Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is a recognized as a hallmark of spondyloarthrtis (SpA), including psoriatic arthritis (PsA). However, it is an underestimated disease domain in both in clinical trials and clinical practice (1).
This systematic literature review (SLR) assessed the efficacy of the available pharmacological options for enthesitis.
Methods: A SLR was conducted following the PRISMA reporting guidelines. Studies were sourced from PubMed and Embase databases, using the MeSH terms: enthesitis, entheses, treatment, spondylarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. The search was limited to articles in English published between January 2000 and July 2020. Two independent reviewers screened the titles and abstracts.
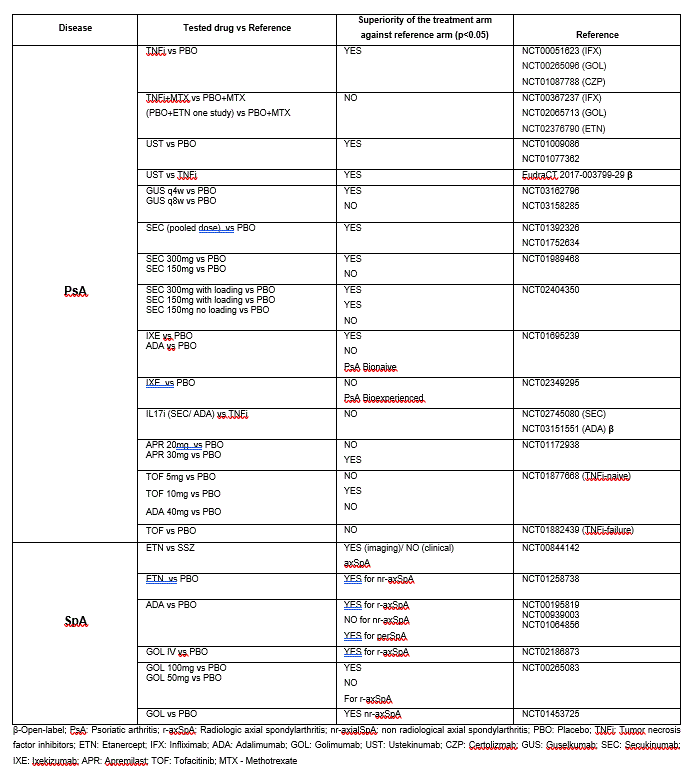
Results: A total of 65 articles matched the research criteria. The included populations, the time to assessment of the primary endpoint and the chosen outcome for assessment of enthesitis was heterogeneous across studies. There were no studies assessing the effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids, or csDMARDs. In PsA, all TNFis showed superiority in monotherapy against placebo (PBO). However, when combined with methotrexate (MTX), only some TNFi showed superiority against MTX monotherapy. In SpA, there was conflicting evidence regarding the efficacy of TNFi in enthesitis. Regarding IL23i in PsA, Ustekinumab was superior to PBO, and to TNFis. Guselkumab was superior to PBO when given every 4 weeks. Regarding IL7i, Secukinumab (SEC) was superior to PBO, only for some dosing schemes. Ixekizumab (IXE) was superior to PBO for the treatment of enthesitis only in TNF-naïve patients. Studies comparing SEC and IXE to ADA, showed no difference. There was no reported data on IL17i for enthesitis in SpA. In PsA, Tofacitinib was superior to PBO in naïve patients, and Tofacitinib 10mg was superior to PBO in bioexperienced patients. Apresmilast 30mg showed superiority to PBO for enthesitis. All findings are summarized on Table.
Conclusion: This SLR emphasizes the current heterogeneity in the assessment and report of enthesitis. There is still an unmet need for further studies to improve our understanding about enthesopathy.
1 – Schett G. et al. Enthesitis: from pathophysiology to treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(12):731-41.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Torres R, Manica S, Santos F. Pharmacological Treatment of Enthesitis – A Systematic Review on the Efficacy of the Available Options [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacological-treatment-of-enthesitis-a-systematic-review-on-the-efficacy-of-the-available-options/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacological-treatment-of-enthesitis-a-systematic-review-on-the-efficacy-of-the-available-options/