Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: With a wide range of disease modifying treatment available, clinical remission is frequently achieved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although a proportion of RA-patients achieves clinical remission on the anchor drug methotrexate (MTX), around 50% of RA-patients require (combination) therapy with a biological DMARD (bDMARD).1 At disease presentation, it is challenging to determine which DMARD-strategy is required for each RA-patient to achieve remission. In this study we combined clinical, laboratory and imaging measures to predict which RA-patients achieve clinical remission on initial MTX-monotherapy and which patients achieve remission on initial treatment with abatacept (ABA) and MTX.
Methods: 1131 ACPA-positive RA-patients from the AVERT 1 and 2 were studied: 388 treated with MTX-monotherapy, 743 treated with ABA+MTX (table 1). Stepwise backward logistic regression was used to determine which clinical baseline characteristics were predictive of DAS28-remission after 6 and 12 months. Clinical characteristics which were included in the model were age, sex, smoking (ever), symptom duration, weight, HAQ-DI and DAS28CRP. Bootstrapping was applied to correct for model-optimism (50 replications). Serological (ACPA, RF, total IgG/IgA/IgM-levels), imaging (MRI-detected synovitis/osteitis/erosions) and genetic (HLA-shared epitope) measures were added to the models to study whether this improved predictive performance. 148 ACPA-positive RA-patients from the Leiden early arthritis cohort were selected as external validation MTX-population.
Results: In the MTX-monotherapy group, 27% and 39% of patients achieved DAS28-remission after 6 and 12-months. In the ABA+MTX group this was 43% and 53%. The consistent factor which appeared predictive for clinical remission in all models and in both treatment groups was baseline DAS28CRP (table 2). Optimism-adjusted model performance (AUROC) for DAS28-remission at 6 and 12-months was 0.66/0.65 in the MTX-group and 0.68/0.59 in the ABA+MTX-group. Adding baseline MRI-detected joint-inflammation, baseline serology or HLA-shared epitope alleles did not significantly improve model performance (table 3). In the Leiden EAC, the MTX-validation population, models had comparable predictive performance; 0.68/0.57 for DAS28-remission at 4 and 12-months (table 2).
Conclusion: Determining which patients achieve clinical remission upon MTX or ABA+MTX treatment remains challenging using clinical and imaging variables at diagnosis. Disease activity at disease presentation appeared most important for achieving clinical remission after 1 year.
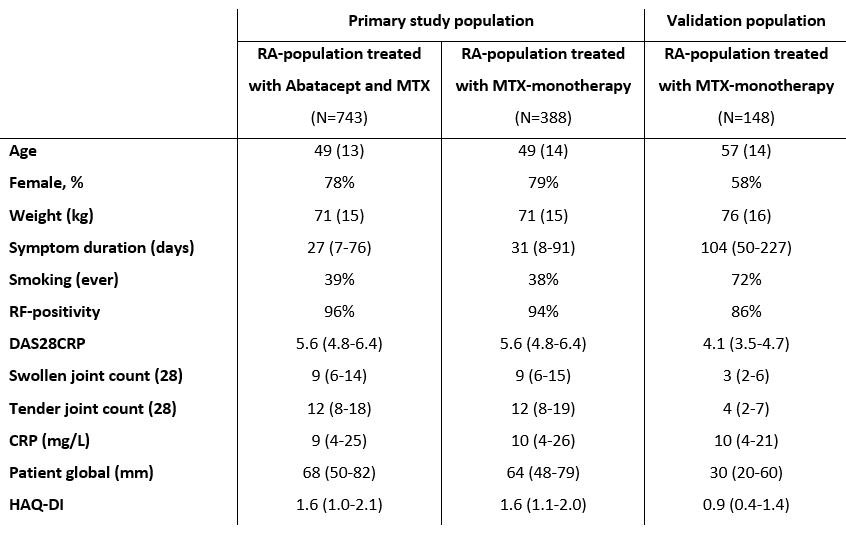
Baseline characteristics of the treatment groups of the primary study population and baseline characteristics of the validation population (MTX-treatment). Values are presented as mean (SD), median (IQR) or as percentage.
