Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science Poster (0046–0068)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Heterogeneity in immune cell populations among patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may determine disease expression and treatment response. The objective of this study was to compare peripheral blood immune cell profiles in patients with PsA (before- and after- advanced therapy) and healthy controls using mass cytometry.
Methods: Patients with PsA who were initiating treatment with advanced therapies for active peripheral musculoskeletal disease were recruited along with healthy controls. We performed mass cytometry (CyTOF) using a panel of 30 metal-tagged antibodies (Maxpar Direct, Fluidigm) to characterize over 37 immune cell populations in whole blood from patients (before- and 3 months after therapy) and controls. The frequencies of the different immune cells populations were automatically quantified for each sample based on combinations of their associated canonical cellular markers using Probability State Modelling algorithms in a commercially available automated analysis system (MaxparPathsetter, Fluidigm). The levels (counts per 100 cells) of the different cell populations were compared between PsA patients vs. controls and among patients with PsA (before- and after- therapy) using Mann-Whitney U test and cluster analysis was performed using differential cell population levels.
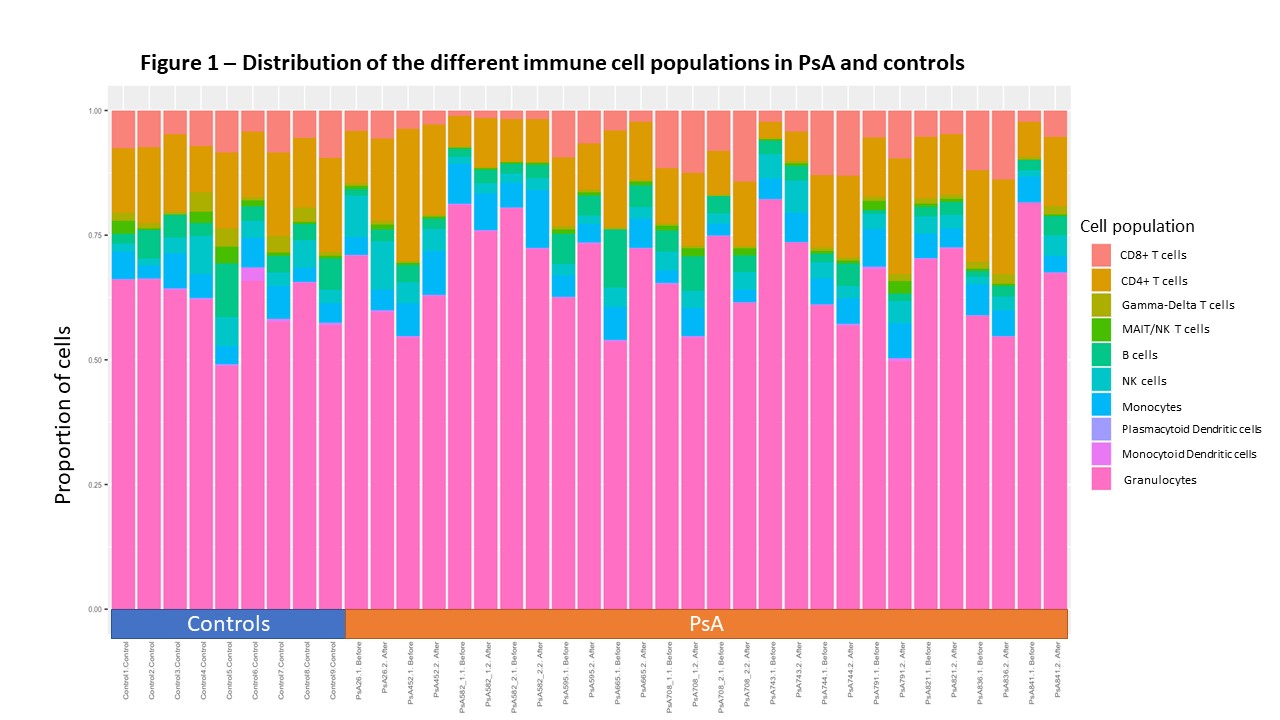
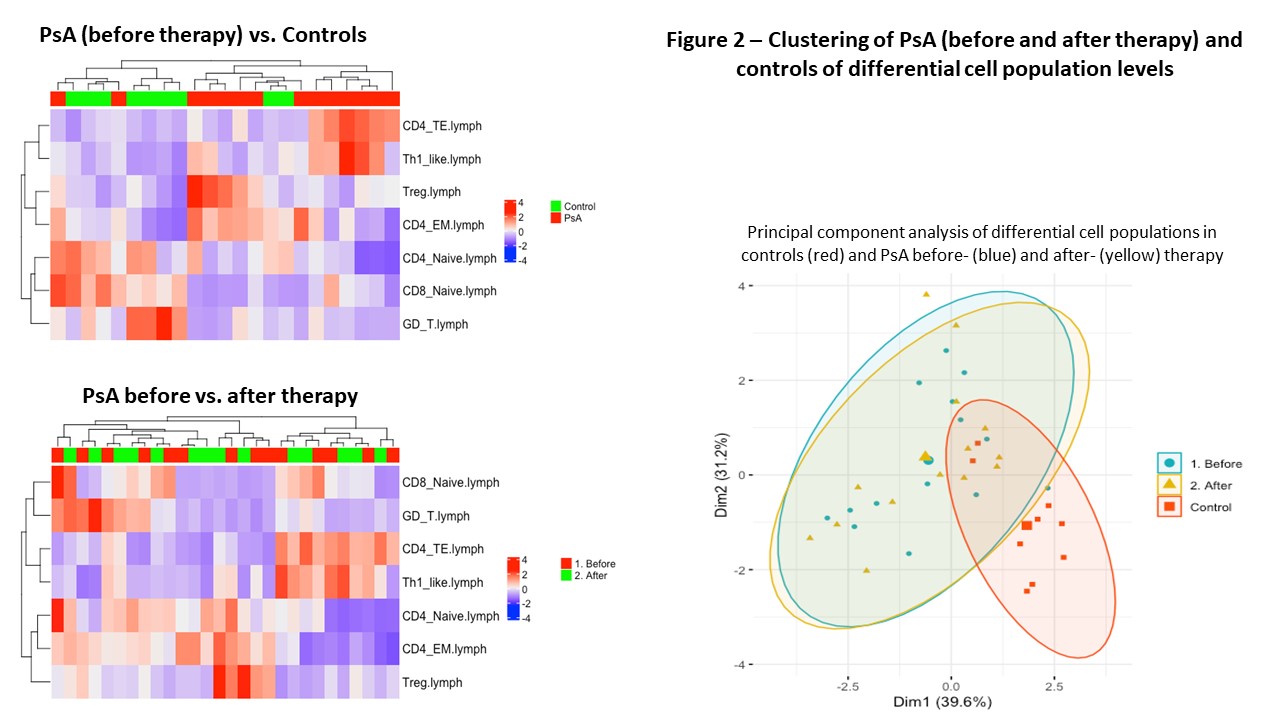
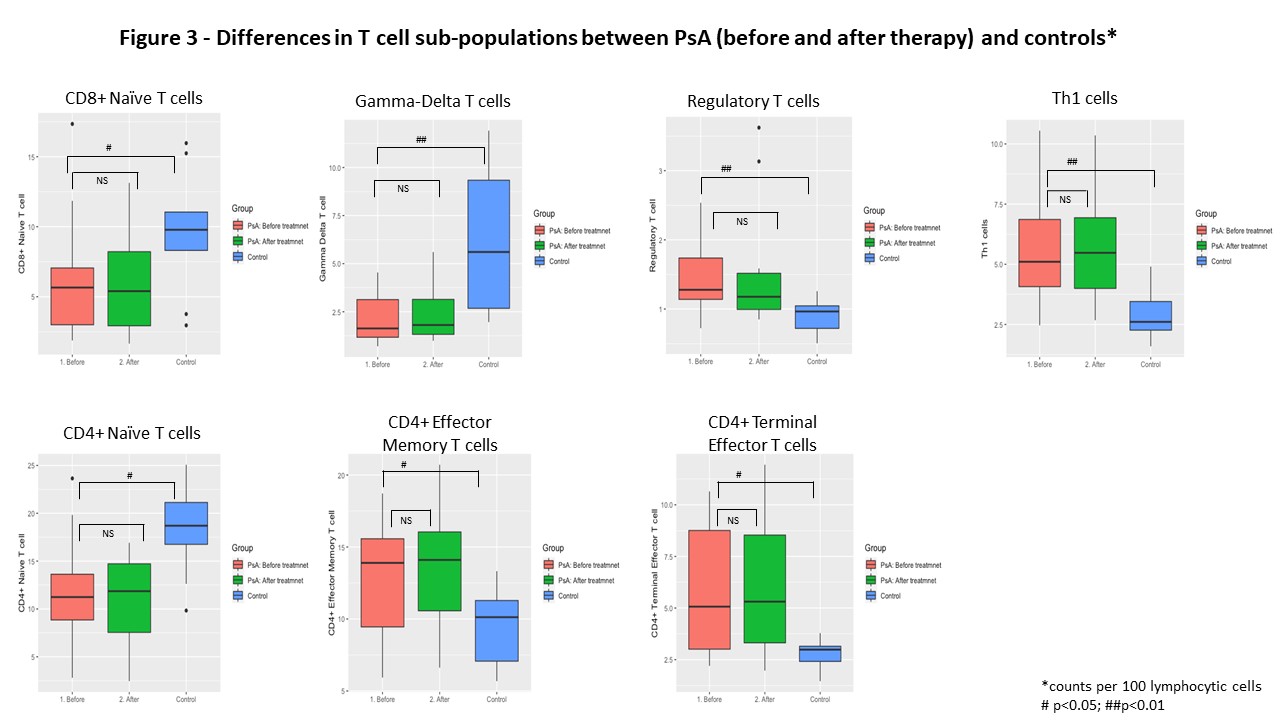
Results: A total of 37 samples from 12 patients with PsA (14 treatment periods) and 9 controls were analyzed. In general, large variability was found in the different cell populations across patients with PsA, while the levels were more homogenous across the controls (Figure 1). Most variability was found in the lymphocytic cells populations, in particular among the T cell sub-populations, thus the analysis was restricted to lymphocytic cells. We found significant differences in T cell sub-populations between PsA and controls (Figures 2). Patients with PsA had higher levels of CD4+ Terminal effector and CD4+ Effector memory T cells, CD4+ Th1 cells and CD4+ regulatory T cells, while higher levels of CD8+ and CD4+ Naïve T cells and gamma-delta T cells were found in controls (Figure 3). No significant differences were found in lymphocytic cell populations before and after advanced therapy. In addition, no significant differences were found in the levels of the following cell types and their sub populations between PsA vs. controls and among PsA patients before and after treatment: B cells, NK cells, granulocytes, monocytes and dendritic cells.
Conclusion: Considerable variability was found in T cell sub-populations among patients with PsA. Differences in the levels of specific T cell populations with a shift towards terminal and memory T cells as well as Th1 axis was seen in patients with PsA compared to control. Whether immune cell profile predict response to advanced therapy in PsA remains to be examined.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eder L, Ganatra D, Chandran V. Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Profiling in Psoriatic Arthritis: Comparison of Patients with Healthy Controls [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-immune-cell-profiling-in-psoriatic-arthritis-comparison-of-patients-with-healthy-controls/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-immune-cell-profiling-in-psoriatic-arthritis-comparison-of-patients-with-healthy-controls/