Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Assessing clinical improvements in Sjögren’s Disease (SjD) is challenging. Our objective was to describe patterns of improvement in SjD using ESSDAI and ESSPRI indices and identify factors associated with these improvements.
Methods: Patients from the prospective SSAD cohort, which collects biological and clinical data from SjD cases, were included. ESSDAI improvement (ESSDAI-I) was defined by improvement in ≥1 ESSDAI domain (transition from high (H) or moderate (M) to low (L) or no activity (NA) in most domains; from M to L or NA in the glandular domain; and from H to M or NA in the CNS domain) without worsening in any other. ESSPRI improvement (ESSPRI-I) was defined as a reduction ≥2 points or ≥30% from baseline.Patients were classified as improvers if improvement between two visits (3 months apart) was maintained at a subsequent visit 3 months later; the visit preceding improvement was considered baseline. Non-improvers (NI) were defined as patients with baseline ESSDAI or ESSPRI >0 but without observed improvement.Among ESSDAI-I patients, clinical (ClinESSDAI) and isolated biological improvements were analyzed separately. As not all patients received therapeutic interventions at baseline, analyses were conducted for the entire cohort and separately for a subgroup initiating rituximab (RTX) at baseline.Logistic regression models assessed the association of clinical variables with improvement status, adjusting for sex, age, disease duration, and baseline ESSDAI and ESSPRI scores. Fisher’s exact test and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Unadjusted p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Analyses were performed using R v4.4.
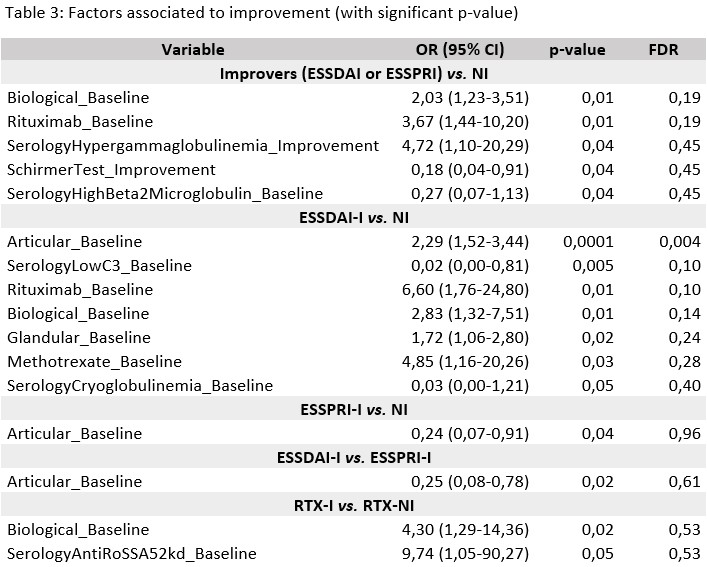
Results: A total of 363 patients susceptible to improvement were analyzed. Improvement was observed in 30 patients (8.3%): 15 (4.1%) showed ESSDAI-I, 14 (3.86%) ESSPRI-I, and 1 patient (0.27%) showed simultaneous improvement in ESSDAI and ESSPRI. Four of the 16 ESSDAI-I cases improved only in the biological domain.Overall improvement (ESSDAI or ESSPRI) was positively associated with higher baseline biological domain scores, initiation of RTX at baseline, and improvements in hypergammaglobulinemia and Schirmer’s test, but negatively with elevated β2-microglobulin (B2M).ESSDAI-I patients showed higher baseline scores in articular, biological, and glandular domains and more frequent RTX or MTX initiation than NI patients. Negative associations were noted with low C3 levels and cryoglobulinemia.ESSPRI-I was positively associated with RTX initiation, higher peripheral nervous system domain and lower articular domain scores. ESSDAI-I patients had significantly higher baseline articular domain scores compared to ESSPRI-I patients.In patients initiating RTX therapy, higher baseline biological scores predicted improvement, and Ro52 positivity trended toward significance.
Conclusion: ESSDAI and ESSPRI improvements rarely coincided in our cohort. Higher baseline biological and articular domain scores predicted ESSDAI improvement. Initiation of RTX strongly correlated with improvement, whereas elevated B2M, low C3 levels, and cryoglobulinemia negatively predicted improvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gómez Gómez A, Martínez Mateu S, Tandaipan J, Fernandez Castro M, gonzalez G, Melchor-Díaz S, Uriarte Ecenarro M, Menor Almagro R, Vela Casasempere P, Paredes-Romero B, Font-Urgelles J, Estrada-Alarcón P, Manrique-Arija S, Blazquez Cañamero M, Moriano C, Alegre-Sancho J, Rodríguez López M, López M, Bonilla G, Ortega-Castro R, Rojas Herrera S, Braña I, López-Núñez L, Narváez J, Rosas Gómez de Salazar J, López-Sánchez R, Galisteo Veiga C, Martínez-Ferrin J, Pérez Venegas J, Manzano-Canabal G, Peralta-Ginés C, Sánchez Bilbao L, Andrés Román Ivorra J, Cáliz-Cáliz R, Serrano-Benavente B, Fernández-Aguado S, Boix- Martí N, Kirkegaard-Biosca E, Alvarez Saez I, Selles-Rius A, Pérez M, Cañete J, Marsal S, Andreu J. Patterns and Predictors of Clinical Improvement in Patients with Sjögren’s Disease: A Longitudinal Analysis of ESSDAI and ESSPRI Improvements [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patterns-and-predictors-of-clinical-improvement-in-patients-with-sjogrens-disease-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-essdai-and-esspri-improvements/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patterns-and-predictors-of-clinical-improvement-in-patients-with-sjogrens-disease-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-essdai-and-esspri-improvements/

.jpg)
.jpg)