Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Cytokines are important in the pathogenesis of RA. Their concentration in the serum rises immediately prior to RA onset, and may be associated with disease outcome. We are not aware of any studies of serum cytokines in relation to mortality in RA. In the present study we examined the accuracy of a profile of 38 cytokines in the prediction of mortality in an RA cohort.
Methods:
We studied RA patient participants in a longitudinal study of RA outcomes who were recruited at a routine visit to a rheumatologist. After a baseline assessment that included a collection of a serum specimen, which was stored for future study, patients were tracked yearly for follow-up. We identified deaths thorough next of kin, physician or public database reports, confirmed by death certificate. We used stepwise logistic regression to examine the association between serum cytokine levels and mortality, adjusting for the confounding influence of age and sex. We used receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves to measure accuracy of mortality prediction.
Results:
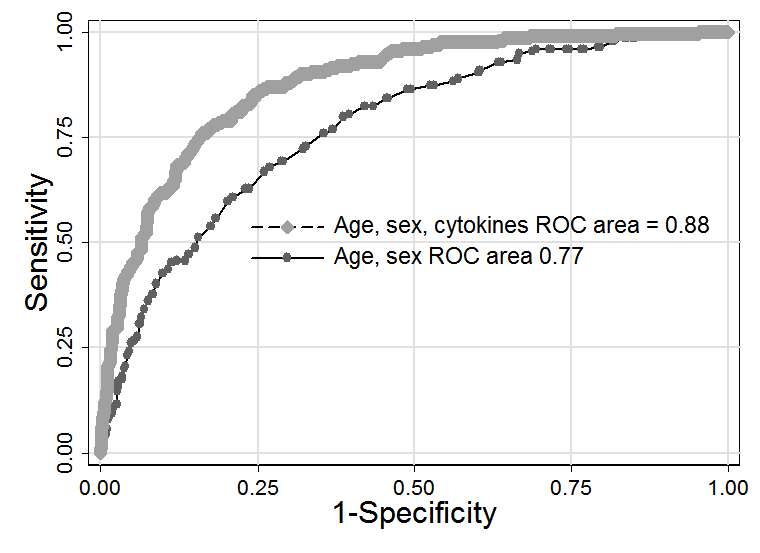
We studied 1,328 RA patients. A serum sample for cytokine measurement was available in 1,217 patients, who accrued 5,965 person-years of observation, or an average of 4.9 years per patient (range 1 day to 15 years). During this time, 204 deaths occurred for a mortality rate of 3.4 per 100 patient-years, 95% CI 3.0 to 3.9. Using age- and sex-adjusted stepwise logistic regression to identify cytokines associated with mortality, we found that the serum concentrations of the following 8 cytokines were independently associated with increased mortality: IP-10, 1.48 (1.03, 2.11); EGF, 1.27 (1.05, 1.54); TNF-a, 1.47 (1.12, 1.91); MCP-1, 1.60 (1.14, 2.24); IL-8, 1.75 (1.36, 2.23); IL-3, 1.67 (1.05, 2.67); IFN-g, 1.4 (1.08, 1.80); and GRO, 2.08 (1.40, 3.09). In the same model, the following 5 cytokines were independently associated with reduced mortality: MDC, 0.36 (0.26, 0.51); GCSF, 0.54 (0.39, 0.74); MIP-1a, 0.75 (0.62, 0.90); and IL-17, 0.71 (0.57, 0.89). Values shown are odds ratios (95% CI). The area under the mortality prediction ROC curve for a model including age and sex plus the above 13 cytokines was significantly higher than a model that included age and sex alone (0.876 vs. 0.776, P < 0.001) (see figure).
Conclusion:
A serum cytokine profile is significantly associated with mortality in RA, and its accuracy in predicting mortality within 5 years is superior to that of age and sex alone. We are not aware of any previous reports of mortality prediction in RA using serum cytokine profiles.
Disclosure:
A. Escalante,
None;
R. W. Haas,
None;
D. F. Battafarano,
None;
I. Del Rincon,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-mortality-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-a-serum-cytokine-profile/