Further studies with different measures of cognition and larger sample size are necessary to understand the impact of race in these models.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee A, Phillips S, Crofford L. Predictors of Cognitive Impairment in Individuals with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-cognitive-impairment-in-individuals-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-cognitive-impairment-in-individuals-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/