Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a systemic auto-immune disease with a heterogeneous clinical presentation. Recently, ACR-EULAR criteria were proposed for classification of SS, which combine features of the ACR and AECG criteria. The aim of this analysis was to assess the performance of the ACR-EULAR classification criteria for SS in a well-defined prospective diagnostic cohort from daily practice.
Methods: The study population consisted of consecutive patients who were referred to the University Medical Center Groningen Sjögren expertise center. Inclusion criteria were suspicion of SS, presence of sicca complaints and age of >18 years. Patients who did not complete the full diagnostic workup were excluded. The standardized diagnostic work-up included evaluation of focus score (FS) in minor salivary and/or parotid gland biopsy, anti-SSA antibodies, unstimulated whole salivary flow (UWS), Schirmer’s test and ocular staining score (OSS). Patients had to score ≥4 points to fulfill the ACR-EULAR criteria for SS, receiving 3 points for FS≥1 and anti-SSA positivity, and 1 point for UWS ≤0.1 ml/min, Schirmer ≤5 mm/5min and OSS ≥5. Classification according to ACR-EULAR criteria was compared with clinical diagnosis according to the treating rheumatologist.
Results: Between December 2013 and March 2016, 119 patients were included at the start of their diagnostic work-up, of which 5 were excluded due to missing data. Of the 114 patients, 46 (40%) fulfilled the ACR-EULAR criteria for SS, of which 1 patient was classified as secondary SS. Comparing separate tests between SS (n=46) and non-SS patients (n=68), FS≥1 occurred in 85% vs. 4% of the patients, anti-SSA positivity in 78% vs. 6%, UWS ≤0.1 ml/min in 54% vs. 39%, Schirmer ≤5 mm/5min in 83% vs. 55% and OSS ≥5 in 53% vs. 14% (figure). Preliminary analysis showed that agreement between diagnosis according to the treating rheumatologist and classification according to ACR-EULAR criteria was excellent with Cohen’s kappa of 0.87 and an absolute agreement of 94%. The ACR-EULAR criteria had a sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 93%.
Conclusion: In our prospective, multidisciplinary diagnostic cohort derived from daily clinical practice, 40% of the patients fulfilled the ACR-EULAR classification criteria for SS. FS≥1, anti-SSA positivity and OSS ≥5 occurred almost exclusively in SS patients, whereas UWS ≤0.1 ml/min and Schirmer ≤5 mm/5min were often found in non-SS patients too. Agreement between the ACR-EULAR criteria and clinical diagnosis was excellent. The present findings support use of the proposed ACR-EULAR criteria to classify SS patients for clinical diagnostic as well as research purposes. In future analysis, classification of SS according the ACR-EULAR criteria will be compared with classification according to an expert panel of rheumatologists. 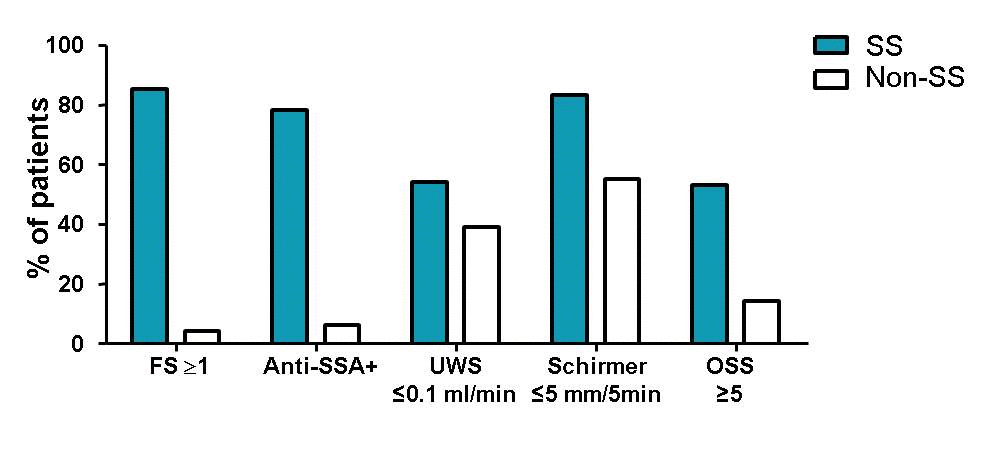 Figure: Proportion of SS and non-SS patients fulfilling the separate ACR-EULAR criteria.
Figure: Proportion of SS and non-SS patients fulfilling the separate ACR-EULAR criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Nimwegen JF, van Ginkel MS, Arends S, Verstappen GM, Haacke EA, van der Vegt B, Sillevis Smitt-Kamminga N, Spijkervet FKL, Kroese FGM, Vissink A, Bootsma H. Performance of the Proposed ACR-EULAR Criteria for Sjogren’s Syndrome in a Prospective Multidisciplinary Diagnostic Cohort from Daily Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-proposed-acr-eular-criteria-for-sjogrens-syndrome-in-a-prospective-multidisciplinary-diagnostic-cohort-from-daily-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-the-proposed-acr-eular-criteria-for-sjogrens-syndrome-in-a-prospective-multidisciplinary-diagnostic-cohort-from-daily-clinical-practice/