CRP: C-reactive protein, HAQ-DI: health assessment questionnaire disability index, IQR: interquartile range, RF: rheumatoid factor, SD: standard deviation
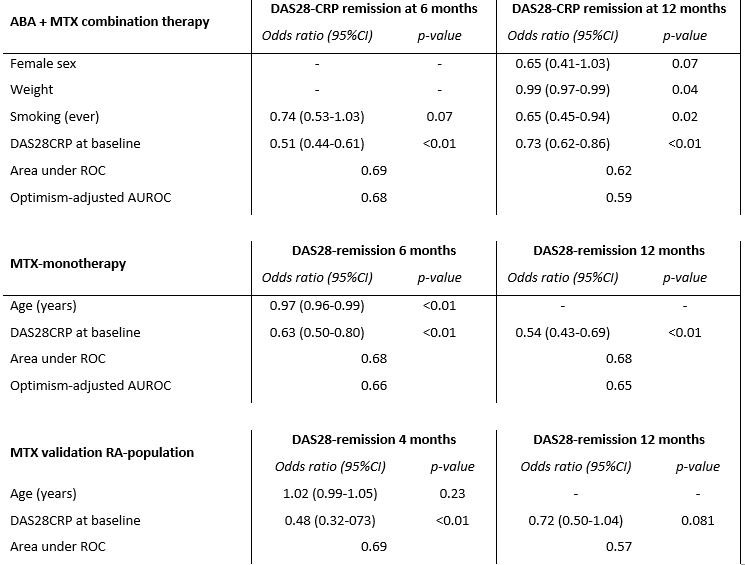
Predictive factors resulting from stepwise backward logistic regression in both treatment groups in the primary study population and in the MTX-validation population. Baseline clinical characteristics included in the stepwise logistic regression were; age, sex, smoking (ever), symptom duration, weight, HAQ-DI and DAS28CRP. Baseline disease activity was a constant factor which appeared predictive for DAS28-remission at both 6 and 12-months in both treatment groups. Optimism-adjusted AUROC, obtained by means of bootstrapping, are presented. Model performance of the selected predictors were comparable in the external MTX-validation population. Missing DAS-information in the validation population was imputed using multiple imputation with chained equations (100 cycles, 30 datasets). Model performance in the validation population was comparable to the primary study population.
DAS: disease activity scores, ROC: receiver operating characteristic curve
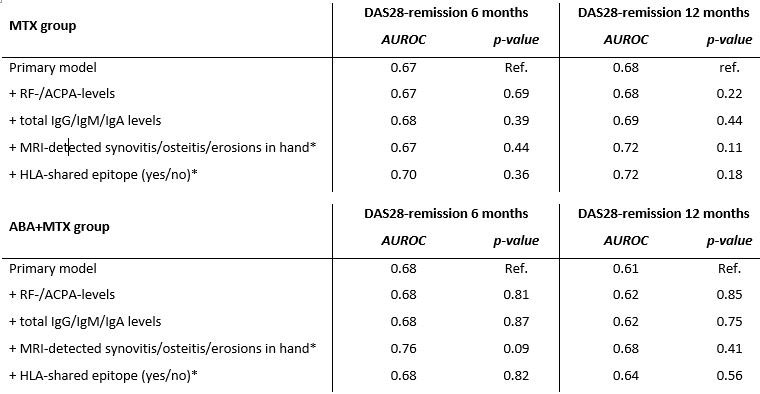
Predictive performance, by means of area under the ROC, of the primary model and of the model in which serological, imaging and genetic information was added. In the MTX-group, model performance of the model for DAS28 remission at 12-months significantly increased after adding MRI-detected joint-inflammation of the hand. The other models did not improve after adding extra serological, imaging or genetic information.
* Data on MRI-detected inflammation and data on SE were only available in a subgroup of the total ABA+MTX population: n=54, n=187
** Data on MRI-detected inflammation and data on SE were only available in a subgroup of the total ABA+MTX population: n=111, n= 545
DAS: disease activity scores, ROC: receiver operating characteristic curve
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Verstappen M, Niemantsverdriet E, Huizinga T, van der Helm-van Mil A, Bergstra S. Predictors of Achieving Clinical Remission in ACPA-positive RA-patients Treated with Abatacept and Methotrexate or Methotrexate Monotherapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-achieving-clinical-remission-in-acpa-positive-ra-patients-treated-with-abatacept-and-methotrexate-or-methotrexate-monotherapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-achieving-clinical-remission-in-acpa-positive-ra-patients-treated-with-abatacept-and-methotrexate-or-methotrexate-monotherapy/