Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II (1364–1390)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Digital ulcers (DUs) affect half of the patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and can be complicated by gangrene and amputation. Platelets are known to be activated in SSc, therefore, platelet inhibitors might represent a therapeutic option in the management of DUs. However, until now, there is no clinical study to assess the importance of platelet inhibitors in the occurrence of DUs in patients with SSc. The aim of the study was to develop and validate a prediction model for the occurrence of DUs in patients with SSc based on platelet inhibitors and other parameters.
Methods: This study used prospectively collected data from the European Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR) registry. Patients fulfilling the 2013 ACR/EULAR SSc classification criteria with complete longitudinal data on the presence of DUs and platelet inhibitors were included in the analysis. Multiple imputation using a random forest algorithm was implemented to handle missing values.
The dataset, containing the information of the last follow-up visit of every patient, was split into a derivation cohort (patients recorded before 2017-01-01 in the EUSTAR registry) and validation cohort (patients recorded after 2017-01-01). To investigate the response for the binary dependent variable of DUs, binary logistic regression was implemented to develop a prediction in the derivation cohort and to validate it using ROC analysis and calibration plots to address discrimination and calibration, respectively.
Results: Of 3,710 patients (14.6% males, 67.8% limited cutaneous SSc, median age 56.97 years, median disease duration 8.94 years), 486 had current DUs at the baseline and 150 were exposed to platelet inhibitors. At the follow-up visit (median follow-up time 1.03 years) 487 had current DUs and 90 remained exposed to platelet inhibitors.
Factors associated with absence or presence of DUs at the next follow-up visit are shown in figure 1. This confirmed the risk factors for the presence of DUs identified by previous studies.
The discrimination ability of the model evaluated by ROC curve analysis showed an AUC = 80.8% (95% CI = [78.7% to 83.0%]) for the derivation cohort (2,827 patients) and AUC = 83.4% (95% CI = [80.0% to 86.8%]) for the validation cohort (883 patients), respectively, corresponding to an acceptable discrimination (figure 2). The calibration plots revealed an adequate calibration of the model (figure 3).
Amongst other predictive factors, our model revealed that exposure to platelet inhibitors is associated with a reduced odds ratio of DUs occurrence at the next follow up visit (OR = 0.25, 95%CI [0.07-0.77]).
Conclusion: Our model shows good discrimination and adequate calibration for the difficult task of predicting the occurrence of DUs at a one-year follow up visit. Use of platelet inhibitors was among the factors predicting lower probability of DUs occurrence at follow-up.
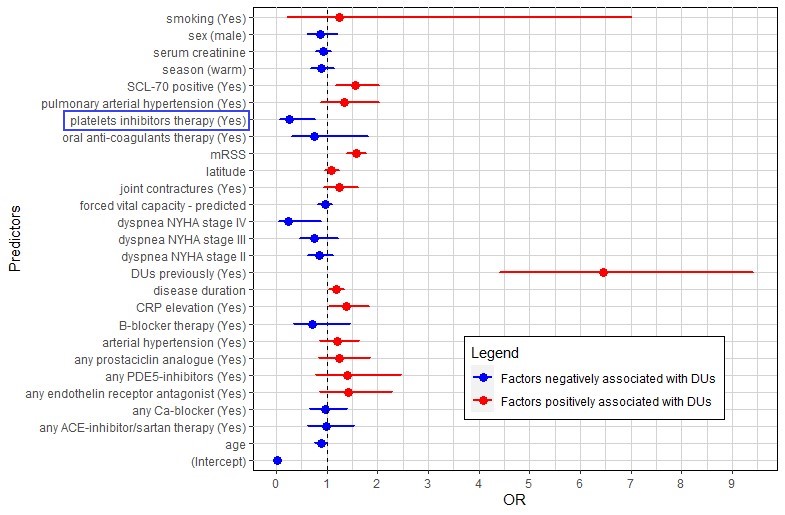 FIgure 1: Forest plot displaying the OR of the logistic classification model
FIgure 1: Forest plot displaying the OR of the logistic classification model
 Figure 2: ROC curves displaying the discrimination ability of the fitted model in the derivation and validation cohort, respectively
Figure 2: ROC curves displaying the discrimination ability of the fitted model in the derivation and validation cohort, respectively
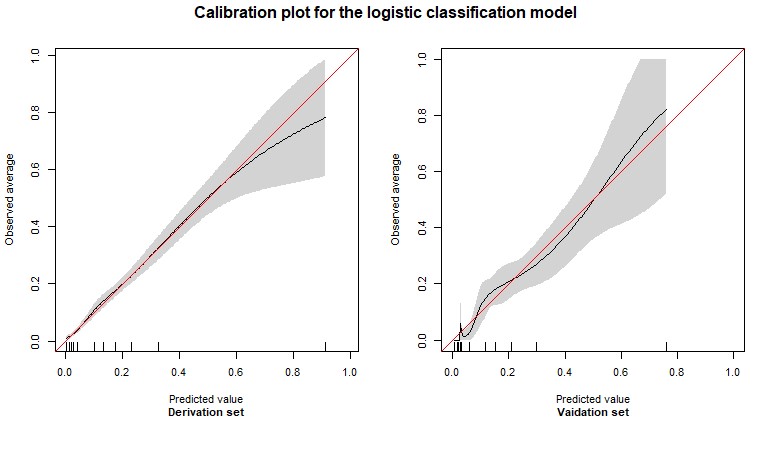 Figure 3: Calibration plots for the logistic classification model – the figure shows the calibration plot of the model in the derivation cohort (left side) and in the validation cohort (right). On the X‐axis, the model’s predicted probability of the occurrence of DUs is plotted against the observed risk of presence of DUs on the Y‐axis (0 = absence of DUs, 1 = presence of DUs). The red line represents perfect prediction, meaning that the predicted risk is exactly the same as the observed risk across the whole range. Ideally, the lines obtained should lie exactly on top of the red line.
Figure 3: Calibration plots for the logistic classification model – the figure shows the calibration plot of the model in the derivation cohort (left side) and in the validation cohort (right). On the X‐axis, the model’s predicted probability of the occurrence of DUs is plotted against the observed risk of presence of DUs on the Y‐axis (0 = absence of DUs, 1 = presence of DUs). The red line represents perfect prediction, meaning that the predicted risk is exactly the same as the observed risk across the whole range. Ideally, the lines obtained should lie exactly on top of the red line.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garaiman A, Steigmiller K, Gebhard C, Matucci-Cerinic M, Henes J, de Vries-Bouwstra J, Smith V, Doria A, Allanore Y, Dagna L, Anic B, Montecucco C, Kowal-Bielecka O, Martin M, Tanaka Y, Hoffmann-Vold A, Held U, Distler O, Becker M. Prediction of Digital Ulcers in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Based on the Use of Platelet Inhibitors and Other Parameters – A EUSTAR Study on Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-digital-ulcers-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-based-on-the-use-of-platelet-inhibitors-and-other-parameters-a-eustar-study-on-derivation-and-validation-of-a-clinical-prediction-mod/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-digital-ulcers-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-based-on-the-use-of-platelet-inhibitors-and-other-parameters-a-eustar-study-on-derivation-and-validation-of-a-clinical-prediction-mod/
