Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease mainly affecting sacroiliac joints and spine. Peripheral arthritis, dactylitis and enthesitis may also occur. Acute anterior uveitis (AAU) is the most frequent extra musculo-skeletal manifestation of axSpA which may lead to severe functional impairment. Moreover, an AAU attack can be the presenting symptom that may lead to diagnosis of axSpA. However, there is limited data regarding the factors predicting the development of AAU attacks in patients with axSpA.
Purpose: To examine the factors associated with the AAU attacks in patients with axSpA in a longitudinal axSpA cohort.
Methods: In total 469 axSpA patients (272 [58%] male; 297 [63%] with AS and 172 [36%] with non-radiographic (nr)-axSpA) who have followed up to three years were included in this observational study. Baseline disease characteristics and follow-up data including the development of AAU attacks, concurrent disease activity, serum CRP levels, usage of conventional synthetic and biological disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (cs-DMARD, bDMARD) were collected on 3, 6, 12, 24 and 36th months. The longitudinal relationship between AAU attacks (dependent) and potential predictive factors (independent) tested by using generalized estimating equations (GEE) which is a technique for longitudinal data analysis allowing the use of all available data even deviated from normality.
Results: Overall, 99 (%21) of 469 patients had experienced at least one AAU attack (77 [78%] on history and 31 of them also in follow up, 11 patients [11%] presented with AAU in their first visits and 11 have developed their first AAU attacks on follow up) (Table 1). In total 89 AAU attacks were observed during follow up (35 attacks on presentation, 10 attacks at 3nd month, 4 attacks at 6th month, 12 attacks at 12ndmonth, 16 attacks at 24th month and 12 attacks at 36th months of follow up). At baseline patients with the AAU history were older (p=0.001), had more peripheral arthritis (p< 0.001), higher BASMI