Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) and polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) are often overlapping inflammatory diseases that occur in people older than 50 years. Both diseases can affect the quality of life, due to the burden of vascular inflammation and ischemia-related symptoms (GCA), joint symptoms (PMR) and systemic symptoms (GCA and PMR), in addition to the side-effects of long-term treatment with glucocorticoids. We hypothesized that GCA and PMR have both short- and long-term impact on the quality of life. We therefore documented patient reported outcomes (PROs) on the quality of life in GCA and PMR patients for five years.
Methods: We followed treatment-naïve GCA (n=44) and PMR (n=40) patients since diagnosis for up to five years. At each visit, PROs were recorded by the Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI), the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and the Short Form (SF)-36. Data were compared with age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs) that were also followed for up to five years.
Results: At diagnosis, both GCA and PMR patients reported significantly worse on each PRO compared to HCs. On each of the eight domains of the SF-36, patients scored substantially lower than HCs, with PMR patients scoring slightly worse than GCA patients (Figure 1). Initiation of GC treatment rapidly improved PROs, however, scores either never recovered to HC values (GFI, SF-36 (Figure 2)) or increased again after two years (HAQ-DI).
Conclusion: GCA and PMR patients experience both short-term and long-term impact on their quality of life, likely caused by both the disease and its treatment. Future studies should document whether a direct start of additional treatment such as methotrexate or tocilizumab substantially improve PROs in these patients.
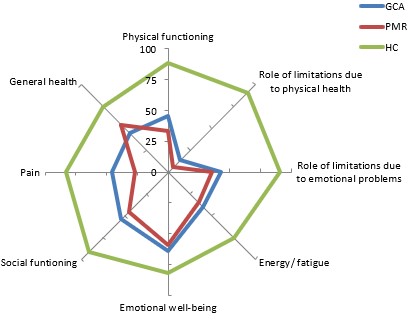 Figure 1: Scores of the eight domains of the SF_36 at baseline in GCA and PMR patients. Data are compared to age- and sex-matched HCs. Scores range from 0_100; a score of 100 indicates the most healthy outcome.
Figure 1: Scores of the eight domains of the SF_36 at baseline in GCA and PMR patients. Data are compared to age- and sex-matched HCs. Scores range from 0_100; a score of 100 indicates the most healthy outcome.
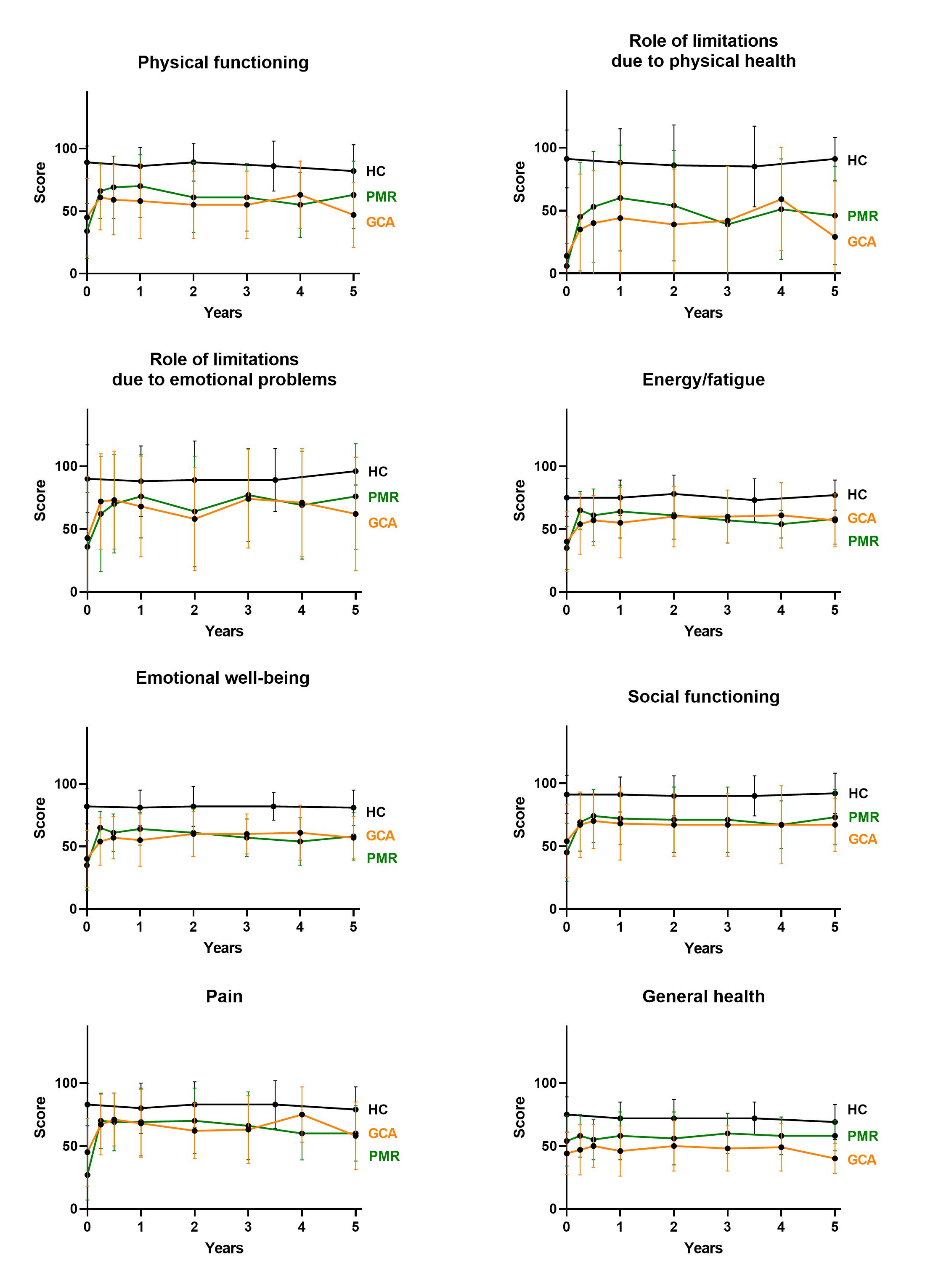 Figure 2: Scores of the eight domains of the SF_36 throughout the disease course in GCA and PMR patients. Data are compared to age- and sex-matched HCs.
Figure 2: Scores of the eight domains of the SF_36 throughout the disease course in GCA and PMR patients. Data are compared to age- and sex-matched HCs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Sleen Y, van der Geest K, Boots A, Sandovici M, Brouwer E. Patient Reported Outcomes on Quality of Life in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-on-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-and-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-on-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-and-polymyalgia-rheumatica/
