Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes (1909–1914)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-2:45PM
Background/Purpose: Previous studies showed a discrepancy between patient’s and HealthCare Professional (HCP) perspective on the burden of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs), where HCPs often underestimate the burden. However, it is unknown which factors determine whether a patient perceives an ADR as burdensome. This study aimed to provide more insight into the burden of ADRs reported by patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases that are attributed to the use of biologics, by identifying the factors that determine patient-perceived burden. Furthermore, this study aimed to compare both patient’s and rheumatologist’s perspective on these factors, to give more insight in the discrepancy between their perspectives.
Methods: Qualitative data from the Dutch Biologic Monitor (DBM) was used to assess the patient’s perspective on the burden of ADRs. In the DBM, immune-mediated inflammatory disease patients were asked to fill out a bimonthly questionnaire on experienced ADRs attributed to the biologic, start and stop date, course, and the burden of the ADR using a five-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (no burden) to 5 (very high burden). Inclusion criteria for this substudy were: patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (i.e. rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis), reporting an ADR, and elaboration on the burden in an open text-field. Answers of the patients in open-text fields on the burden of the experienced ADR was analysed with a thematic analysis to develop a conceptual framework. Semi-structured interviews with 13 rheumatologists were performed and used to develop a conceptual framework on their perspective on the burden of ADRs. The two frameworks were compared to each other to highlight differences in perspectives.
Results: A total of 440 unique patients were included in this study. Seven themes were identified that lead to the burden of ADRs according to patients. These were: effect on medication prescription, impact on appearance, impact on autonomy, impact on daily life, psychological consequences, distressing aspects of ADRs, and physical consequences. Each theme consisted of several subthemes, shown in Figure 1. Most of these themes were also mentioned by the rheumatologists, but some subthemes were missing, e.g. influence on making plans (Fig. 2). Conversely, one subtheme was only mentioned by the rheumatologists, i.e. ‘ADR is confronting’, where the ADR would confront them with being ill or dependent on medication. In comparison to the patient’s perspective, the rheumatologists paid less attention to the impact on the patient’s autonomy and daily life, and more attention to the psychological aspects.
