Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: RGB-19 is a proposed biosimilar to tocilizumab, a monoclonal antibody that competitively inhibits the binding of interleukin-6 (IL-6) to its receptor. Results of a Phase 3 study (jRCT2031220512) assessing the clinical equivalence in efficacy between RGB-19 and reference tocilizumab at Week 12, and comparing secondary efficacy, safety and immunogenicity outcomes up to Week 24, have been previously reported.1 Here, secondary outcomes up to Week 52 (safety to Week 54) are reported.
Methods: This Phase 3, randomized, double-blind study enrolled Japanese adults with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate, a baseline Disease Activity Score based on 28 joints with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) of ≥3.2, and swollen/tender joints (≥6 from 66/68). Participants were randomized 1:1 to intravenous infusions of either RGB-19 8 mg/kg or tocilizumab 8 mg/kg, administered every 4 weeks to Week 52, and participants were followed to Week 54. The primary endpoint was the mean change from baseline (CfB) in DAS28-ESR at Week 12 (previously reported).1 Key secondary outcomes included efficacy, serum concentration, pharmacodynamics (PD; absolute neutrophil count [ANC], C-reactive protein [CRP], and soluble IL-6 receptor [sIL-6R]), and immunogenicity up to Week 52, and safety up to Week 54.
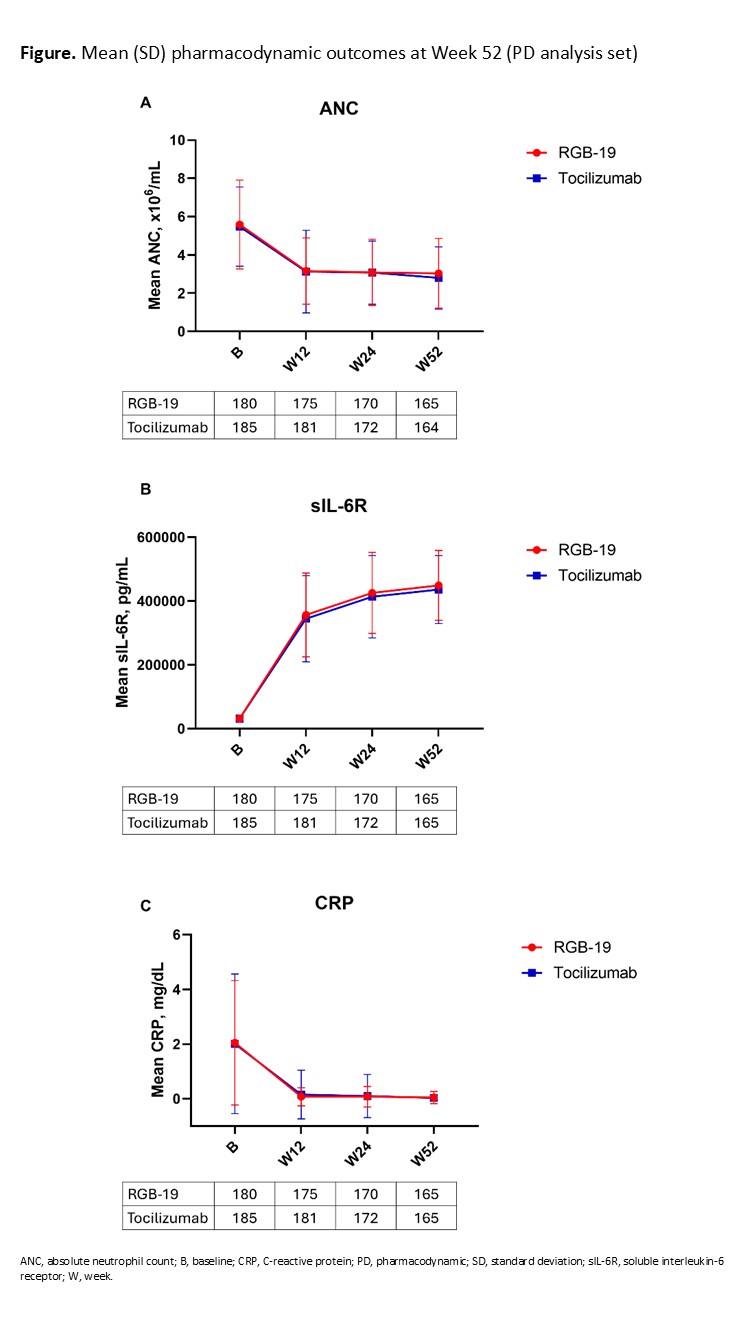
Results: Overall, 368 participants were randomized. A total of 335 participants completed the secondary evaluation period from Week 12 to Week 52 (RGB-19 n=169; tocilizumab n=166). The most common reason for withdrawal from the secondary evaluation period was adverse events (AEs; RGB-19 n=3; tocilizumab n=8). Baseline demographics were balanced between groups, as previously reported.1The CfB in DAS28-ESR at Week 52 was similar between groups (confidence intervals within the primary endpoint equivalence margin of ±0.6; Table 1). Achievement/disease remission rates (American College of Rheumatology [ACR] 20/50/70, Simplified Disease Activity Index [SDAI], Clinical Disease Activity Index [CDAI], and European League Against Rheumatism [EULAR]) were also similar up to Week 52 (Table 1). Mean serum concentration time profiles and ANC, CRP, and sIL-6R PD outcomes were all similar between groups up to Week 52 (Figure).Safety profiles were similar between groups, with comparable incidences of treatment-emergent AEs, and adverse drug reactions up to Week 54 (Table 2). The incidence of treatment-emergent antidrug antibodies (RGB-19 2.7%, tocilizumab 5.4%) and neutralizing antibodies (RGB-19 2.7%, tocilizumab 4.3%) was similarly low in both groups.
Conclusion: Similar efficacy, serum drug concentration, PD, safety and immunogenicity outcomes were shown for RGB-19 and tocilizumab up to the end of this Phase 3 study. These results support previously reported data that demonstrated the clinical equivalence in efficacy at Week 12 and similarity in secondary outcomes between treatments at Week 24.1Reference1. Choy E, et al. European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Congress 2025. Abstract 1398.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester G, Matsuno H, Choy E, Okada M, Dias R, Horvát-Karajz K, Dancer G, Karibe Y, Masuda S, Kiefer J, Emery P. Phase 3 Study of the Efficacy, Safety and Immunogenicity of the Proposed Tocilizumab Biosimilar RGB-19, Intravenously Administered to Participants With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: 52-Week Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phase-3-study-of-the-efficacy-safety-and-immunogenicity-of-the-proposed-tocilizumab-biosimilar-rgb-19-intravenously-administered-to-participants-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-52-week-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phase-3-study-of-the-efficacy-safety-and-immunogenicity-of-the-proposed-tocilizumab-biosimilar-rgb-19-intravenously-administered-to-participants-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-52-week-data/

.jpg)
.jpg)