Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1221–1255) Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster II: Connective Tissue Disease
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Physician Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PhGA) are commonly used outcome measures in pediatric rheumatology. For childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE), the traditional visual analog scale (range: 0 – 10; 0=inactive; 10=very active; PhGA0-10) but also the SELENA-SLEDAI (range: 0-3; 0= none, 1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe; PhGA0-3) are used to measure treatment response, flare, and Lupus Low Disease Activity Status (LLDAS) with PhGA0-3 ≤1. Thus, the purpose of this study was to compare the measurement properties of the PhGA0-10 and the PhGA0-3 in cSLE and with scores of the SLEDAI-2k, and the SELENA-SLEDAI.
Methods: Secondary data analysis from a convenience sample of 100 cSLE followed every 3 months for up to 7 visits (1). Ratings of PhGA0-10, PhGA0-3, parent assessment of patient well-being (ParGA; range: 0= very poorly, 10=very well), SLEDAI-2k and SELENA-SLEDAI were compared. After linear transformation of PhGA0-10 to a 0-3 range (tPhGA0-10) frequency of PhGA0-3≤1 were compared.
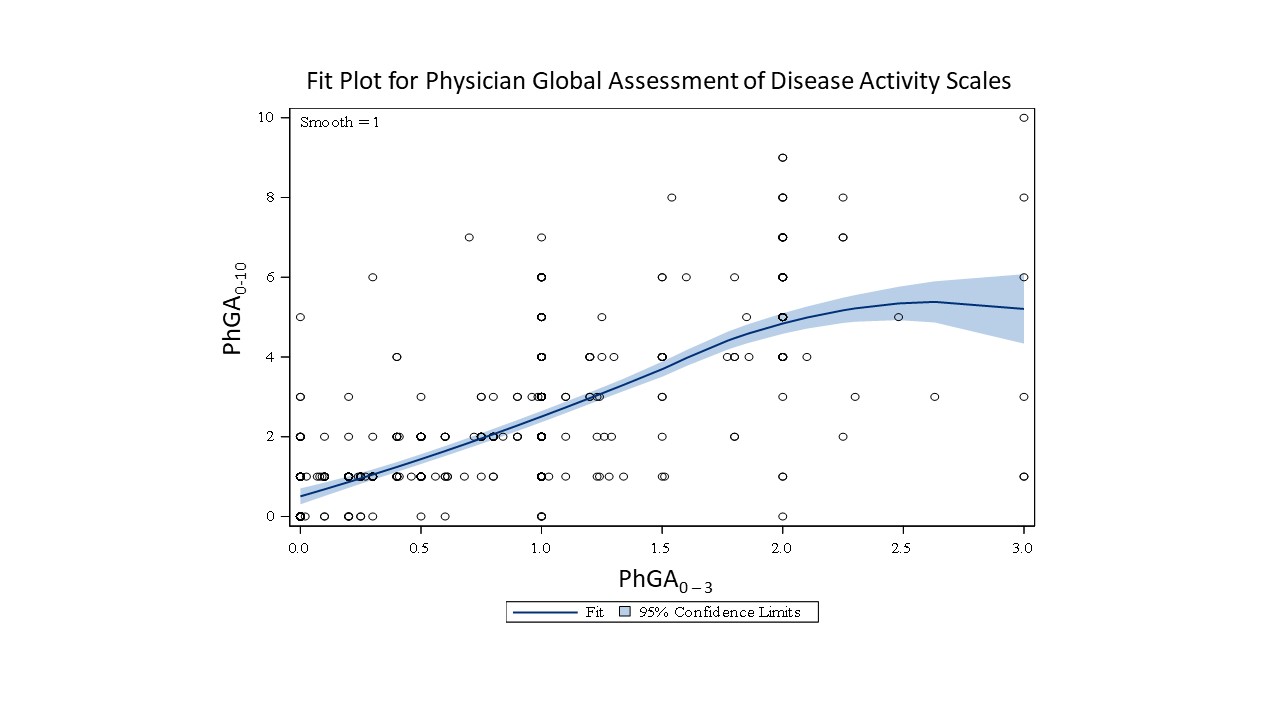
Results: In 601 visits, mean (SD)/median (range) of PhGA0-10, PhGA0-3, SLEDAI-2K and SELENA-SLEDAI were 2.13 (1.87)/2 (0-10), 0.79 (0.64)/1(0-3), 4.63 (4.14)/ 4 (0-28) and 4.51 (4.1) / 4 (0-32) respectively. PhGA0-10 were moderately correlated with PhGA0-3 (r=0.73; p< 0.0001; Figure 1) with more variability for PhGA0-3 ≥2. ParGA was weakly correlated with PhGA0-10, PhGA0-3, SLEDAI-2k and SELENA-SLEDAI scores (r = -0.34, -0.30, -0.19 and -0.20). SELENA-SLEDAI and SLEDAI-2k scores were highly (r=0.98) correlated with each other. However, SLEDAI-2K/SELENA-SLEDAI scores were weakly correlated with PhGA0-3 (r=0.28/0.28; p < .001) and moderately correlated with PhGA0-10 (r= 0.56/0.54; p < .0001). There were 490/497 of 601 visits with PhGA0-3 ≤1 / tPhGA0-10 ≤1 [Kappa (SE) =0.59 (0.04), McNemar p=0.4].
Conclusion: Using the traditional PhGA0-10 in cSLE yields almost identical LLDAS rates compared to the PhGA0-3. Given its closer association with the scores of disease activity indices in cSLE, use of the PhGA0-10 may be preferable in pediatric populations.
References: (1) Mina R, Klein-Gitelman MS, Nelson S, Eberhard BA, Higgins G, Singer NG, Onel K, Tucker L, O’Neil KM, Punaro M, Levy DM, Haines K, Martini A, Ruperto N, Lovell D, Brunner HI. Validation of the systemic lupus erythematosus responder index for use in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Feb;73(2):401-6. PMID: 23345596.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogbu E, Brunner H, Huggins J, Merritt A, Quilan-Waters M, Robben C, Chen C, Lovell D, Huang B. Physician Global Assessment of Disease Activity in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Does the Approach Matter? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physician-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-does-the-approach-matter/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physician-global-assessment-of-disease-activity-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-does-the-approach-matter/