Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients can develop progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease (PF-ILD), linked to a poor outcome. This study aims to establish a reliable prediction model of PF-ILD in SSc-ILD patients, to achieve early risk stratification, and to help better preventing disease progression.
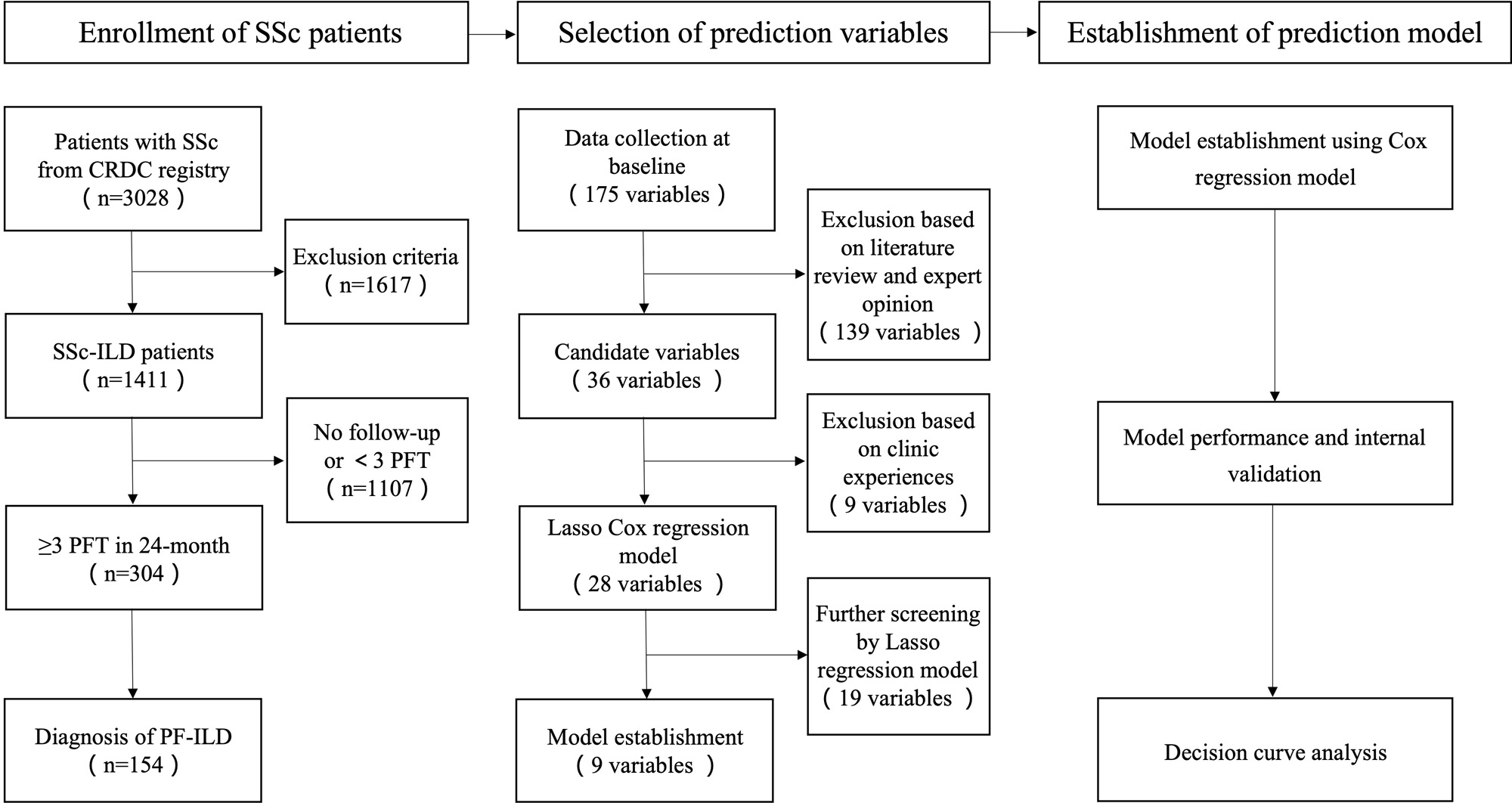
Methods: Three hundred and four SSc-ILD patients registered on Chinese Rheumatism Data Center (CRDC) database since January 2008, with no less than three pulmonary function tests within 6-24 months, were included. The major outcome was development of PF-ILD, which was defined as an absolute annualized forced vital capacity (FVC) decline ≥5% predicted. We collected data at baseline and compared differences between SSc patients with PF-ILD (SSc PF-ILD) group and SSc patients without PF-ILD (SSc non-PF-ILD) group. Lasso regularization regression was performed for further screening. Multivariable Cox regression were used to construct the prediction model, which were presented as nomogram and forest plot.
