Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Methods: Results: Enrolled pts (FAS; N=733) had longstanding disease (mean±SD 8.9±9.1 years), HDA (mean±SD DAS28[ESR] 6.3±1.1, RAPID3 16.1±5.6, CDAI 40.2±13) and over half (55.5%) were prior TNF inhibitor failures. At Wk12, 64.7% (238/368) and 76.4% (279/365) of pts randomized to RAPID3 and CDAI, respectively, were classed as responders (Table 1). At Wk52, 31.5% (75/238) of Wk12 RAPID3 responders, and 32.3% (90/279) of Wk12 CDAI responders, achieved DAS28(ESR) LDA or better (Table 1) demonstrating similar positive predictive values of these measures. No new safety signals were observed. Conclusion: In pts with chronic, severe RA the physician-based assessment detected greater CZP response at Wk12 compared with the patient-reported tool. Although the two outcome measures were not statistically comparable at Wk12, the positive predictive value for LDA at Wk52 for both assessments was similar. Further analysis is needed to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of these measures for clinical disease activity assessments and treatment decisions in RA. References: 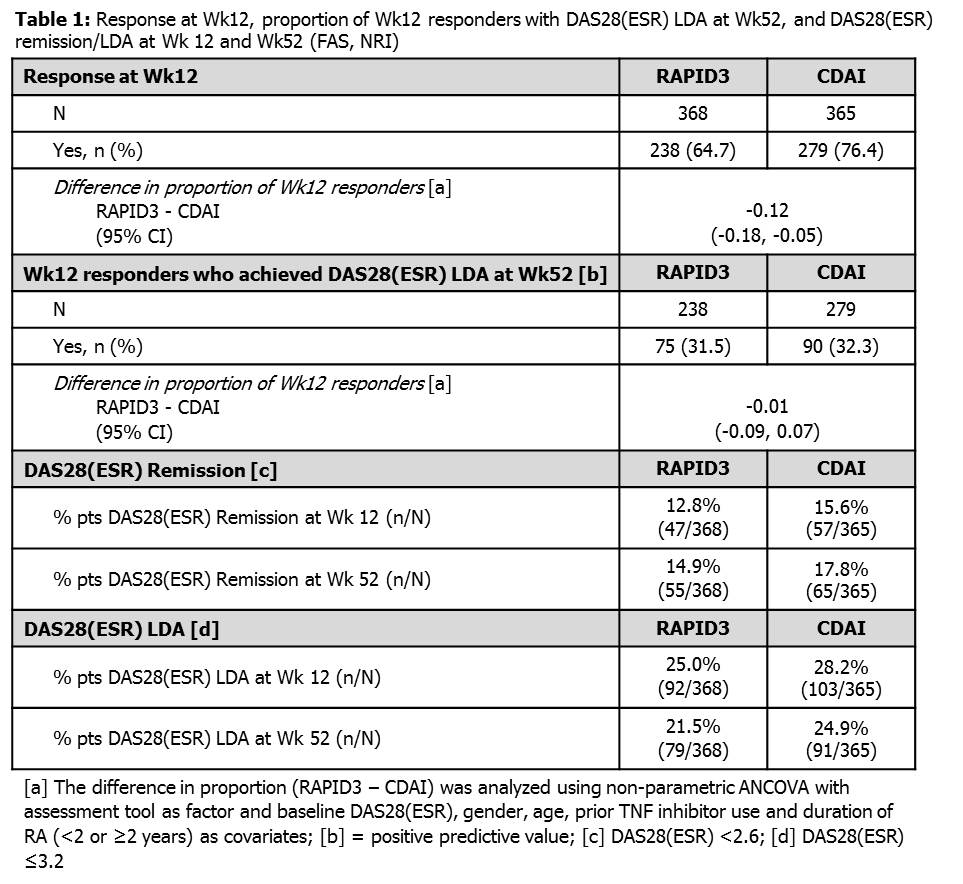
Disclosure:
J. R. Curtis,
Roche, Genentech, UCB Pharma, Janssen, CORRONA, Amgen, Pfizer, BMS, Crescendo, AbbVie,
2,
Roche, Genentech, UCB Pharma, Janssen, CORRONA, Amgen, Pfizer, BMS, Crescendo, AbbVie,
5;
W. Koetse,
UCB Pharma,
3,
UCB Pharma,
1;
J. Tambiah,
UCB Pharma,
3;
L. Ionescu,
U.B Pharma,
3,
UCB Pharma,
1;
Y. Yazici,
BMS, Genentech, Celgene,
2,
Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Genentech, Pfizer, UCB Pharma,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-week-52-treatment-response-based-on-a-week-12-assessment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-receiving-certolizumab-pegol-comparison-of-a-patient-reported-instrument-versus-physician-based/
