Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab, which targets the B Cell activator and survival factor BLyS, is an approved treatment for systemic lupus (SLE) and has demonstrated efficacy in multiple clinical trials around the world. Nevertheless, like other SLE treatments, belimumab can have disappointing results in a significant proportion of this heterogenous population, a problem further complicated by the unpredictable impact of various combination treatments used with belimumab in trials and clinical practice. Using gene expression variables, we aim to identify SLE patients prior to treatment who will respond favorably to belimumab treatment.
Methods: A prospective open-label study of belimumab was conducted in 24 SLE patients with active but non-organ threatening disease, who were required to withdraw other immune suppressants (only antimalarials or low dose steroids allowed). At baseline, after blood samples obtained, patients were given optional steroid injections for temporary relief, then followed for six months on intravenous belimumab (10 mg/kg). The primary endpoint was time to treatment failure (flare, treatment change or study withdrawal) compared to historical controls from the BOLD study1 (same protocol but without treatment after initial steroids). Response was also evaluated at six months by the SLE Responder Index (SRI-4) or the BILAG-based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA). Before and during treatment, PAX gene tubes were collected, and RNA sequenced, using the same methods for healthy control samples. To maximally discriminate clinical responders from non-responders by baseline gene expression patterns in a small, heterogenous population, principal component analysis was conducted with modules (metagenes) comprised of differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
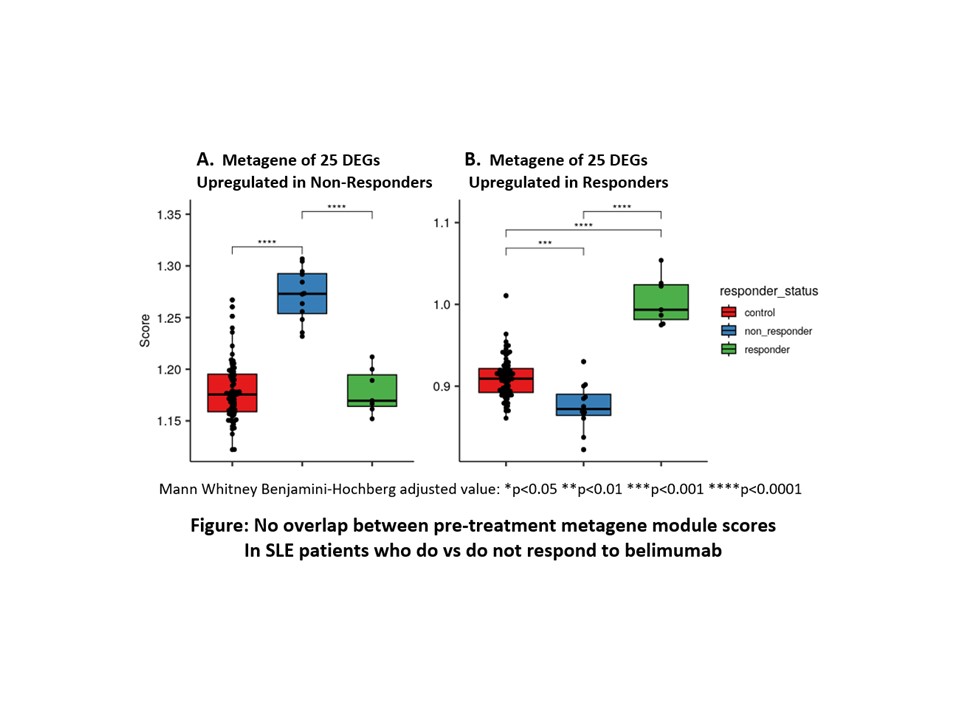
Results: Of 24 patients entering the study, 20 completed 6 months of treatment. The mean survival time without treatment failure was 18.4 weeks (CI 15.3-21.5) compared to the 41 BOLD participants with mean survival 9.829 weeks (CI 0.999-7.871) (p< 0.001 by log rank test). At 6 months, 14 patients who received belimumab (58%) and 1 from the BOLD study (2.4%) remained free of flare. The SRI-4 was met by 7 patients in this study (29.2%), the BICLA by 9 (37.5%). SRI-4 response was used as the basis for modeling two metagenes comprised of baseline expression of the 25 most upregulated genes in non-responders and the 25 most upregulated genes in responders with no overlap between metagene scores of responders vs non-responders (figure). After 3 months of treatment with belimumab the metagene scores corrected towards levels in healthy controls. The most discriminatory DEGs included protein transcription factors and long non-coding RNA (some being known transcription regulators).
Conclusion: When background immune suppressants are excluded, belimumab still achieves SRI 4 or BICLA response for a subset of patients, and most do not flare for at least six months. Preliminary identification of a composite metagene model as a potential predictor of belimumab response provides an intriguing model which will require testing in prospective confirmation studies. 1Merrill, Arth Rheum 2017 69:1257
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smith M, Thomas K, Dominguez N, Macwana S, DeJager W, Kamp S, Guthridge C, Parrish B, Arriens C, James J, Merrill J, Guthridge J. Pre-treatment Differentially Expressed Metagenes Characterize Systemic Lupus Patients Who Subsequently Achieve Clinical Response to Belimumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pre-treatment-differentially-expressed-metagenes-characterize-systemic-lupus-patients-who-subsequently-achieve-clinical-response-to-belimumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pre-treatment-differentially-expressed-metagenes-characterize-systemic-lupus-patients-who-subsequently-achieve-clinical-response-to-belimumab/