Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Despite an inter-play between objective physical function measures and various patient characteristics, no large-scale investigations in knee osteoarthritis (KOA) have explored complex interactions or established patient-specific reference values for these tests across sex, age, radiographic severity, and body mass index (BMI). The purpose of this study was to: 1) determine the extent to which interactions among patient characteristics were associated with objective physical function, and 2) use a large community-based cohort of adults with or at risk for KOA to establish patient-specific reference values of objective physical function tests.
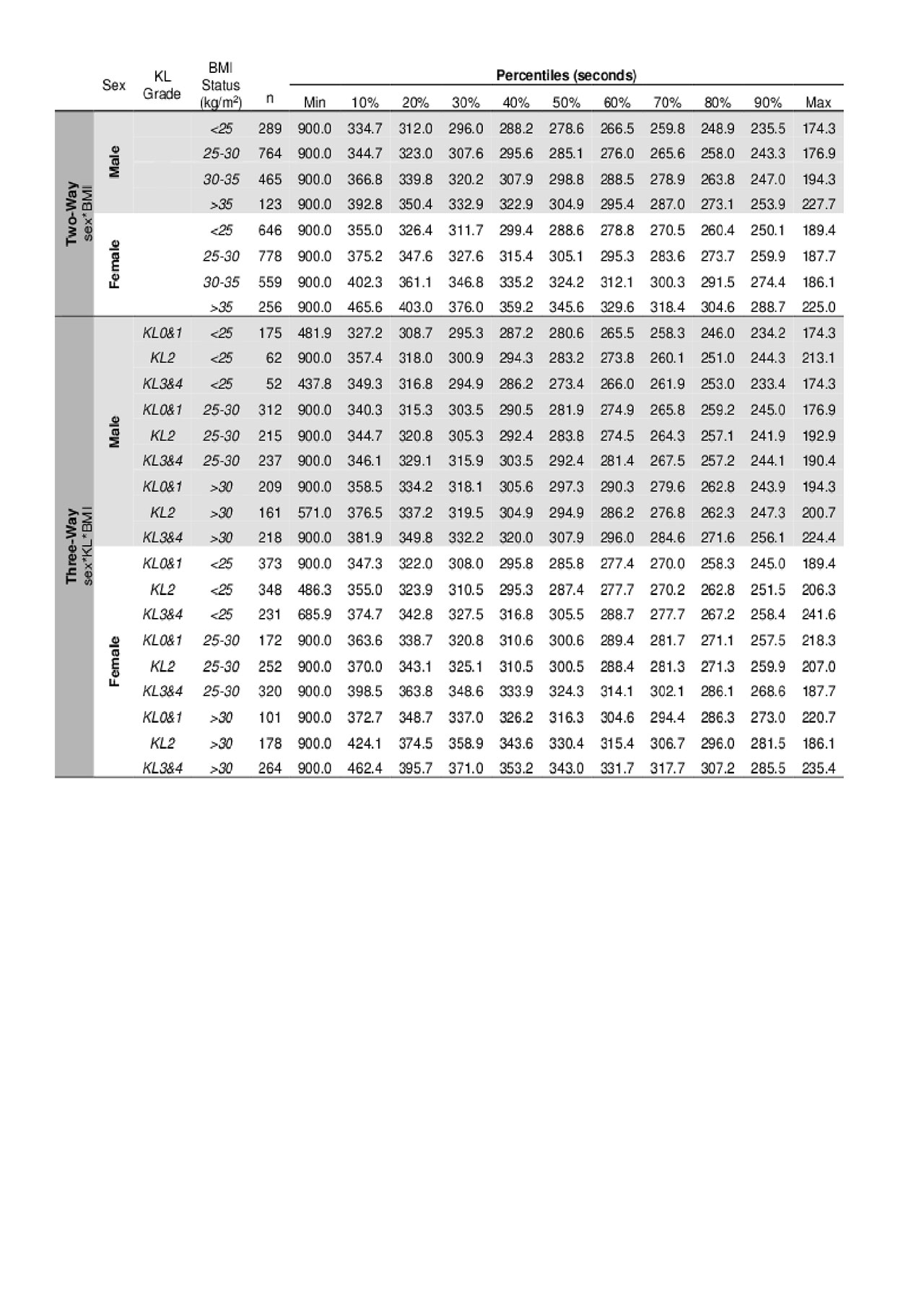
Methods: We included participants from the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI) with data on objective physical function tests and patient characteristics (i.e., age, BMI, and radiographic KOA severity: Kellgren-Lawrence Grade [KL]) at the baseline visit. We included three objective physical function tests: 20-meter walk test (20m), chair stand test (CS), and 400-meter test (400m). For the 20m, participants completed two trials at their habitual walking speed. For the CS, participants completed two trials in which they completed sit-to-stands as quickly as possible. For the 400m, participants completed one trial of walking ten 40-meter laps at their habitual walking speed. To determine how each objective physical function is influenced by any combination of these patient characteristics, we used a single linear regression model to evaluate all two-, three-, and four-way interactions. To establish patient-specific reference values for each objective physical function test, we created percentile scores from minimum to maximum in 10% increments for all combinations of the patient characteristics for each test. Subsets for two-way reference values were separated by: sex (male, female); age (five-year increments from 45-80 years); KL (KL0 – KL4); and BMI (18.5-25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, 30-35 kg/m2, >35 kg/m2). Due to smaller subset sample sizes, three- and four-way references were separated by: age (45-60, 60-70, and 70-80 years); KL (KL0/1, KL2, KL3/4); and BMI (18.5-25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, >30 kg/m2).
Results: We included 3,880 individuals who were on average 61+9 years old with a BMI of 29+5 kg/m2. For all physical function tests, there was no statistically significant four-way interaction between sex, age, KL, and BMI (Table 1). However, all physical function tests had at least one significant three-way or two-way interaction. Figure 1 highlights the interaction between sex, KL, and BMI for the 400m. We created reference value tables for each physical function test across all combinations of patient characteristics for two-, three-, and four-way interactions. Table 2 provides an example of two- and three-way interaction tables for the 400m.
Conclusion: Rather than rely on a single cut-off for all adults with or at risk for KOA, our analysis highlights the need for reference values within clinically relevant subsets that indicate a patient’s relative level of physical function. Further work is needed convert these extensive reference value tables to a format that can be easily translated into clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harkey M, Price L, Reid K, Lo G, Liu S, Lapane K, Dantas L, McAlindon T, Driban J. Patient-Specific Reference Values for Objective Physical Function Tests: Cross-Sectional Analysis Using Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-specific-reference-values-for-objective-physical-function-tests-cross-sectional-analysis-using-data-from-the-osteoarthritis-initiative/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-specific-reference-values-for-objective-physical-function-tests-cross-sectional-analysis-using-data-from-the-osteoarthritis-initiative/