Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the performance of the proposed American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in Korean patients
Methods: We conducted medical chart review study of patients with SLE and defined rheumatic diseases as control group. The clinical diagnosis was used as the gold standard. The classification based on 1997 ACR criteria, 2012 Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) criteria and the newly proposed ACR/EULAR criteria were examined with analysis of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predicted value.
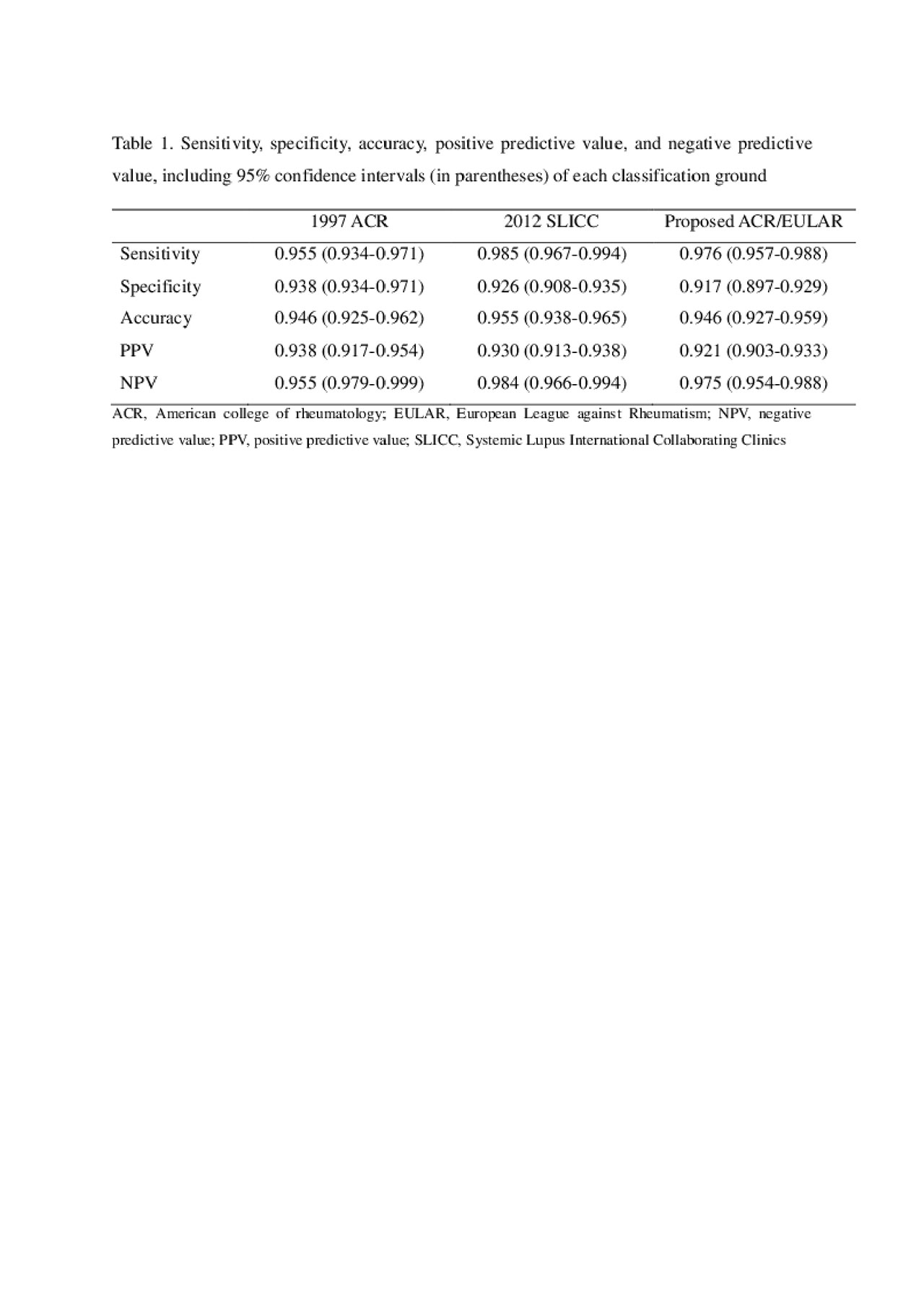
Results: A total of 335 SLE patients and 337 non-SLE patients were included in the analysis. Non-SLE patients included rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=92), anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS) (n=57), mixed connective tissue disease (CTD) (n=52), systemic sclerosis (n=43), primary Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) (n=39), undifferentiated CTD (n=28), RA with secondary SS (n=24), dermatomyositis (n=1) and spondyloarthropathy (n=1). The sensitivity of the proposed ACR/EULAR criteria was 97.6% (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.957-0.988) compared with 98.5% (95% CI, 0.967-0.994) for the 2012 SLICC criteria. The specificity for the proposed ACR/EULAR criteria and 2012 SLICC criteria were 91.7% (95% CI, 0.897-0.929) and 92.6% (95% CI, 0.908-0.935), respectively. Eight patients who were classified as SLE with the proposed ACR/EULAR criteria but not with 2012 SLICC criteria, had a tendency of having arthritis domain and highly specific antibody domain which counts for a score of 6. One patient classified as SLE according to the proposed ACR/EULAR criteria had malar rash and arthritis and one patient had serositis, leukopenia and fever (constitutional domain). Three APS patients who were classified as SLE according to the 2012 SLICC criteria did not meet the proposed ACR/EULAR criteria due to the entry criterion of positive anti-nuclear antibody. The ACR/EULAR score ≥ 12 rather than a score ≥ 10, resulted in higher specificity, positive predictive value, and accuracy and higher sensitivity than 1997 ACR criteria.
Conclusion: The proposed ACR/EULAR criteria for SLE had comparable performance in respect of diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity in this Korean population of SLE and other rheumatic diseases. However, the proposed criteria could not reach higher specificity than 2012 SLICC criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee E, Lee E, Lee E, Park J, Ahn S, Song Y. Performance of the Proposed American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Korean Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-proposed-american-college-of-rheumatology-european-league-against-rheumatism-classification-criteria-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-korean-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-proposed-american-college-of-rheumatology-european-league-against-rheumatism-classification-criteria-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-korean-patients/