Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
In 2011, we started a cardiovascular (CV) risk management program for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients visiting Reade in the Netherlands. We previously reported the presence of under treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertension [1].
The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness of our CV risk management program after one year.
Methods:
CV risk screening was performed at baseline and we informed the general practitioner (GP) about the results, including advices regarding the initiation of cardio preventive drugs. In high risk patients (i.e. a 10-year CV risk score ≥20%), antihypertensives were recommended when systolic blood pressure > 140 mm/Hg and statins were recommended when low-density lipoprotein >2.5 mmol/l. The decision to start preventive medication was left to the GP. CV risk screening was repeated after one year. Patients completed a questionnaire about the actions that were taken following the results of the initial screening.
Results:
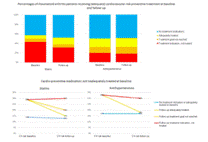
Of the 266 patients 202 (76%) were female, the mean age was 58 ±11 years. After one year, 88 out of 134 patients who received inadequate or no treatment at baseline were still untreated or undertreated. Of the 188 (71%) patients who were at high CV risk and who did have an indication to start therapy, only 7.5% was contacted by their GP and another 6.8 % arranged an appointment themselves. While the 10-year CV risk did not decrease in the group as a whole, a risk reduction was found in the patients that started medication. Remarkably, 42% of patients reported lifestyle changes, including more exercise (20%), diet adaption (16%) and weight loss (9%).
Table 1. Cardiovascular risk factors at baseline and after one year
|
|
Baseline |
Follow-up |
|
CV disease history |
20 (7.5) |
23 (8.6) |
|
CV risk <10% |
43 (16.2) |
52 (19.5)* |
|
CV risk 10-20% |
60 (22.6) |
62 (23.3) |
|
CV risk >20% |
143 (53.8) |
129 (48.5)* |
|
SBP in mm/Hg |
135 ±17 |
135 ±18 |
|
Body Mass Index in kg/m2 |
26.4 ±5.0 |
26.3 ±4.8 |
|
TC in mmol/l |
5.5 ±1.0 |
5.2 ±1.0** |
|
Triglycerides in mmol/l |
1.4 ±0.8 |
1.4 ±0.8 |
|
LDL-cholesterol in mmol/l |
3.2 ±0.9 |
3.0 ±0.9** |
|
HDL-cholesterol in mmol/l |
1.6 ±0.5 |
1.6 ±0.5 |
|
TC/HDL-ratio |
3.7 ±1.2 |
3.7 ±1.2** |
|
Current smokers |
60 (22.6) |
53 (20.1) |
|
Diabetes mellitus |
12 (4.5) |
12 (4.5) |
|
SBP >140 mm/Hg |
95 (35.7) |
96 (36.2) |
|
LDL > 2,5 mmol/l |
208 (78.8) |
180 (68.4)** |
|
TC ≥ 6.5 mmol/l |
37 (13.9) |
26 (9.8) |
|
Antihypertensives |
81 (30.5) |
88 (33.1) |
|
Statins |
38 (14.3) |
57 (21.4)** |
|
CV=Cardiovascular, HDL=high-density lipoprotein, LDL=low-density lipoprotein, TC=total cholesterol, SBP= Systolic blood pressure. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation or n, (%). *p<0.05 **p<0.01 |
||
Conclusion:
It is striking that one year after the introduction of our CV risk management program, only 14,3% patients with an indication for preventive treatment visited their GP and only 14% started with CV risk lowering drugs. This was mainly caused by the small percentage of high risk patients that contacted their GP. On the other hand, a high percentage reported the start of healthy lifestyle. These results underscore the need for a short-term follow-up, in close collaboration with primary care providers to ensure appropriate CV risk management. This is a future implementation project that will be initiated shortly.
References: 1. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:192
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heslinga M, van den Oever I, Griep E, Griep-Wentink H, Smulders YM, Lems W, Boers M, Voskuyl A, Peters MJL, van Schaardenburg D, Nurmohamed M. Poor Cardiovascular Risk Management in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Despite an Explicit Cardiovascular Risk Management Program [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/poor-cardiovascular-risk-management-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-despite-an-explicit-cardiovascular-risk-management-program/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/poor-cardiovascular-risk-management-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-despite-an-explicit-cardiovascular-risk-management-program/