Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The natural history of RA and axSpA comprises periods of low disease activity and flares. However, there are few data linking patient-reported flares to quantifiable outcomes. We previously indicated in the ActConnect study that flares were related to a moderate decrease in physical activity (1). Objective: to predict patient-reported flares based on activity-tracker-provided continuous flows of steps per minute.
Methods: This prospective multi-center observational study (ActConnect) included patients with definite RA (ACR/EULAR criteria) or axSpA (ASAS criteria), owning a smartphone. Over 3 months, physical activity was sampled continuously (each minute) using an activity tracker, and flares were self-assessed weekly using a specific flare question. In this reanalysis of the dataset, Machine Learning statistical methods were used. Physical activity data were first normalized at patient level using each patientÕs mean and standard deviation of steps for a similar timeframe without flares. Then the data were analysed by multiclass Bayesian methods with a Machine Learning software belonging to Orange (2). The software was instructed to find the best predictive model of patient-reported flares. Sensitivities and specificities were calculated. Several sensitivity analyses were performed using different physical activity timeframes, different definitions of flares.
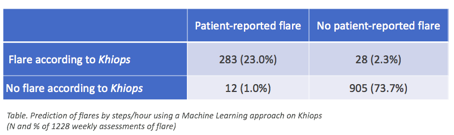
Results: In all, 170/178 patients (91 RA and 79 axSpA patients; 1228 weekly flare assessments and 24,972 1-hour physical activity assessment timeframes) were analyzed: mean age 45.5±12.4 years, mean disease duration 10.3±8.7 years; 60 (35.3%) were males and 90 (52.9%) received biologics. Disease was well-controlled (mean DAS28: 2.3±1.2; mean BASDAI: 3.3±2.1) but flares were frequent: reported in 24% of all the questionnaires. The Khiops generated model detected correctly both flares and absence of flare (Table) with a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 97%. The corresponding positive and negative predictive values were respectively 89% and 99%. Sensitivity analyses were confirmatory.
Conclusion: Machine Learning methods are useful to deal with repeated data in big datasets. The results confirm objectively the functional impact of patient-reported flares. Furthermore, the correct detection of flares by the activity tracker and adapted statistics opens the way for future studies of flares using connected devices with great precision and minimal patient burden.
1 – Jacquemin C et al. Physical activity decreased significantly but moderately during weeks where patients reported flares: A 3-month study of 170 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or axial spondyloarthritis (AXSPA) patients wearing an activity tracker, Ann Rheum Dis 2017 (suppl): EULAR congress, poster FRI0700.
2- Khiops software for data mining, PredicSis; accessed 06/01/2017: https://khiops.predicsis.com
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Guyard F, Leroy D, Lafargue T, Seiler M, Jacquemin C, Molto A, Sellam J, Foltz V, Gandjbakhch F, Hudry C, Mitrovic S, Fautrel B, Servy H. Patient-Reported Flares Were Correctly Predicted By an Algorithm Using Machine-Learning Statistics on Activity Tracker Data on Steps, in a Longitudinal 3-Month Study of 170 Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-flares-were-correctly-predicted-by-an-algorithm-using-machine-learning-statistics-on-activity-tracker-data-on-steps-in-a-longitudinal-3-month-study-of-170-patients-with-rheumatoid-ar/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-flares-were-correctly-predicted-by-an-algorithm-using-machine-learning-statistics-on-activity-tracker-data-on-steps-in-a-longitudinal-3-month-study-of-170-patients-with-rheumatoid-ar/