Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Autoantibodies in SLE can be detected by either immunoblot assay or by ELISA. Both these methods may have variable performance with respect to the antigen being tested. We checked the performance and concordance of these two methods in detecting the eight commonest autoantibodies (antibodies to dsDNA, nucleosomes, histones, SS-A (Ro-60), SS-B, nRNP, Sm & Ribosomal P Protein – RPP) in patients with SLE.
Methods: A total of 180 SLE patients’ (classified as per ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria) serum samples (all positive for Antinuclear antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence at 1:80 dilution) were tested for the above-mentioned autoantibodies using both immunoblot and ELISA (Euroimmune, Germany). The results from ELISA were categorised as positive or negative as per the kit’s cut-off values given by the manufacturers. For immunoblot assay, all the intensities of the bands from 1+ to 3+ were taken as test positive for the respective antibody. Cohen’s kappa was calculated as a measure of agreement between the two tests for each autoantibody. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
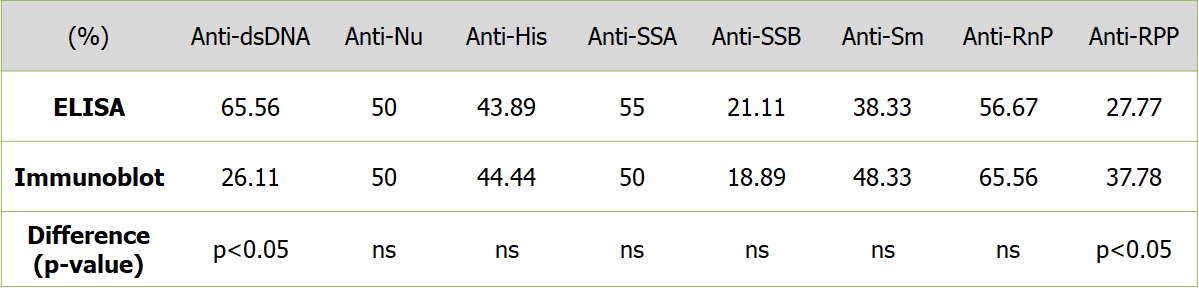
Results: Positivity rates for the ELISA (for the autoantibodies to dsDNA, nucleosomes, histones, SS-A, SS-B, nRNP, Sm & Ribosomal P protein – RPP) were 65.56%, 50%, 43.89%, 55%, 21.11%, 56.67%, 38.33% and 27.77% respectively whereas for immunoblot assay, the positivity rates were 26.11%, 50%, 44.44%, 50%, 18.89%, 65.56%, 48.33% and 37.78% respectively. The differences between the positivity rates were significant for autoantibodies to dsDNA favouring ELISA and RPP favouring immunoblot (p< 0.05 for both). (Table 1)
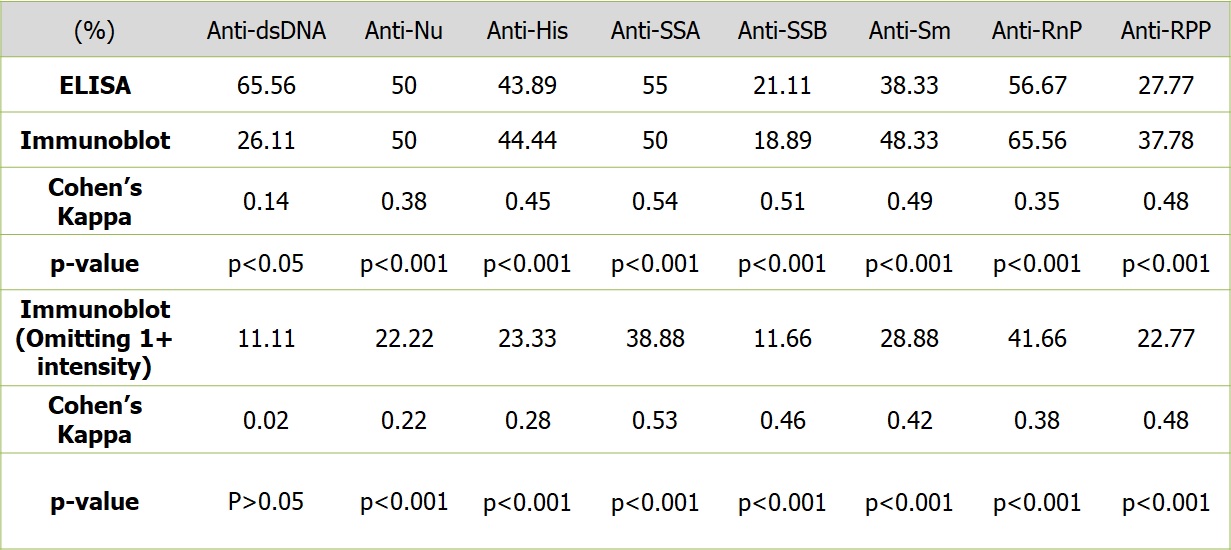
The Cohen’s kappa for the two methods was 0.14, 0.38, 0.45, 0.54, 0.51, 0.35, 0.49 and 0.48 (p< 0.001 for all except for dsDNA – p< 0.05) respectively showing poor to modest concordance. Since low intensity positivity on immunoblot assay could impact the concordance between the two methods adversely, we hypothesized that omitting these from the positive results could improve the concordance. We re-analysed the results after omitting 1+ intensities from the positive results and considering only 2+ and 3+ as positive. This also did not improve the concordance between the two methods for any of the antibodies tested and lead to significant loss of positivity rate for all autoantibodies on the immunoblot assay (11.11%, 22.22%, 23.33%, 38.89, 11.67, 41.67, 28.89% and 22.78% respectively). (Table 2)
Conclusion: Performance of the two methods differs significantly for detecting antibodies to dsDNA (ELISA better) and RPP (Immunoblot better). There is poor (anti-ds DNA antibodies) to modest (anti-SS-A antibodies) agreement between the two methods for detecting autoantibodies in SLE. Discounting the low grade (i.e. 1+) positivity on immunoblot assay leads to significant drop in the positivity rates for all antibodies and also does not improve the concordance with ELISA results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta R, Rajput S, Goswami R, Kumar J, Aggarwal A. Performance and Concordance of Two Different Methods of Detecting the Commonest Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-and-concordance-of-two-different-methods-of-detecting-the-commonest-autoantibodies-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/performance-and-concordance-of-two-different-methods-of-detecting-the-commonest-autoantibodies-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/