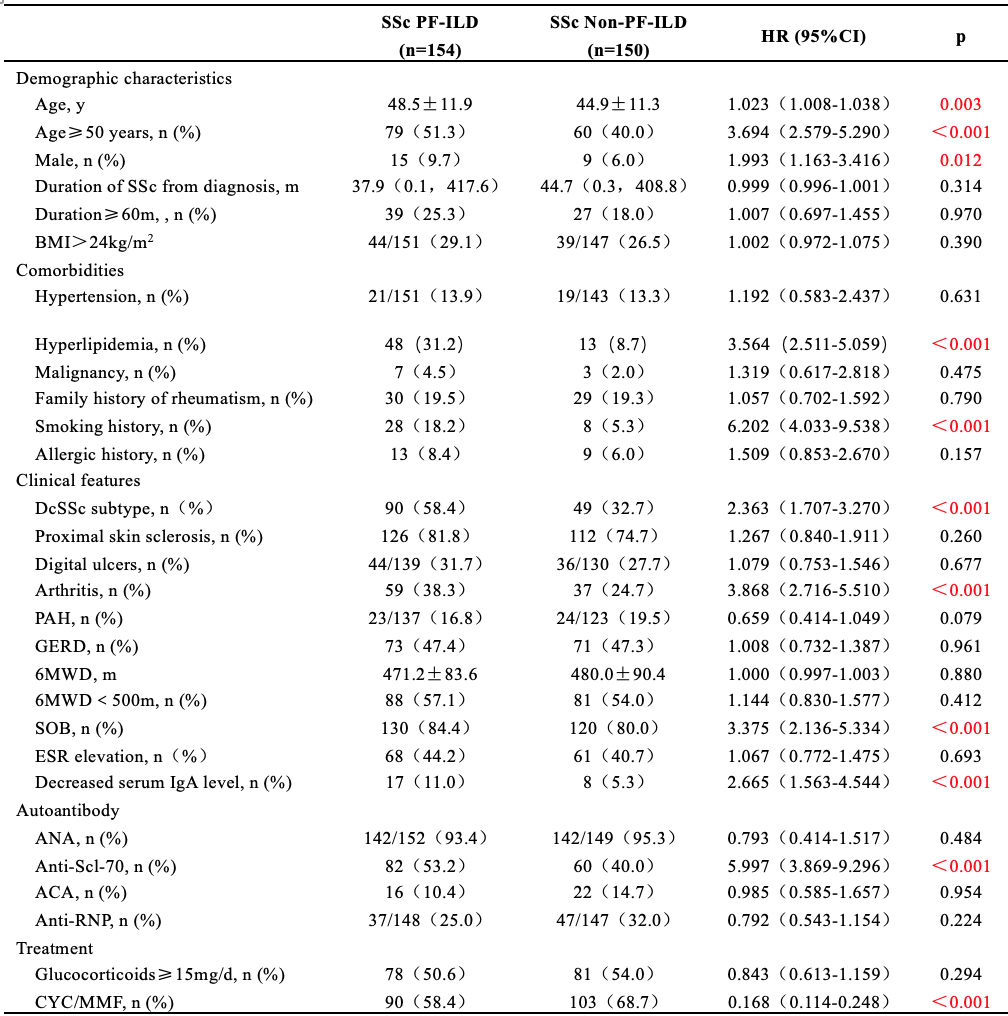
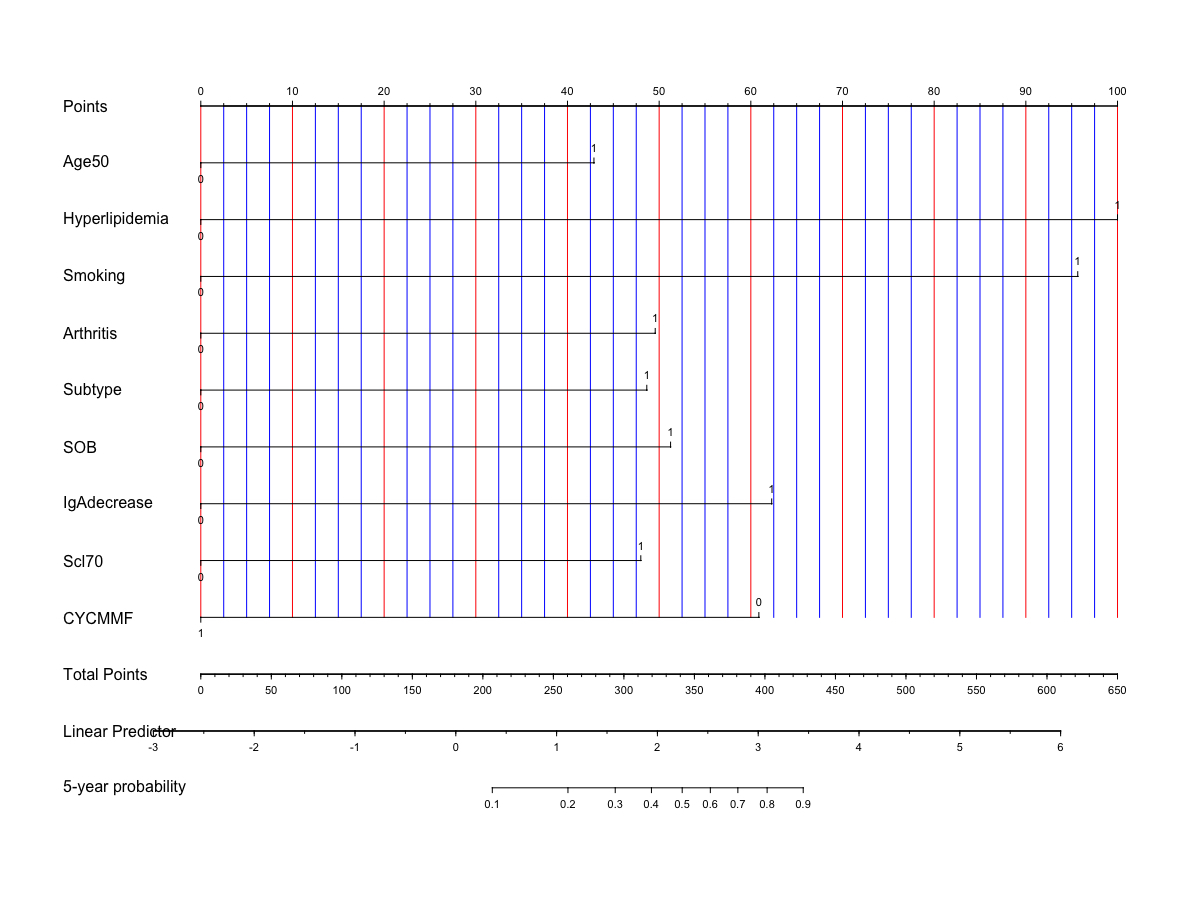
Results: SSc-ILD patients were divided into SSc PF-ILD group (n=154) and SSc non-PF-ILD group (n=150). Compared with SSc non-PF-ILD group patients at baseline, SSc PF-ILD patients were at older age (48.5±11.9 years vs 44.9±11.3 years, p< 0.001), had more male patients (9.7% vs 6.0%, p=0.012), more diffused SSc (dcSSc) subtype (58.4% vs 32.7%, p< 0.001), and a significant higher incidence of hyperlipidemia (31.2% vs 8.7%, p< 0.001), smoking history (18.2% vs 5.3%, p< 0.001), arthritis (38.3% vs 24.7%, p< 0.001), shortness of breath (84.4% vs 80.0%, p< 0.001) and anti Scl-70 antibody positivity (53.2% vs 40.0%, p< 0.001), as well as more serum IgA deficiency (11.0% vs 5.3%, p< 0.001). The use of cyclophosphamide (CYC) and/or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) were less common in SSc PF-ILD group compared with SSc non-PF-ILD group (58.4% vs 68.7%, p< 0.001). Based on the results of univariable Cox analysis and Lasso regularization regression, a 9-variable prediction model was constructed, including age≥50 years, hyperlipidemia, smoking history, dcSSc subtype, arthritis, shortness of breath, serum IgA deficiency, positive anti-Scl70 antibody and usage of CYC/MMF. C-index for the model was 0.874, while the Brier scores were 0.144 after bootstrap resampling internal validation.
Conclusion: This study developed the first prediction model for PF-ILD in SSc-ILD patients based on data from CRDC database, and internal validation showed favorable accuracy and stability of the model.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hui M, Duan X, Zhou J, Li M, Wang Q, Zhao J, Hou Y, Xu D, Zeng x. Prediction of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis Patients: Insight from the CRDC Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-progressive-fibrosing-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-insight-from-the-crdc-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-progressive-fibrosing-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-insight-from-the-crdc-cohort-study/