Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The treatment response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is heterogeneous. In clinical practice, both patients and clinicians are interested to know how likely a patient will achieve a major response after initiating TNFi. The objective of this study is to develop a predictive model for a favorable response to TNFi based on baseline clinical features in patients with active AS.
Methods: We obtained individual patient data from randomized clinical trials of Adalimumab and Etanercept in active AS, and aggregated the participant data in the TNFi arms for a pooled analysis. The main outcome was major response at week 12, defined by achieving Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment 40% (ASAS40) response. Baseline characteristics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), disease duration, spondyloarthritis features, C-reactive protein (CRP), HLA-B27 positivity, and patient reported outcomes were included as predictors. The entire cohort was split by 5:1 for model development and validation. We used Random Forest algorithm to develop the predictive model with ranking of the importance of features, and the performance was examined using receiver operating characteristics area under the curve (ROC – AUC). The process was repeated independently for 5 times, and the final AUC was the average.
Results: A total of six RCTs of Adalimumab or Etanercept in patients with active AS were identified, and 1090 subjects who were in the TNFi arms were eligible and included in the analysis. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Average age was 38.7 +/- 11.7 years, 75.3% were male patients, and 85.5% were HLA-B27 positive. Fifty-one percent of subjects achieved ASAS40 response at week 12. The Random Forest models had a small to medium effect with average AUC of 0.66 (Figure 1). At baseline, higher CRP level, worse night pain, younger age, worse patient global assessment, and lower BMI were the most important features that predicted a major response.
Conclusion: Using Random Forest algorithm, we developed a model to predict treatment response to TNFi in patients with active AS. Preliminary analysis showed a small to medium effect with AUC of 0.66. At baseline, higher CRP, worse night pain, younger age, worse patient global assessment, and lower BMI are the most important features in the prediction model.
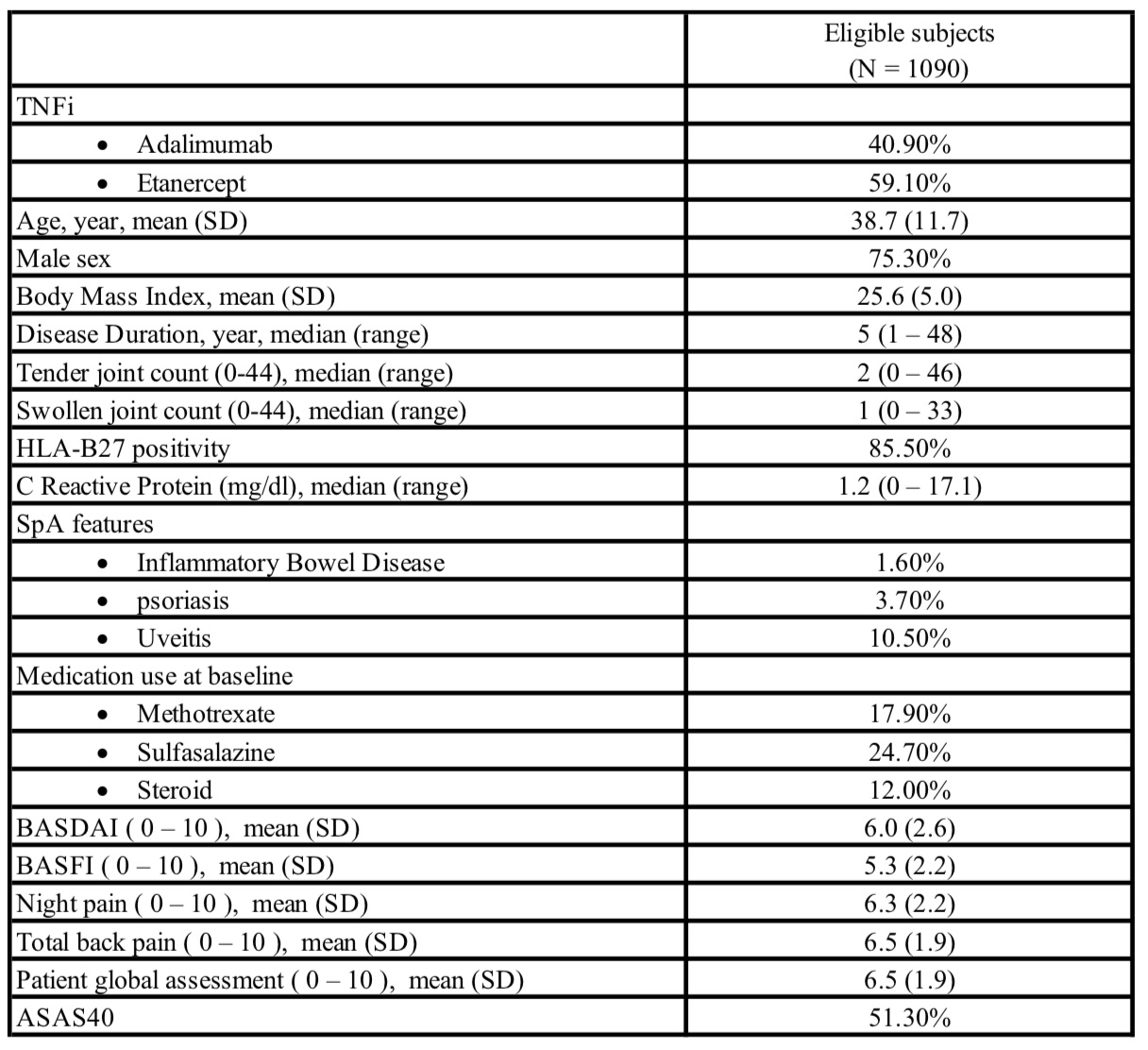 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of eligible subjects. SD: standard deviation; SpA: spondyloarthritis; BASDAI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index; BASFI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index; ASAS40: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) 40% response criteria.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of eligible subjects. SD: standard deviation; SpA: spondyloarthritis; BASDAI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index; BASFI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index; ASAS40: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) 40% response criteria.
 Figure 1. Performance of Random Forest Models in testing set using Receiver Operating Characteristic curves. ROC: receiver operating characteristic; AUC: area under the curve.
Figure 1. Performance of Random Forest Models in testing set using Receiver Operating Characteristic curves. ROC: receiver operating characteristic; AUC: area under the curve.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang R, Dasgupta A, Ward M. Predicting Major Treatment Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitorsin Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-major-treatment-response-to-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitorsin-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-major-treatment-response-to-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitorsin-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
