Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Physical activity has numerous benefits for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients such as reducing symptoms like fatigue and pain and improving physical function. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire – Short Form (IPAQ-SF) is a widely used self-administered questionnaire consisting of seven items that measures physical activity levels in minutes and metabolic equivalents (METs) over the previous week. The aim of this study was to evaluate physical activity levels in RA patients and explore potential associations with patient characteristics, disease activity, functional capacity, quality of life, anxiety, depression, and treatment.
Methods: Multicenter, analytical, observational, cross-sectional study. Patients ≥ 18 years old with a diagnosis of RA (ACR-EULAR 2010) were included. Sociodemographic data, habits, comorbidities, body mass index (BMI), RA characteristics, Clinimetrics measures and treatment were collected. In addition, participant’s physical activity levels were assessed using the IPAQ-SF. Statistical analysis:Descriptive statistics. The results of IPAQ-SF were compared according to patient characteristics, disease activity, functional capacity, quality of life, anxiety, depressionand treatment by means of an appropriate test: Student T-test, Wilcoxon, Pearson, ANOVA, or Spearman. Significance level was set at 0.05.
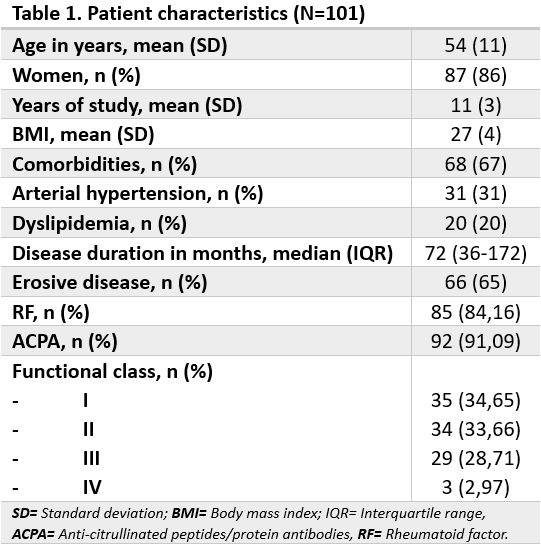
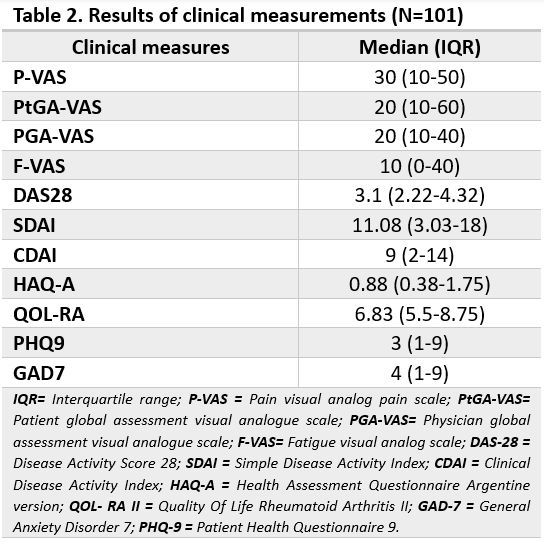
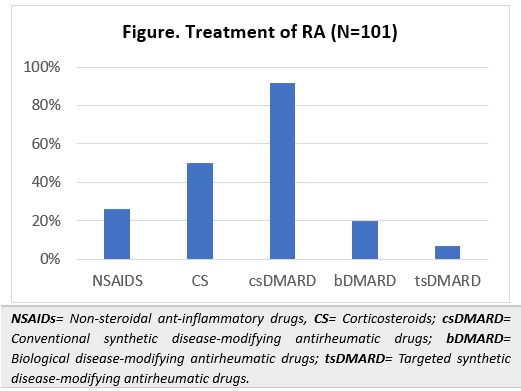
Results: A total of 101 patients from five centers were included. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Results of clinical measurements can be observed in Table 2 and RA treatment in the Figure.A total of 31% practiced sports, with a mean of 24 months (SD 8.5). The IPAQ-SF reported a median total physical activity of 1386 METs (IQR 594-3066), with an average frequency of 7 days (IQR 3-7) and 119 minutes (SD 94.9) per week: 42% had low activity, 31% moderate, and 28% high. Median sitting time was 4.4 hours per day (IQR 2-7). Total METs median was associated with higher education (p=0.008) and sports practice (p< 0.0001). Correlation was negative with BMI (p=0.01), functional class (FC, p=0.002), P-VAS (p=0.008), PtGA-VAS (p=0.01), fatigue VAS (p=0.02), DAS28 (p=0.009) and HAQ-A (p< 0.0001). Mean total MET was higher in patients who didn’t required assistance in daily activities (p=0.0005). In addition, weekly physical activity minutes showed a negative association with PtGA-VAS (p=0.02). A higher minute mean was observed in those who practiced sports (p=0.0001), had no comorbidities (p=0.04) and didn’t need assistance (p=0.01). Physical activity day mean was higher in non-smokers (p=0.02), sports players (p=0.002), those with no erosive disease (p=0.002) and those with no need for assistance (p=0.001). High physical activity was linked to no comorbidities (p=0.02), sport practice (p< 0.001) and no assistance need (p=0.004). Patients without corticosteroids (p=0.012) and no erosive disease (p=0.012) showed more moderate/high physical activity.
Conclusion: Fifty-eight percent of the patients had moderate/high physical activity, positively associated with sports, lower RA activity and better function. Fewer comorbidities and glucocorticoid treatment were observed in this RA cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dominguez Leiva P, Dapeña J, Bande J, Medina M, caracciolo J, Klajn D, Morbiducci J, Secco A, Sosa J, Kohan M, Pereira D, Papasidero S. Physical Activity in a Cohort of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physical-activity-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physical-activity-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/