Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fatigue is one of the most frequent symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), affecting more than 80% of them. The experience of fatigue is multidimensional. Purpose: to identify the factors associated with fatigue on its different subscales (Physical, Living, Cognitive and Emotional).
Methods: Cross-sectional study. 79 patients were included, patients were being followed up in the rheumatology outpatient clinic of Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain. Data were collected between July 2018 and May 2019. All patients met the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria and they were in treatment with Biological agent (anti-TNF and Non anti-TNF) or Targeted Synthetic DMARD (jakinibs). Main variable: Fatigue was assessed by the multidimensional fatigue scales, the Bristol Rheumatoid Arthritis Fatigue Multidimensional Questionnaire (BRAF-MDQ). Covariables: Sociodemographic, Disease-related variables, clinical and treatment. Statistical analysis. A descriptive analysis was carried out for the different variables. To identify factors independently associated to BRAF-MDQ and its subscales, multivariable linear regression was applied. Results were expressed as coef with their corresponding 95% CI. A value of p < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant.
Results: A total of 79 patients were evaluated, 66 were females (83%), the mean age (SD) was 56.64(11.63) years old and mean disease duration (SD) was 14.81 (7.60) years. RF was positive in 54% of patients. 67% of the patients were in active on work status and 22% were retired. Regarding comorbidities, 42% had dyslipidemia, 43% hypertension, 14% hypothyroidism and 15% depression. DAS28-ESR and SDAI mean scores of the patients were 2.63 (0.94), 8.54 (6.30) respectively. HAQ mean (SD) was 0.88 (0.64) and the rest of the clinical, treatment characteristics, and the scores of the fatigue instruments are shown in Table 1. The factors affecting the BRAF-MDQ and its different subscales was evaluated in multivariate analyze Table 2. Our results shows a correlation between disability and the different dimensions of the BRAF-MDQ (p < 0.001). Patients who reported good sleep quality had less physical and living fatigue. Age and male sex was negatively associated with physical fatigue, besides a positive RF was associated with less physical and living fatigue. In addition, an association between depression and cognitive fatigue was observed. Different disease activity index and treatments did not result statistical significance in the final multivariate model.
Conclusion: It is important to evaluate fatigue in a multidimensional perspective, each of the different subscales could be modulated by different factors. The results of our study indicated that disability predicts in all subscales of fatigue, however, other factors can configure different patterns of fatigue in RA patients, and identify them is key to the approach of this complex symptom.

Table 1. Characteristics of the study group.
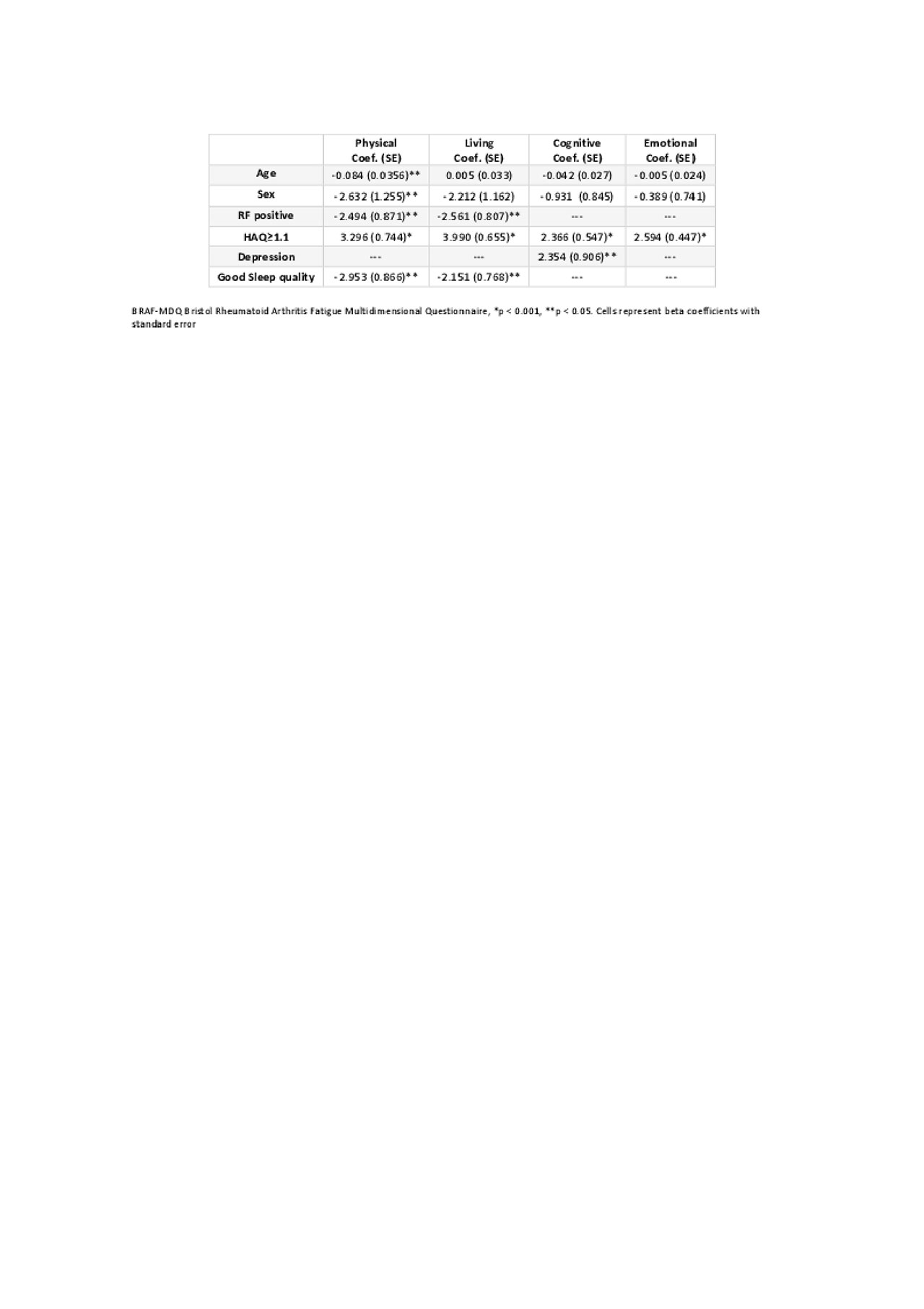
Table 2. Multivariate analyses of BRAF-MDQ and its subscales
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Freites Nuñez D, León L, Redondo M, Vadillo Font C, Lois P, Mucientes Ruiz A, Rodríguez-Rodríguez L, Fernández Gutiérrez B, Jover Jover J, Abasolo Alcazar l. Patterns of Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Who Received Biological and Targeted Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patterns-of-fatigue-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-who-received-biological-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patterns-of-fatigue-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-who-received-biological-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs/
