Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: The Assessment
of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) cohort has been established
to validate the ASAS criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and peripheral
spondyloarthritis (pSpA), which have been released in 2009 and 2011
respectively. Since then, the criteria have received broad international
acceptance, but were criticized for potential misclassification (clinical arm)
and lacking data about predictive validity. Our aim was to establish the predictive
validity of an ASAS SpA, pSpA or axSpA classification by either the ‘imaging
arm’ or the ‘clinical arm’ at baseline, by comparing these classifications with
the final diagnosis after follow up.
Methods: The ASAS-cohort included
975 patients collected from 29 ASAS centers worldwide. 22 of the original ASAS
centres (N=909) participated in the follow-up study, with 10 having more than 75%
of complete follow-up data. Eligible patients had either chronic (>3 months)
back pain of unknown origin and age of onset below 45 years (N=658) or had peripheral
arthritis and/or enthesitis and/or dactylitis (N=251). From these, 345 attended
a follow-up visit and of an additional 219 information was obtained by phone [mean
(range) follow-up time: 4.4 (1.9; 6.8) years]. Baseline-classification according
to the ASAS criteria were tested against the rheumatologist’s diagnosis at
follow-up. For patients evaluated by phone, self-reported (change in) diagnosis
was recorded.
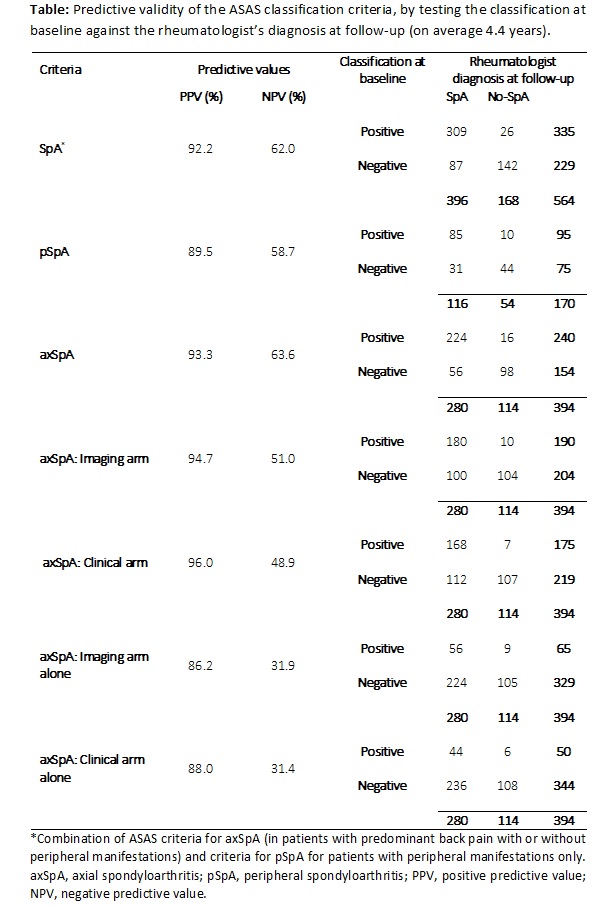
Results: In total 564 patients
(57.8% of the original cohort, 62.0% of the participating centers) were
assessed at follow-up. 396/564 patients received a diagnosis of SpA by the
rheumatologist (280 predominantly axial, 116 predominantly peripheral). Patients
with- and without follow-up data available were comparable regarding the number
of baseline SpA features [mean 2.5 (SD 1.4) vs mean 2.2 (1.4)] irrespective
of the proportion of patients followed in each center. 335 patients fulfilled axSpA
or pSpA criteria at baseline and of these, 309 were diagnosed by their rheumatologist
as ‘SpA’ after follow-up (PPV SpA criteria: 92.2%). Similarly, the PPV of the axSpA
and pSpA criteria was 93.3% and 89.5% respectively. 190 of the 240 (79.2%) patients
fulfilling the axSpA criteria had sacroiliitis on imaging (X-ray and/or MRI) reflecting
the prominent place of imaging in the criteria. Fulfillment of only the ‘clinical
arm’ of the axSpA criteria (thus: imaging negative) yielded a PPV of 88.0%. When
only considering centers with more than 75% of follow-up data available (N=291),
PPV was similarly high, which pleas against ‘channeling bias’.
Conclusion: The positive
predictive value of both the axSpA and pSpA criteria to forecast an expert’s
diagnosis of ‘SpA’ after more than 4 years follow up is excellent. The ‘imaging
arm’ and the ‘clinical arm’ of the axSpA criteria have similar predictive
validity and are truly complementary.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Landewé R, Sepriano A, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J, van der Heijde D. Predictive Validity of the ASAS-Classification Criteria for Axial and Peripheral Spondyloarthritis – a Final Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-validity-of-the-asas-classification-criteria-for-axial-and-peripheral-spondyloarthritis-a-final-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-validity-of-the-asas-classification-criteria-for-axial-and-peripheral-spondyloarthritis-a-final-analysis/