Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Health care professionals tend to focus on adverse drug reactions (ADRs) with the highest clinical impact. Subsequently, ADRs with less obvious clinical impact but with a high impact on patient’s daily lives, might be overlooked. These ADRs may occur frequently and therefore constitute a considerable part of the total perceived burden of ADRs. To develop strategies to reduce the burden of ADRs, it is important to know which ADRs have the highest impact on patients’ lives. The aim of the study was to gain insight into which patient-reported ADRs contribute most to the total experienced ADR burden attributed to the use of etanercept (ETN) and adalimumab (ADA).
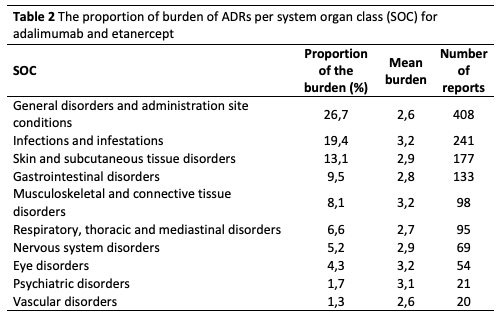
Methods: Data of the Dutch Biologic Monitor (DBM) was used. In the DBM, immune-mediated inflammatory disease patients using biologicals were asked to fill out bimonthly questionnaires on experienced ADRs attributed to the biologic and the burden of the ADR using a five-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (no burden) to 5 (very high burden). Inclusion criteria for the present study were: patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis or spondyloarthritis using ADA or ETN, reporting an ADR with a burden score of 2 or higher. The ADRs reported for ADA and ETN were grouped into system organ classes (SOCs) according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities. Every ADR in the SOC is multiplied with the corresponding burden score, summating the experienced burden per SOC. The total experienced burden of ADA and ETN is the sum of the experienced burdens of all SOCs. The proportion of the burden per SOC is calculated by dividing the burden per SOC by the total burden of all SOCs. ADRs per SOC were further stratified by ADA and ETN use, and analysed separately to identify possible differences.
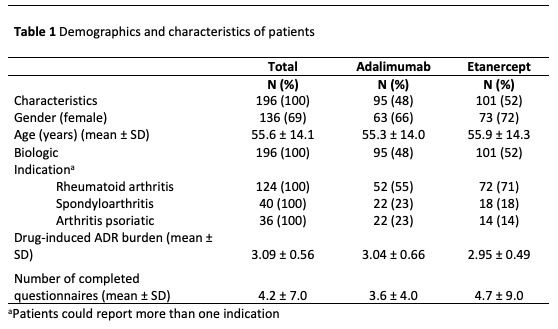
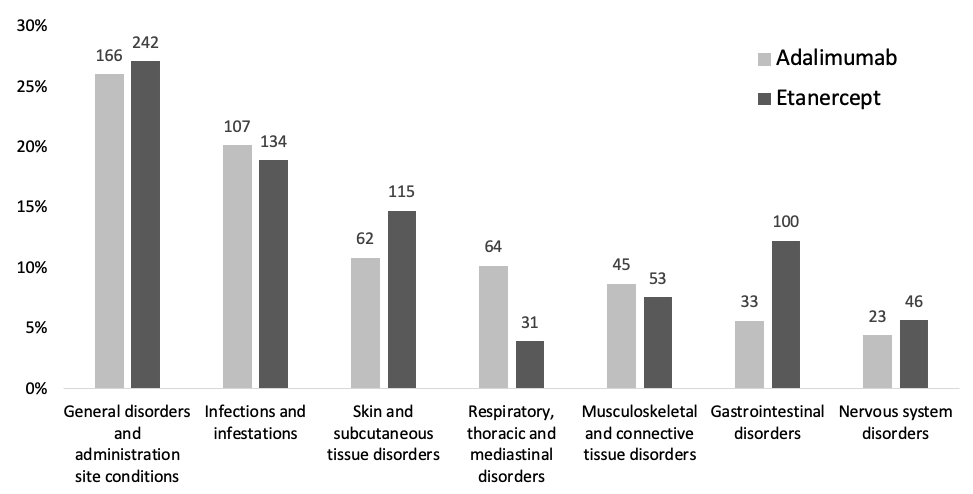
Results: A total 196 patients met the inclusion criteria, of which 95 patients (48%) reported an ADR for adalimumab (575 ADRs) and 101 patients (52%) reported and ADR for ETN (793 ADRs), see Table 1. The proportion of experienced burden attributed to ADA and ETN is summarized in Table 2. The ADRs that account for the highest proportion are general disorders (such as fatigue) and administration site conditions (such as injection site pain), infections and infestations (such as respiratory tract infections and nasopharyngitis), skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (such as dry skin and pruritus). The proportion of burden of ADRs for ADA and ETN are comparable, except for skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders, gastrointestinal disorders and vascular disorders (see Figure 1).
Conclusion: ADRs belonging to the SOCs General disorders and infections are the foremost contributors to the ADR burden. These ADRs are well-known and this outcome is as expected. Less known and new is information the high proportion of burden attributed to ADRs in the SOC skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders. Addressing these ADRs offers opportunities to reduce the burden associated with the use of ADA and ETN. Furthermore, although ADA and ETN are clinically considered comparable, our findings point to differences in proportions of experienced burden of ADRs grouped per SOC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Davelaar J, Jessurun N, Tas S, Nurmohamed M, van den Bemt B, Vonkeman H. Patient-Reported Burden of Adverse Drug Reactions Attributed to the Use of Adalimumab and Etanercept in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-burden-of-adverse-drug-reactions-attributed-to-the-use-of-adalimumab-and-etanercept-in-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-burden-of-adverse-drug-reactions-attributed-to-the-use-of-adalimumab-and-etanercept-in-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases/