Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: [Background]
Oral Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) show dramatical efficacy to reduce the disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there remain some patients who respond to inadequately JAKi treatment (JAKi-IR)[1,2] and the clinical characteristics of JAKi-IR in RA have not been fully demonstrated.
[Objective]
To clarify the characteristics of JAKi-IR in patients with RA based on cluster analysis.
Methods: This retrospective study comprised 132 RA patients who were treated with JAKi (Tofacitinib or Baricitinib) between July 2013 and September 2019 in five facilities. We assessed the disease activity at the baseline, at 12 weeks after JAKi treatment or at the time point of withdrawing JAKi using the Disease Activity Score (DAS28) and the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) response criteria. JAKi-IR was defined as patients with non-response to JAKi depending on ACR20 non-response or non-improvement in DAS28-CRP (△DAS28-CRP< 1.2 from baseline) in 12 weeks. Discontinuation of JAKi due to remission achievement was excluded from the latter. Hierarchical cluster analysis was performed with the following variables at baseline: gender, age, disease duration, bone erosion, ACR functional classification (Class ≥3), rheumatoid arthritis related interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) or other autoimmune disease (AID), anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA), rheumatoid factor (RF), use/dose of methotrexate (MTX) and prednisolone (PSL), serum ESR/CRP, tender/swollen joint counts (TJC/SJC), visual analog scale by patients (VAS-Pt), and history of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
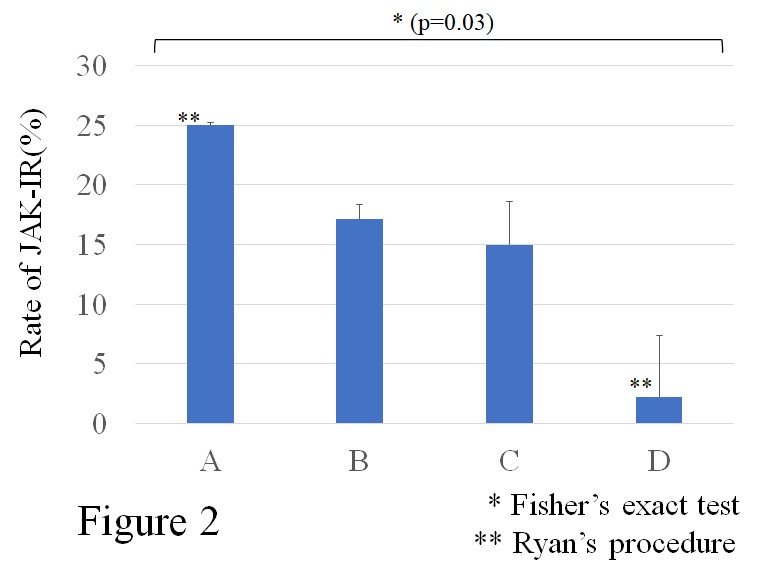
Results: The 132 enrolled patients were classified into four groups (Group A, B, C and D) by cluster analysis (Figure1). The characteristics of each group are as follows, Group A(n=32): seronegative, presence of bone erosion, absence of RA-ILD. Group B(n=35): younger age, seropositive, absence of bone erosion and RA-ILD. Group C(n=20): male, seropositive, presence of RA-ILD. Group D (n=45): older age, seropositive, without MTX treatment, presence of bone erosion and RA-ILD. The rate of JAKi-IR was found in Group A:25%, Group B:17%, Group C:15%, and Group D:2.2%, respectively (Figure2). Notably, Group A showed higher rate of JAKi-IR compared with Group D (Fisher’s exact test (p=0.03) and Ryan’s procedure).
Conclusion: We identified the characteristics of JAKi-IR. Seronegative but destructive phenotype without lung disease may less benefit from JAKi treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sugawara M, Fujieda Y, Noguchi A, Tanimura S, Shimizu Y, Nakagawa I, Takahashi H, Kono M, Kato M, Oku K, Amengual O, Atsumi T. Prediction of Responder and Non-responder to JAK Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study with Integrative Cluster Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-responder-and-non-responder-to-jak-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-pilot-study-with-integrative-cluster-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-responder-and-non-responder-to-jak-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-pilot-study-with-integrative-cluster-analysis/