Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Nails are a challenging body area to treat in patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA)1. Previous research found that nail psoriasis is closely related to distal interphalangeal joint disease, and that greater proportion of patients with complete resolution of both was achieved over 52 weeks (W) through targeting IL-17A with ixekizumab (IXE) compared to TNF-α with adalimumab (ADA)2. In this analysis we sought to understand whether baseline (BL) nail involvement is an important indicator of treatment response in pts with PsA from the SPIRIT H2H (NCT03151551) study.
Methods: This descriptive post hoc analysis included 565 pts with PsA from SPIRIT-H2H treated with either IXE or ADA with Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI) >0 or NAPSI=0 at BL. All pts satisfied the CASPAR classification criteria guidelines for PSA3. Parameters assessed included Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis-Low Disease Activity (DAPSA-LDA), Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) 90 and 100, Minimal Disease Activity (MDA; calculated with PASI instead of BSA), swollen (SJC) and tender joint count (TJC), SF-36 Physical (PCS) and Mental (MCS) Component Summary score, and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Non-responder imputation was used to handle missing data.
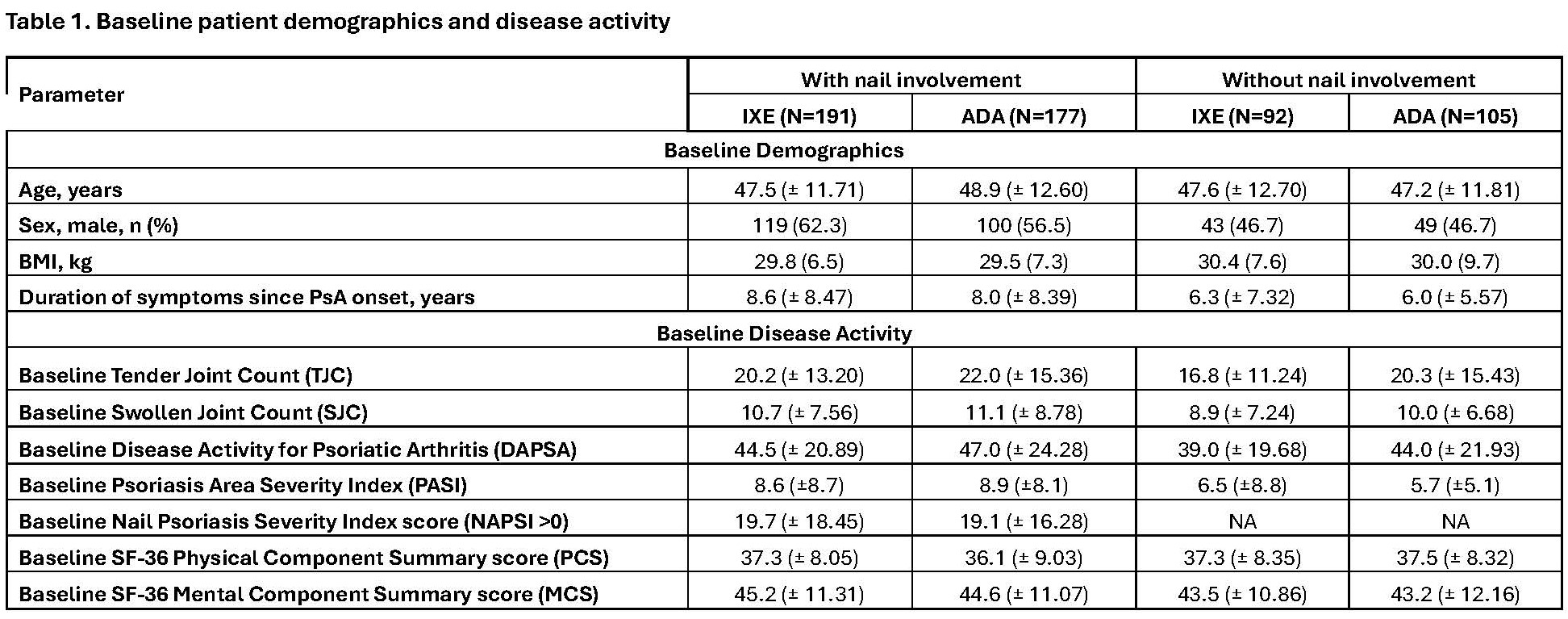
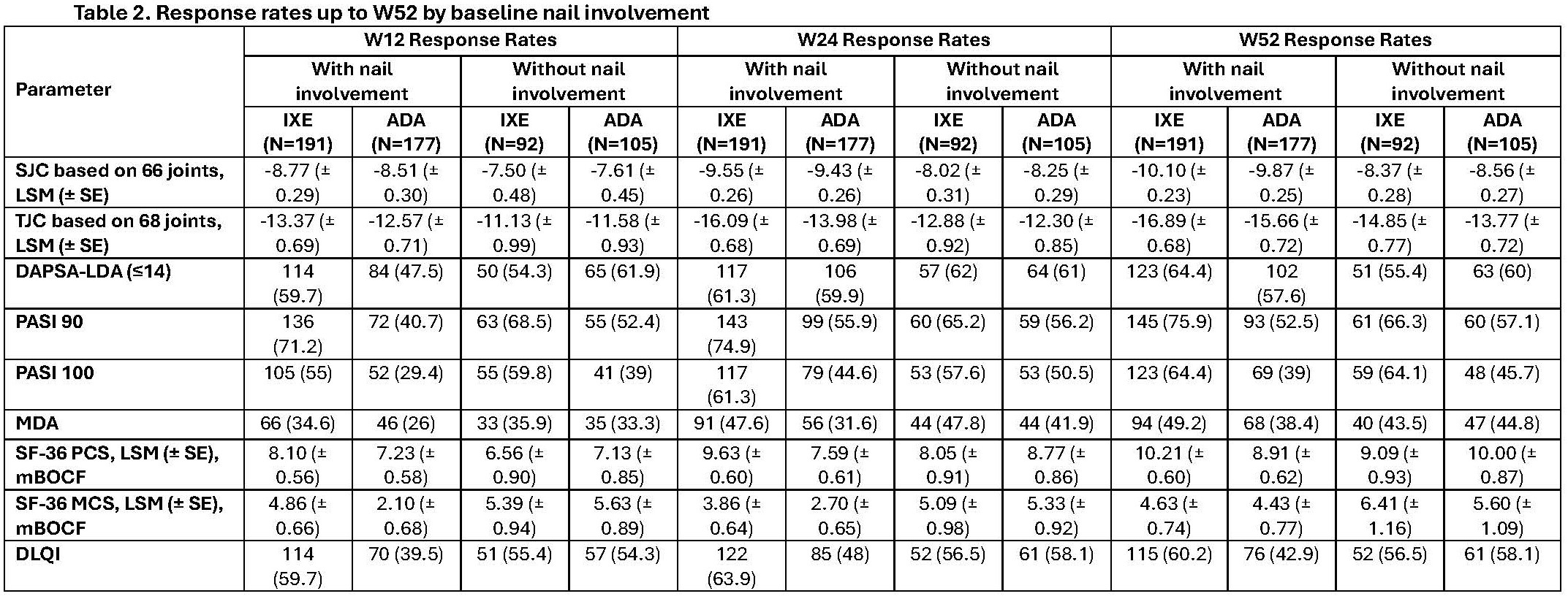
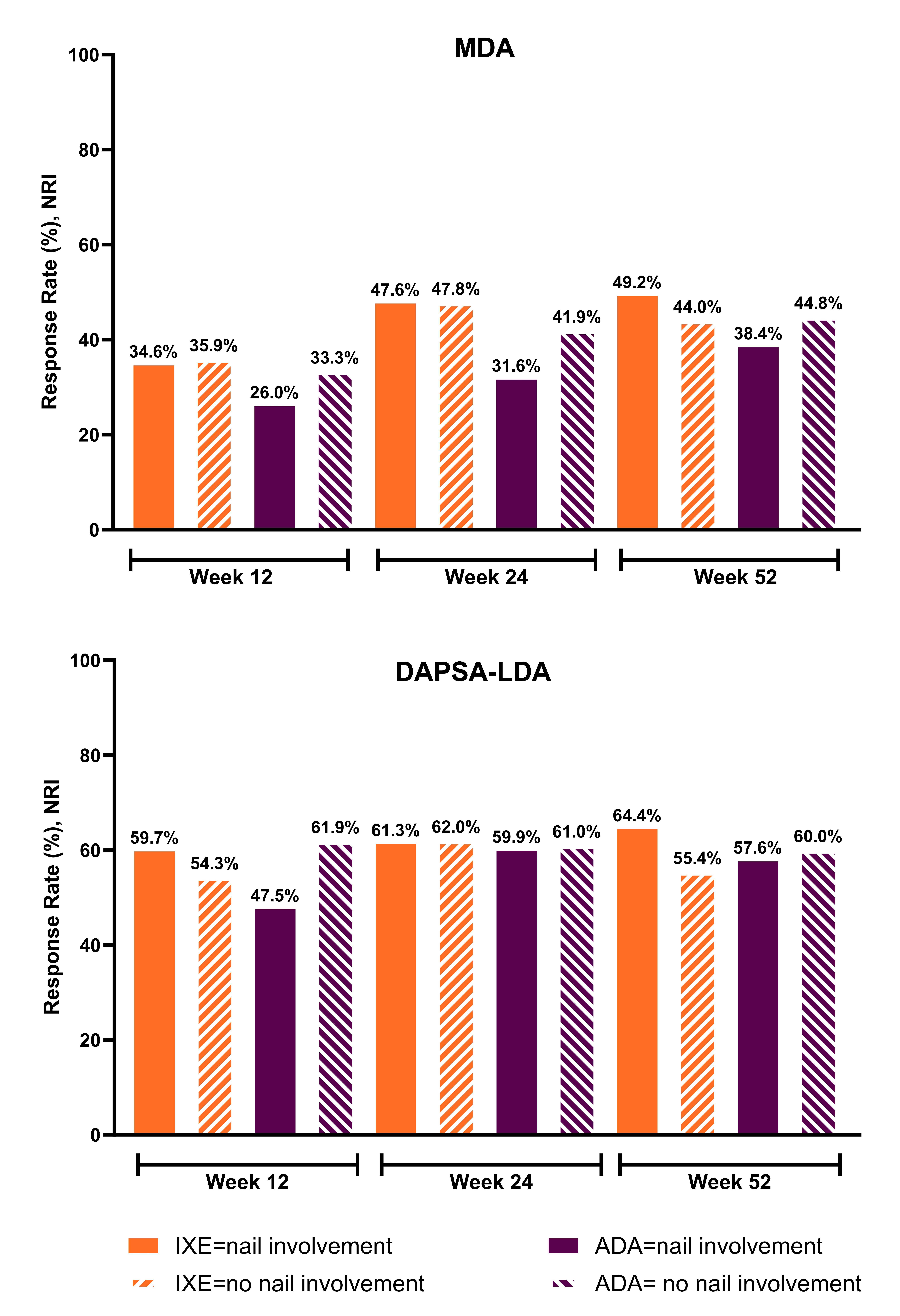
Results: Of the 565 pts at BL, 368 had nail involvement (NAPSI >0) and 197 had no nail involvement (NAPSI=0). BL characteristics were similar for age and body mass index, with differences based on nail involvement at BL evident for sex, duration of symptoms since PsA onset, SJC and TJC, and PASI score, which were higher in pts with nail involvement (table 1). Pts with nail involvement at BL demonstrated higher SJC and TJC improvement vs those without involvement at W12, W24 and W52 following treatment with IXE and ADA compared to patients without nail involvement at BL (table 2). IXE achieved rapid response for DAPSA-LDA as early as W12 (59.7%) and maintained this response up to W52 (64.4%). For PASI 90 and MDA IXE achieved a more rapid and high response rates compared to ADA in pts with and without nail involvement at BL (table 2). In pts with nail involvement, IXE demonstrated improvement in SF-36 MCS and PCS as early as W12 and maintain up to W52 compared to ADA. (table 2).
Conclusion: IXE and ADA both showed numerically greater SJC reduction in those with nail disease. Further, IXE and ADA both demonstrated joint improvement in pts with and without nail involvement at BL. In the subset of pts with BL nail involvement, numerically higher proportions of pts treated with IXE compared to ADA achieved DAPSA-LDA, PASI 90, MDA, and SF-36 as early as W12, and sustained up to W52.
References:
1. Kirkham et al. Rheumatol Ther 2023; 10(5): 1127-46.
2. McGonagle et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2024.
3. Taylor et al. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54(8): 2665-73.
Without nail involvement is NAPSI=0; with nail involvement is NAPSI>0. Abbreviations: DAPSA= Disease activity in psoriatic arthritis; LDA=low disease activity; LSM=least squares mean; MDA=minimal disease activity; N=number of patients in overall population; n=number of patients in specified category; NRI=non-responder imputation; W=week.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zabotti A, Ogdie A, Okada M, Bolce R, Lisse J, Ngantcha M, taher m, Jing Ng K, McGonagle D. Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis from a Phase 4 Head-to-Head Study Stratified by Nail Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-from-a-phase-4-head-to-head-study-stratified-by-nail-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-from-a-phase-4-head-to-head-study-stratified-by-nail-involvement/