Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies Poster II: Clinical Trials & Basic Science
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is characterized by a build-up of uric acid crystals in and around the joints. Uric acid crystal formation and dissolution is affected by pH. There are reports in the literature of the use of alkalization agents, such as sodium bicarbonate, to treat gout. Theoretically, an alkalinizing agent such as sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) may increase the systemic and/or local pH and may allow pH sensitive uric acid crystals to dissolve resulting in temporary relief of pain and shortening duration of a gout flare, however oral sodium bicarbonate use causes intolerable gastrointestinal side-effects. Purpose of study was to determine if sodium bicarbonate in a patented transdermal drug delivery system can effectively and safely reduce pain and shorten duration of an acute gout flare. This delivery system has been shown to effectively deliver sodium bicarbonate transdermally in prior animal and human studies.
Methods: This pilot study is prospective, double-blinded, randomized, and placebo-controlled in design. Twenty-four subjects, female and male, aged 18+, with clinical diagnosis of gout, history of uric acid >6.8mg/dl, on stable medication regimen, presenting in clinic within 36 hours of initiation of acute gout attack and prescribed 0.6 mg/daily colchicine were included. Exclusion criteria included >stage 3 kidney disease, tophaceous gout, and recent/concurrent initiation of other pain medications (e.g. NSAID, corticosterioids). Subjects were randomized to receive placebo lotion or sodium bicarbonate transdermal lotion (33% sodium bicarbonate and 0.5% menthol) and instructed to apply to the entire limb of up to three affected joints (target joint and up to two other joints). Outcome measures included pain (numeric rating scale, 0-10), time to resolution (50% reduction in pain), range of motion and subject satisfaction. Time-points were baseline,15 & 30 min, and 1,2,4,6,8,10,12, and 14 days. Adverse events were collected. Statistical analysis was repeated measures ANOVA with p< 0.05 as significant.
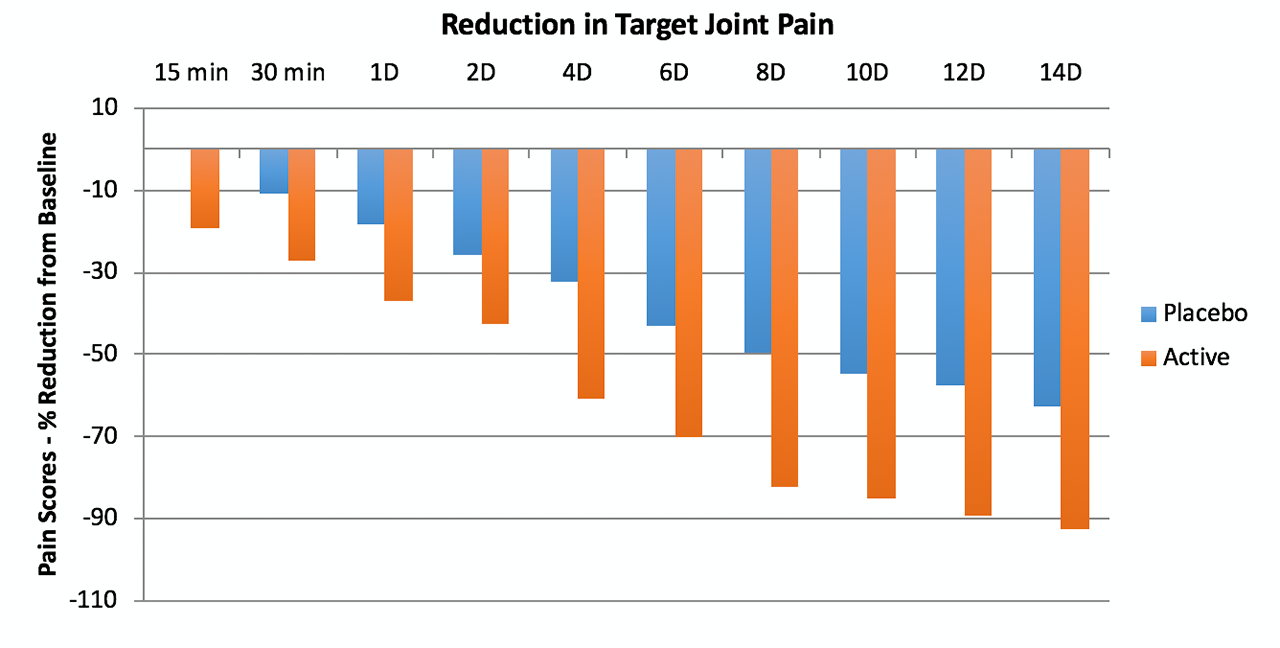
Results: The active treatment subjects (N=12) had pain scores that averaged about 1.3 points lower than the placebo patients (N=12) (p=0.004). The figure shows the % reduction in pain scores over time in the target joint. The secondary joint (N=9 for both groups) also had a significant (p=0.04) reduction in pain with average pain of 1.2 points lower than control. The mean time to resolution for the target joint was 4.1 days in placebo group and 2.2 days in the active group. The mean time to resolution for the secondary joint was 2.8 days in the control group and 1.6 days in the active group. Among those who attained improved ROM, average time was 2.5 days in placebo group and 1.7 days in active group. No treatment related adverse events reported.
Conclusion: Topical transdermal sodium bicarbonate lotion use resulted in a highly significant (p=0.004) reduction in pain, as early as 15 min, and may speed resolution of acute gout attacks and improvement of range of motion.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reddy S, Mabaquiao R, Misell L. Pilot, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo Controlled Efficacy AndSafety Study of a Transdermal Alkalinizing and Pain Relieving Treatment ForAcute Gout Flare [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pilot-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-efficacy-andsafety-study-of-a-transdermal-alkalinizing-and-pain-relieving-treatment-foracute-gout-flare/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pilot-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-efficacy-andsafety-study-of-a-transdermal-alkalinizing-and-pain-relieving-treatment-foracute-gout-flare/