Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The ANA is a critical test in the evaluation of patients with suspected lupus and other connective tissue diseases. Clinical laboratories have relied increasingly on automated solid phase methods for its detection and, more recently, on automated pattern recognition systems for the indirect immunofluorescence (IFA) technique. The performance characteristics of both methods have not been rigorously evaluated and have not been studied prospectively.
Methods: Patients who were seen by an academic rheumatologist, who had ANA’s obtained within 30 days by both Elisa (Zeus ElisaTM) and IFA (Euroimmune ANA Diagnostics TM), and whose diagnosis had yet to be established, were evaluated. Patients were followed to establish a diagnosis. Patients were classified at their last office visit by clinical diagnosis, confirmed by independent review, and were further grouped into those with: 1) Connective tissue disease (CTD) including pts with definite and probable CTD who were also receiving DMARD/ immunomodulating therapy; 2) Early undifferentiated connective tissue disease (EUCTD) which included CTD, possible CTD, as well as undiagnosed inflammatory polyarthritis (IPA); and, 3) inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) which included all with EUCTD as well as patients with RA.
Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, likelihood and diagnostic odds ratios and their confidence intervals were calculated and compared.
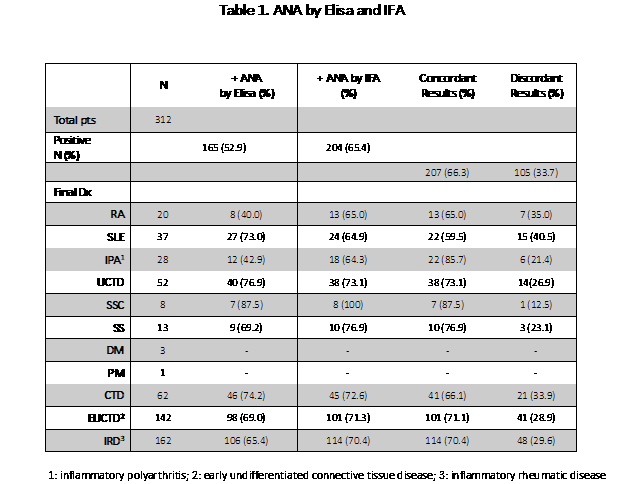
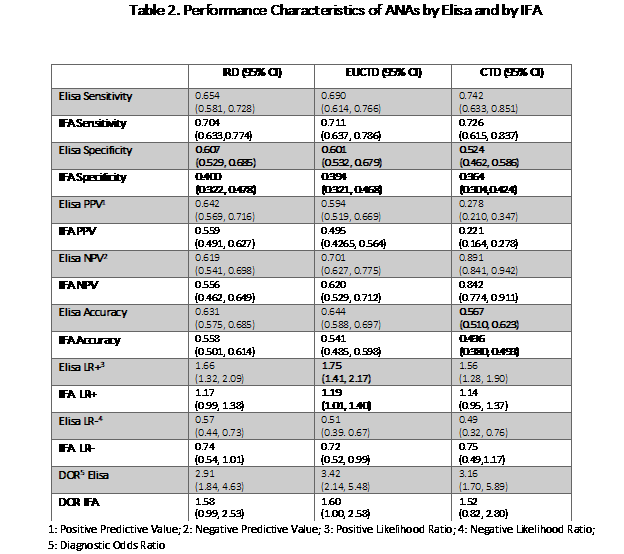
Results: 312 patients were identified and followed for a median of 9.96 months (IQR: 1.9, 18.5). At their last visit the following diagnoses were established: CTD- 62 (SLE-37, SS-13, SSC-8, DM-3, PM-1), EUCTD-142, IRD-162. Percent positive ANAs by Elisa and IFA were 52.9% and 65.4% respectively. Concordance of results was found in 66.3% The performance characteristics of the two ANA techniques are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
In general, the test methodologies provided comparable results. IFA was somewhat more sensitive (NS) while Elisa was more specific (p< 0.05). Diagnostic accuracy was higher with Elisa than with IFA for definite CTD (0.567 vs 0.436, p < 0.05). Diagnostic odds ratios where higher with Elisa (2.91-3.42) than with IFA (1.52-1.60) although the differences did not achieve statistical significance.
Conclusion: ANA by Elisa and ANA by IFA performed similarly in this short-term, prospective study. Elisa appears to be more specific and possibly more accurate in patients who had developed a definite CTD. Further observation will be necessary to definitively determine any meaningful differences in testing approaches.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lobo G, Luggen M, Crutchfield C. Performance Characteristics of ANA by Elisa and Immunofluorescence [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-characteristics-of-ana-by-elisa-and-immunofluorescence/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-characteristics-of-ana-by-elisa-and-immunofluorescence/