score (p=0.007), and higher serum CRP levels (p=0.016). Those patients with a positive AAU history have been also using cs- and bDMARD more commonly. Univariate longitudinal analysis revealed that the development of AAU attacks was significantly associated with the history of AAU, male gender, the presence of extraspinal involvement, concomitant cs-DMARD usage, BASDAI scores, ASDAS-CRP, and PGA of disease activity. However, multivariate analysis showed that the presence of AAU history and concurrent disease activity assessed by BASDAI were the only independent determinants of the development of AAU attacks in axSpA patients (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our results showed that AAU attacks were significantly higher in axSpA patients who had history of AAU and higher disease activity. Moreover, the presence of AAU might have an impact on treatment in axSpA patients.
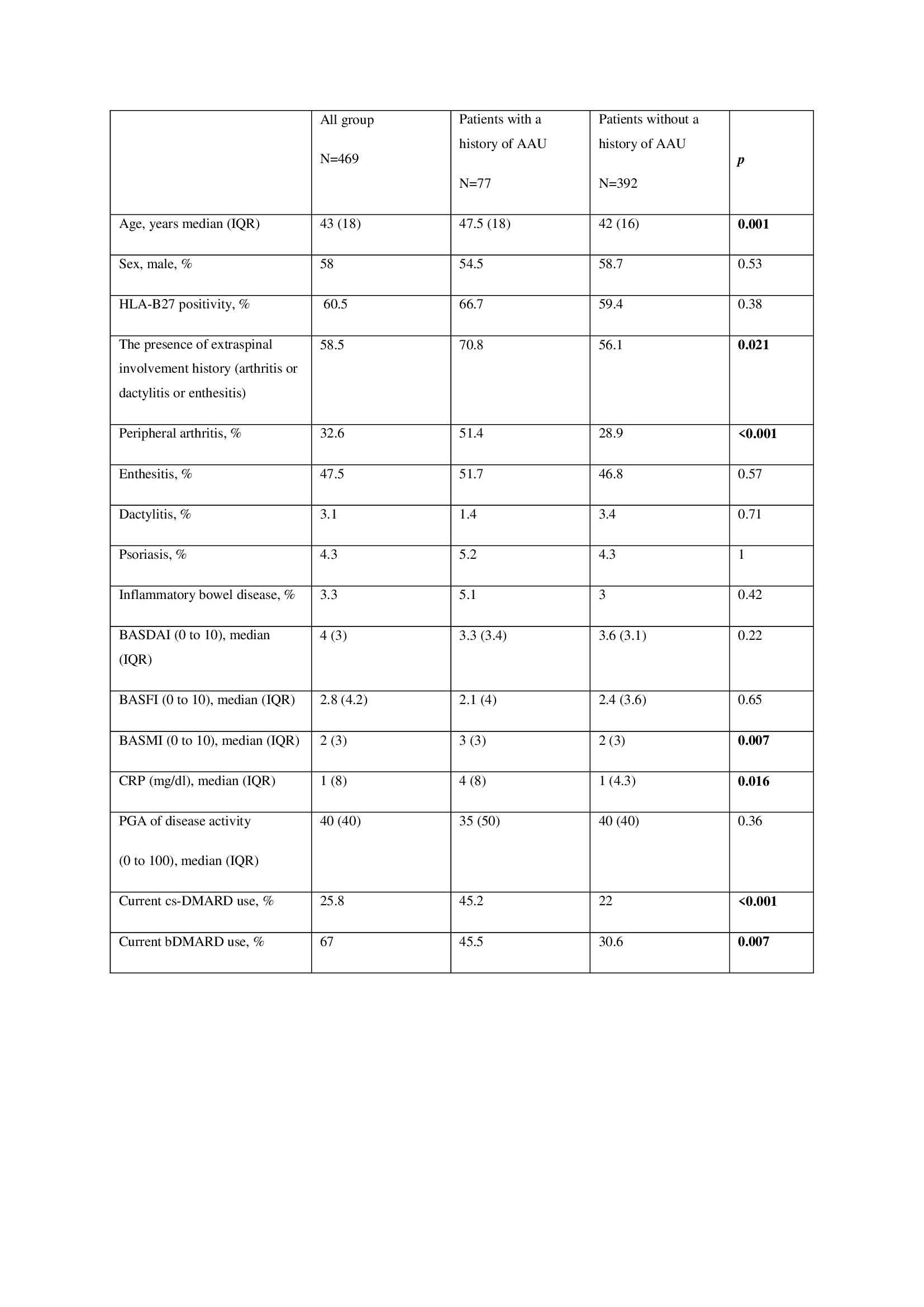 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of axSpA patients with and without history of uveitis
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of axSpA patients with and without history of uveitis
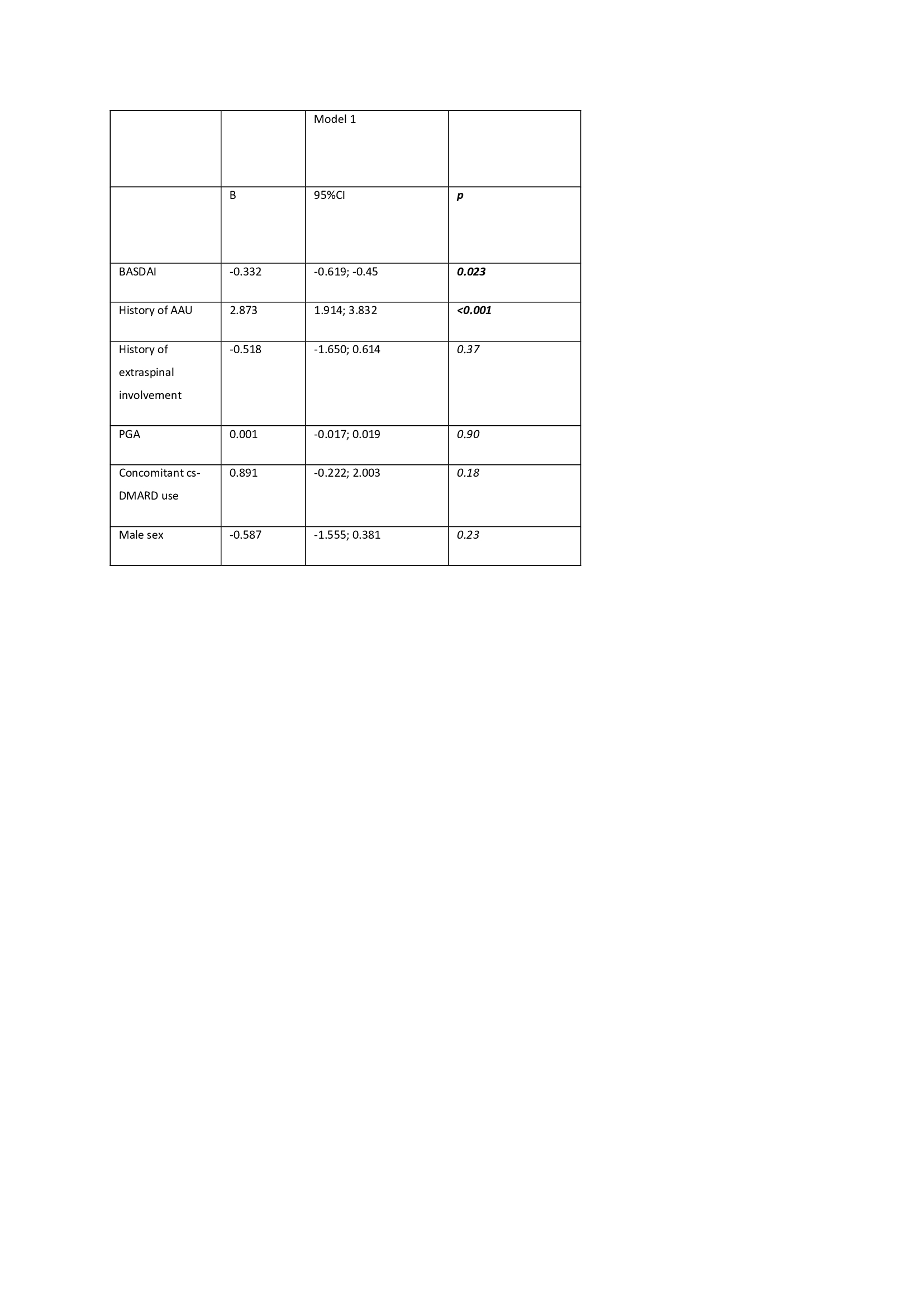 Table 2. The factors assosiated with uveitis attacks in patients with axSpA
Table 2. The factors assosiated with uveitis attacks in patients with axSpA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cinaklı H, Ediboglu E, Otman Akat E, Solmaz D, Alp G, Erpek E, Gücenmez S, Ozmen M, Akar S. Predictive Factors for the Development Acute Anterior Uveitis Attacks in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis; The Results of a Longitudinal Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-factors-for-the-development-acute-anterior-uveitis-attacks-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-the-results-of-a-longitudinal-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-factors-for-the-development-acute-anterior-uveitis-attacks-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-the-results-of-a-longitudinal-analysis/
