Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: AWARE (Comparative & Pragmatic Study of Golimumab [GLM] Intravenous [IV] vs Infliximab [IFX] in RA) is a Phase 4 study designed to provide a real-world assessment of GLM IV and IFX in pts with RA. Patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) experience significant symptoms (eg, pain and fatigue) and impact on physical function. Using the Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS), a validated disease agnostic set of health assessment instruments,1 we assessed outcomes related to social, mental, and physical well-being through the 8th infusion (≈1 year of treatment).
Methods: AWARE is a prospective, noninterventional, multicenter (88 sites), observational study in the United States (US). A total of 1270 RA pts were enrolled when initiating treatment with GLM or IFX. The 52 Week Analysis Set reported here included pts with ≥1-year treatment or those discontinued for any reason and, while enrolled, completed PROMIS-29 or PROMIS short form (SF) questionnaires. The PROMIS instruments were administered at baseline and prior to infusions 2, 5, and 8. PROMIS-29 consists of 7 domains (Depression, Anxiety, Physical Function, Pain Interference, Fatigue, Sleep Disturbance, and Social Participation) and a pain intensity 0-10 visual analogue scale. The PROMIS SFs Fatigue 7a and Pain Interference 6b were also completed. The raw score of each domain was converted into a standardized T-score with a mean of 50 (general population mean) and a standard deviation (SD) of 10. All PROMIS T-scores are based on observed data without any imputation rules applied. Higher PROMIS scores represent more of the domain concept being measured.
Results: At baseline, treatment groups were balanced based on demographics and medical characteristics. The majority of pts were white (87.0% GLM, 86.2% IFX) and female (83.4% GLM, 82.4% IFX). Mean ages were 58.5 ±12.96 years for GLM and 59.6 ±13.24 years for IFX. Overall, 35.3% GLM and 42.9% IFX pts were bionaïve. The proportion of GLM and IFX pts with prior exposure to 1 or 2 biologics was similar; however, 20.1% GLM pts vs 10.8% IFX pts had exposure to ≥3 biologics. Methotrexate use was similar between GLM (76.4%) and IFX pts (75.0%). Based on mean PROMIS T-scores at baseline (Table), Fatigue, Pain Interference, and Physical Function domains assessed by PROMIS in RA pts indicate that these assessments were worse than those of the general US population. Among all PROMIS domains, mean Depression T-scores were closest compared with the general population (51.9 GLM, 52.5 IFX). Through the 8th infusion, GLM- and IFX-treated pts achieved meaningful improvement based on mean changes from baseline in all PROMIS-29 domains and respective SFs. The percentage of GLM or IFX pts with improvements of ≥3, ≥5, or ≥10 units change in T-scores increased from infusion 2 through infusion 8.
Conclusion: RA pts treated with GLM or IFX achieved comparable improvements across social, mental, and physical well-being PROMIS measures. PROMIS-29 was able to detect change to subsequent anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapies.
Reference:
- http://www.healthmeasures.net/score-and-interpret/interpret-scores/meaningful-change/165-meaningful-change
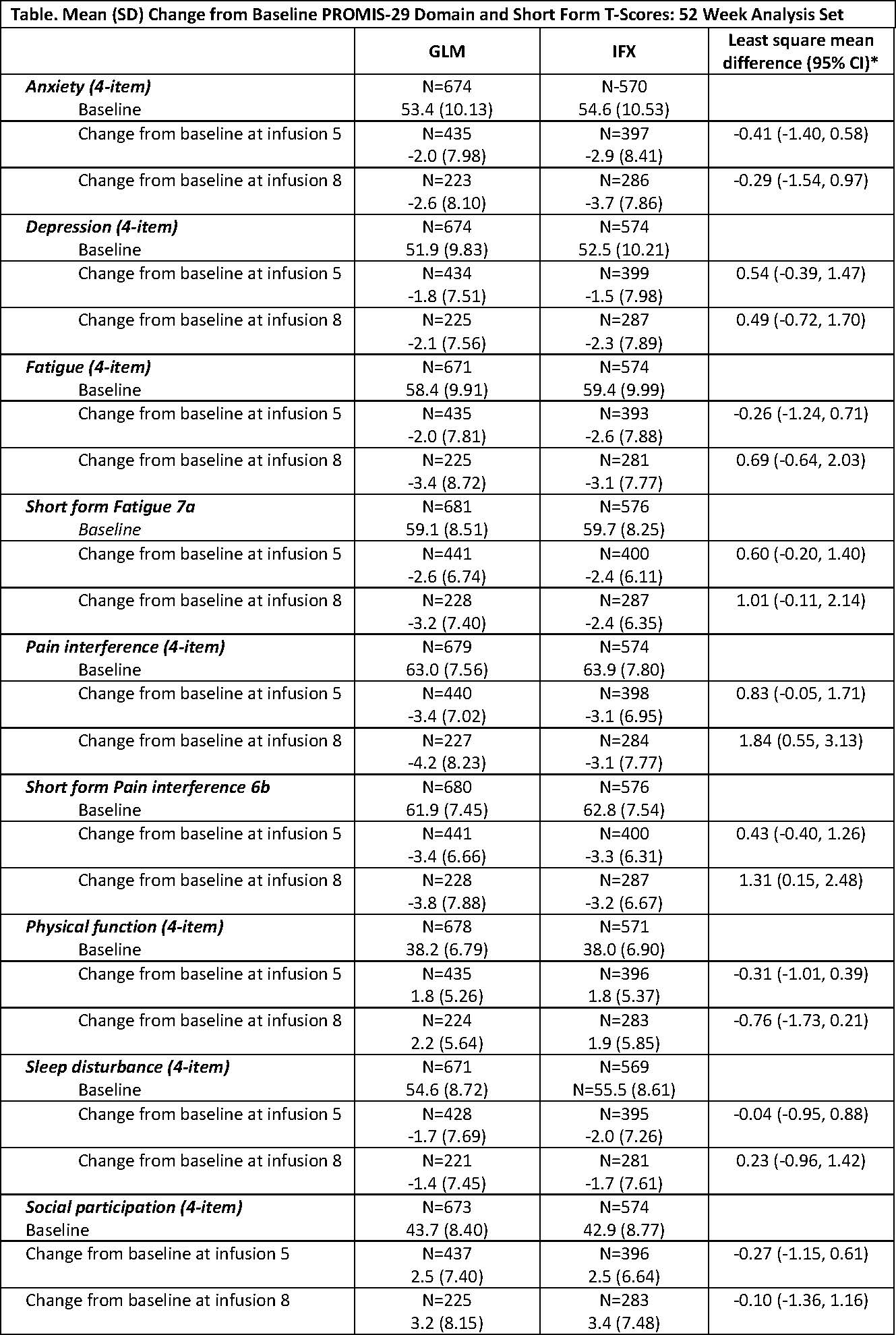 *The least square mean difference and confidence interval (CI) are based on analysis of covariance controlling for baseline PROMIS score using inverse probability of treatment weighted propensity score.
*The least square mean difference and confidence interval (CI) are based on analysis of covariance controlling for baseline PROMIS score using inverse probability of treatment weighted propensity score.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bingham III C, Kafka S, Black S, Xu S, Langholff W, Curtis J. Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Assessment of Response to Treatment with Golimumab IV or Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Results from a Phase 4 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-measurement-information-system-promis-assessment-of-response-to-treatment-with-golimumab-iv-or-infliximab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-from-a-phase-4-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-measurement-information-system-promis-assessment-of-response-to-treatment-with-golimumab-iv-or-infliximab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-from-a-phase-4-study/