Conclusion: Overall, the patient perspective and the rheumatologist perspective on burden of ADRs were broadly comparable, but rheumatologists likely underestimated practical aspects that lead to burden of ADRs, and overestimated the psychological burden. The insights of this study facilitate the development of a Patient-Reported Outcome Measure on the burden of ADRs and create more awareness among rheumatologists.
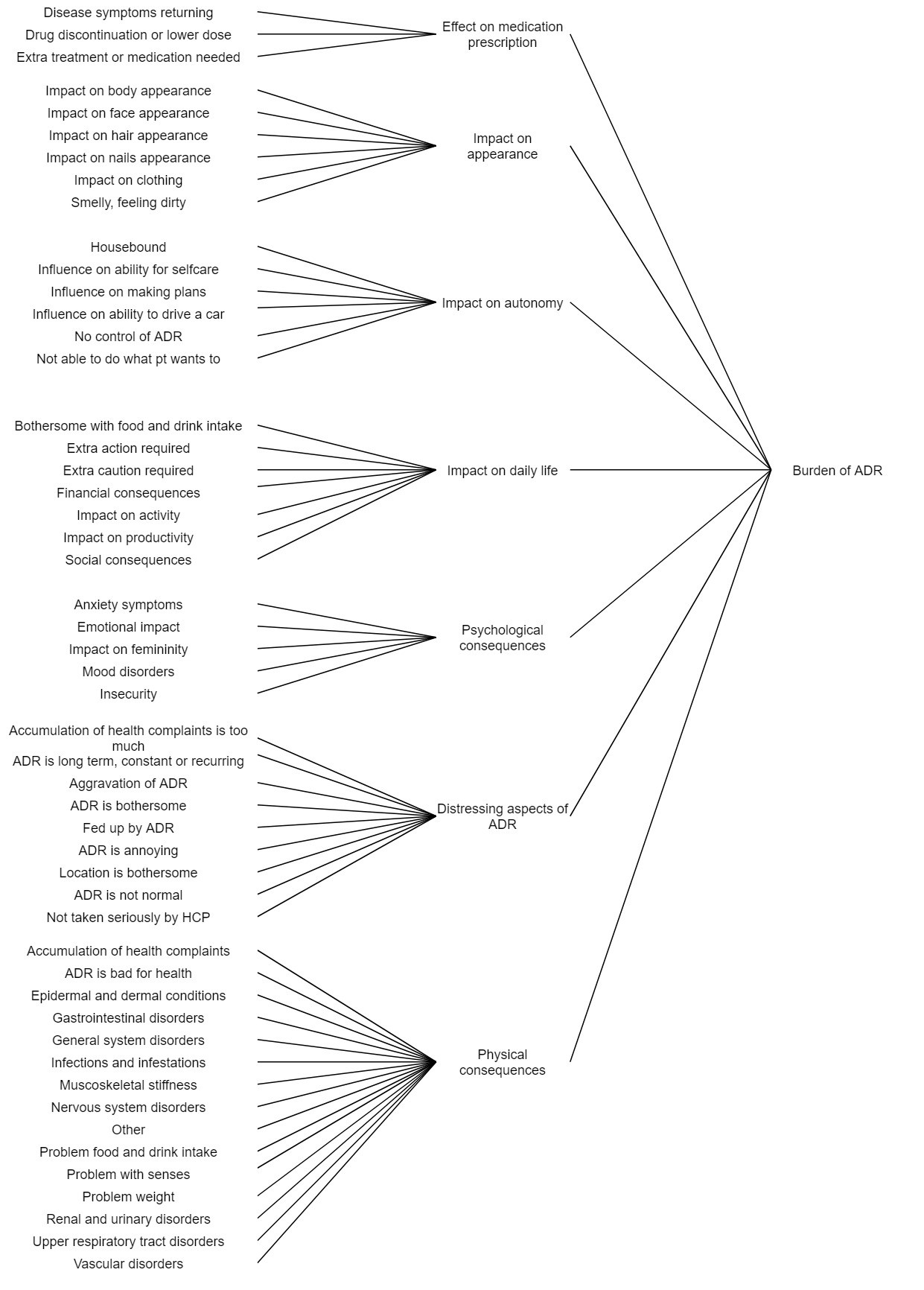 Conceptual framework of ADR burden attributed to biologics from the patient’s perspective. Participants were inflammatory rheumatic disease patients (n=440). ADR = Adverse Drug Reaction. HCP = HealthCare Professional. Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA®) terminology (version 21.0) was used for various subthemes in psychical consequences.
Conceptual framework of ADR burden attributed to biologics from the patient’s perspective. Participants were inflammatory rheumatic disease patients (n=440). ADR = Adverse Drug Reaction. HCP = HealthCare Professional. Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA®) terminology (version 21.0) was used for various subthemes in psychical consequences.
 Conceptual framework of ADR burden attributed to biologics from the rheumatologist’s perspective. Themes emerged from interviews with rheumatologists (n=11) and rheumatologists in training (n=2). ADR = Adverse Drug Reaction. HCP = HealthCare Professional. Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA®) terminology (version 21.0) was used for various subthemes in psychical consequences.
Conceptual framework of ADR burden attributed to biologics from the rheumatologist’s perspective. Themes emerged from interviews with rheumatologists (n=11) and rheumatologists in training (n=2). ADR = Adverse Drug Reaction. HCP = HealthCare Professional. Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA®) terminology (version 21.0) was used for various subthemes in psychical consequences.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Westerink H, Kosse L, Jessurun N, van Tubergen A, Vonkeman H, Nurmohamed M, van den Bemt B, de Vries M. Patient’s and Rheumatologist’s Perspectives on the Burden of Adverse Drug Reactions Attributed to Biologics: A Qualitative Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-and-rheumatologists-perspectives-on-the-burden-of-adverse-drug-reactions-attributed-to-biologics-a-qualitative-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-and-rheumatologists-perspectives-on-the-burden-of-adverse-drug-reactions-attributed-to-biologics-a-qualitative-study/
