Background/Purpose
We explored the utility of peripheral CD19+ CD5+ B-cells (CD5+ B-cells) as biomarkers in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV)
Methods
CD5+ B-cells were measured longitudinally by flow cytometry in patients randomized to rituximab (RTX, n = 99) or CYC followed by AZA (CYC/AZA, n = 98) for the treatment of AAV (RAVE trial). Number of CD5+ B cells/mL and %CD5+ B-cells within the total population of CD19+ B-cells were determined. Outcomes assessed were disease activity, induction treatment failure, disease severity, relapse, and in the RTX arm, relapse-free survival according to %CD5+ B-cells at B-cell redetection (10-68 CD19+ B-cells/mL) and reconstitution (≥ 69 CD19+ B-cells/mL) using %CD5+ B-cells as dichotomous (>30% and ≤30% [1]) and categorical predictor. Repeated measure ANOVA, Wilcoxon, Fisher’s, logrank and Cox PH tests were used
Results
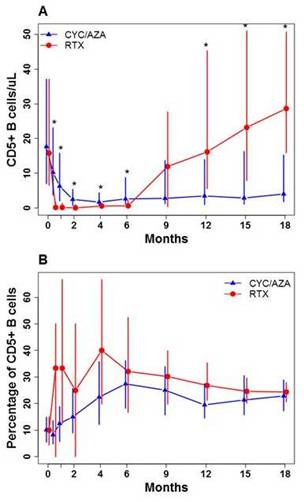
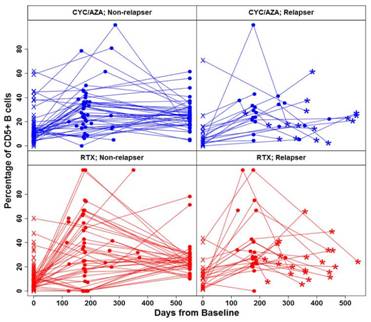
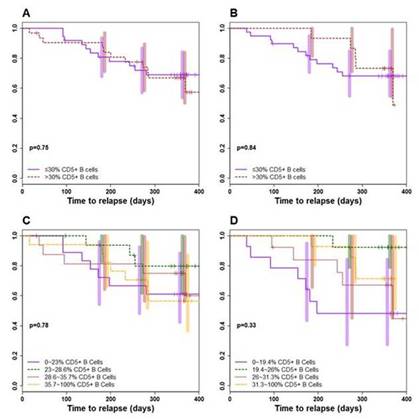
Median CD5+ B-cell numbers and %CD5+ B-cells were comparable between groups at baseline. After an initial decline, CD5+ B-cell numbers increased in the RTX arm, but remained low in the CYC/AZA cohort. In both groups, %CD5+ B-cells increased during remission induction and declined thereafter (Fig 1). %CD5+ B-cells correlated inversely with disease activity in RTX-treated patients (baseline 12%, remission 28% and relapse 23%; p < 0.05), but not in CYC/AZA-treated patients (Fig 2). No significant association was observed between CD5+ B-cells and induction failure or disease severity. Disease relapses were not preceded consistently by declines in %CD5+ B-cells. Once B-cells returned in the RTX arm, %CD5+ B-cells did not predict time to flare (Fig 3). The hazard ratio (HR) for relapse in patients with >30% CD5+ B-cells (versus ≤30%) at B-cell redetection was 1.14 (95% CI 0.49-2.64; P = 0.75). The HR for relapse in patients with >30% CD5+ B-cells (versus ≤30%) at B-cell reconstitution, was 0.9 (95% CI 0.31-2.55; P = 0.84). Division of patients by quartiles of %CD5+ B-cells upon B-cell repopulation failed to show any trend in time to relapse following the order of the strata
Conclusion
In patients with AAV treated with CYC or RTX CD5+ B-cells do not predict treatment response, relapse or disease severity
Fig 1
Fig 2
RTX n = 68 (22 relapsers); CYC/AZA n = 60 (16 relapsers); x = baseline; ● = remission; * = relapse
Fig 3
A/C redetection; B/D reconstitution
1 Bunch DO. CJASN 2013
Disclosure:
S. Unizony,
None;
N. Lim,
None;
V. Carey,
None;
D. J. Phippard,
None;
N. Tchao,
None;
E. M. Miloslavsky,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5;
P. A. Merkel,
None;
P. Monach,
None;
W. St. Clair,
None;
R. F. Spiera,
roche-genetech,
2;
A. Asare,
None;
P. Seo,
None;
C. A. Langford,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2;
G. S. Hoffman,
None;
C. Kallenberg,
None;
U. Specks,
None;
J. H. Stone,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-cd5-b-cells-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/