Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Etanercept (ETN) is approved in the EU for the treatment of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) categories of polyarticular, extended oligoarticular (eoJIA), enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but little evidence is currently available regarding predictors of clinical remission. We evaluated characteristics that may have predicted the achievement of clinical remission with ETN in the CLIPPER study.
Methods: In this ongoing, Phase 3b, open-label study, pediatric patients with eoJIA (2–17 y), ERA (12–17 y), or PsA (12–17 y) received ETN 0.8 mg/kg once weekly (maximum, 50 mg) for up to 96 weeks. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics that were significantly different (p<0.05) between children in remission or with active disease were analysed post hoc as categorical predictors (i.e., dichotomized continuous characteristics) in univariate logistic regression models; response and disease activity status after 12 weeks of ETN treatment were also considered as predictive factors. Clinical remission was defined with the JIA ACR Wallace 2011 remission criteria or Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score 71-joint reduced count (JADAS71) clinical remission criteria (≤1) persisting for ≥24 weeks.
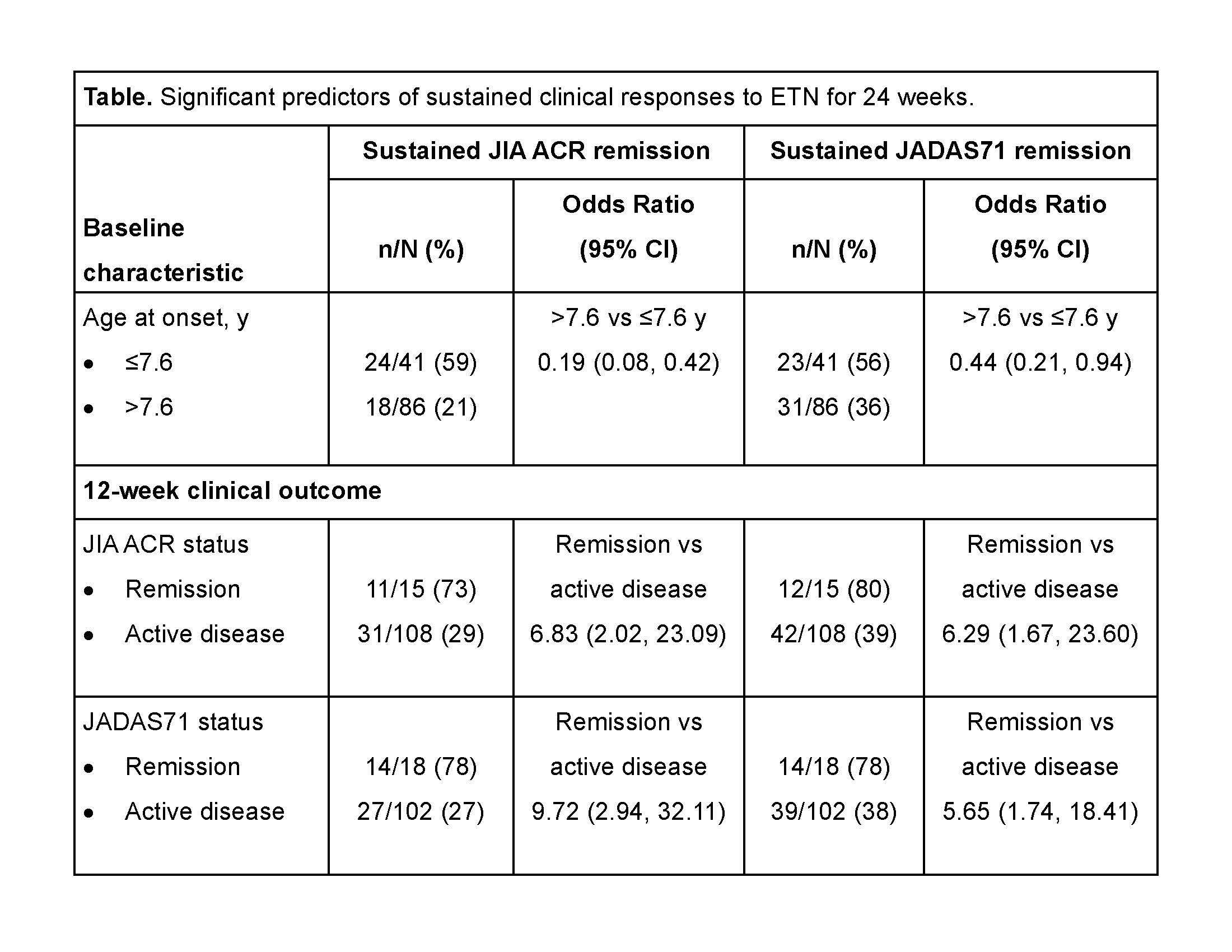
Results: Of the 127 patients enrolled in the trial, 42 (33%) and 54 (43%) achieved JIA ACR or JADAS71 clinical remission over 24 weeks, respectively. In univariate analyses, patients who had lower BMI and were shorter at baseline and those who were younger at the time of disease onset were significantly more likely to achieve JIA ACR and JADAS71 remission (table). Age >11 vs ≤11 years at baseline and C-reactive protein level >2.4 mg/L vs ≤2.4 were significant predictors of JIA ACR remission; HLA-B27+ vs HLA-B27– status and >11 vs ≤11 joints with limitation of motion at baseline were predictors of JADAS71 remission. Induction of JIA ACR and JADAS71 responses at 12 weeks was also predictive of sustained ACR and JADAS71 responses for 24 weeks.
Conclusion: Clinical remission after 12 weeks of etanercept treatment was the most important predictor of sustained clinical response over 24 weeks in pediatric patients with eoJIA, ERA, or PsA JIA subtypes. Trial registration identifying number: NCT00962741/NCT01421069
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ruperto N, Consolaro A, Horneff G, Burgos-Vargas R, Constantin T, Foeldvari I, Vojinovic J, Dehoorne J, Panaviene VV, Susic G, Stanevicha V, Kobusinska K, Zuber Z, Mouy R, Rumba-Rozenfelde I, Dolezalová P, Job-deslandre C, Wulffraat NM, Pedersen R, Bukowski JF, Hinnershitz T, Vlahos B, Martini A. Predictors of Clinical Remission with Etanercept in Pediatric Patients with Extended Oligoarticular, Enthesitis-Related Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis: Findings from the Clipper Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-clinical-remission-with-etanercept-in-pediatric-patients-with-extended-oligoarticular-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-findings-from-the-clipper-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-clinical-remission-with-etanercept-in-pediatric-patients-with-extended-oligoarticular-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-findings-from-the-clipper-study/