Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I (0387–0413)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
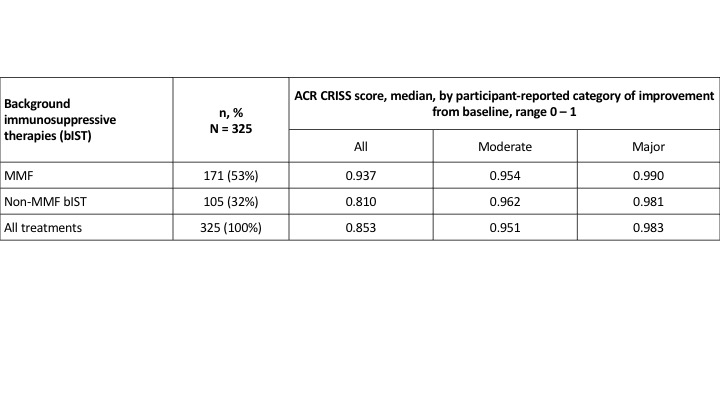
Background/Purpose: ACR CRISS score is the probability of improvement from baseline in each participant (pt) ranging from 0 to 1 (no to high probability), based change in 5 core items: mRSS, FVC%, PtGA, MDGA, and HAQ-DI. Development of this score was done by experts who assessed profiles of dcSSc pts who were recruited in clinical practice on bIST, so its performance and reflection of pt opinion of improvement is unknown in clinical trials in which bIST such as mycophenolate (MMF) are widely used. Revised ACR CRISS (rCRISS) responses are the proportion of pts who improve in ≥ 3/5 core items by certain percentages, for example, 30% (except ≥ 5% in FVC%). Performances were assessed of ACR CRISS score (prospectively as primary endpoint) and rCRISS responses (retrospectively) in a Phase 3 trial in which bIST were allowed.
Methods: Data were analyzed from a 1-year Phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled study of lenabasum in pts with dcSSc ≤ 6 years duration, with stable doses of bIST allowed. Pts completed a Patient Global Assessment of Change to categorize their improvement as None, Slight, Moderate, or Major. All cohorts were combined for analyses as the primary endpoint was not meet. Pre-specified analyses had identified a statistically significant effect of MMF on ACR CRISS score in this study, so analyses were done first in pts on MMF, then results validated in other patients.
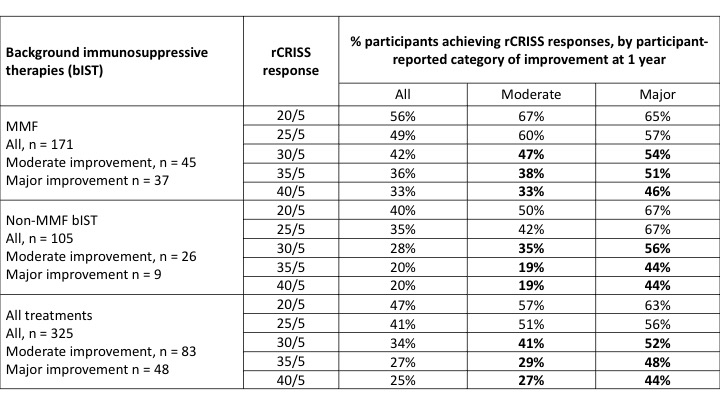
Results: 276/325 (85%) pts were on bIST. Among 171 pts on MMF, 65% of pts reported improvement at 1 year, which was moderate or major in 48%. ACR CRISS score had a ceiling effect (median = 0.937), with similar scores in pts reporting moderate and major improvement (Table 1). rCRISS responses were examined for potential to distinguish between higher levels of treatment effect, reported by pt opinion. Pts on MMF who reported moderate or major improvement had ~3 core items that improved by ≥ 20% vs. ~2 core items in pts reporting no improvement, supporting requirement for ≥ 3 core items to improve when defining rCRISS responses. rCRISS responses of at least 30/5 (≥ 3 core items improved by ≥ 30%, except ≥ 5% for FVC%) were numerically greater in pts on MMF who reported major vs. moderate improvement (Table 2), with greater discrimination using 35/5 and 40/5 than 30/5 responses. The rCRISS 30/5, 35/5, and 40/5 responses were 52%, 48%, and 44%, respectively, in pts reporting major improvement on background MMF (Table 2). All these findings were directionally confirmed in pts on non-MMF bIST.
Conclusion: In this Phase 3 trial, bIST provided treatment effect, with about half the pts on background MMF reporting moderate or major improvement at 1 year. Use of the ACR CRISS score to prove efficacy on top of bIST was constrained by its ceiling effect. rCRISS 30/5 or greater responses may help distinguish high level treatment effects on top of bIST. rCRISS responses may be ~ 50% in pts given placebo on top of bIST, setting a high bar for proving additional treatment effect. Use of rCRISS responses to improve the ACR CRISS score may decrease the ceiling effect, provide an equal weight for 5 core items, and improve the interpretation of data (similar to ACR 20% response in RA). These findings should be confirmed in other trials in which pts receive current standard treatment with bIST.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khanna D, Spiera R, White B. Performance of ACR CRISS Score and Revised ACR CRISS Response in a Phase 3 Trial of Lenabasum in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc) in Which Background Immunosuppressive Therapies (bIST) Were Allowed [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-acr-criss-score-and-revised-acr-criss-response-in-a-phase-3-trial-of-lenabasum-in-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-dcssc-in-which-background-immunosuppressive-therapies-bist-wer/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-of-acr-criss-score-and-revised-acr-criss-response-in-a-phase-3-trial-of-lenabasum-in-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-dcssc-in-which-background-immunosuppressive-therapies-bist-wer/