Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0357–0386) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite broadening treatment options for RA, several challenges and unmet needs remain. The 2021 ACR guideline for the treatment of RA marked a significant step in expanding the integration of patient voices in guideline development, incorporating patient perspectives to inform treatment decisions based on their preferences. This study aimed to characterize patient satisfaction with, and preferences for, current RA treatments as well as a novel vagus nerve-mediated neuroimmune modulation device, which recently demonstrated safety and effectiveness in treating biologic-experienced RA patients.
Methods: A web-based patient survey was conducted in combination with a discrete choice experiment (DCE) to capture the experiences, perspectives, and preferences of patients living with RA in the US. Patient satisfaction with current RA pharmacologic therapies was determined using the Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM), a validated instrument to measure patient satisfaction. DCEs are widely utilized tool in economics research that can elicit an individual’s distinct valuation of several options and account for trade-offs between them based on their personal experiences. The DCE in this study included 12 choice sets which contained a device profile and drug profile featuring 8 clinically relevant attributes for RA patients.
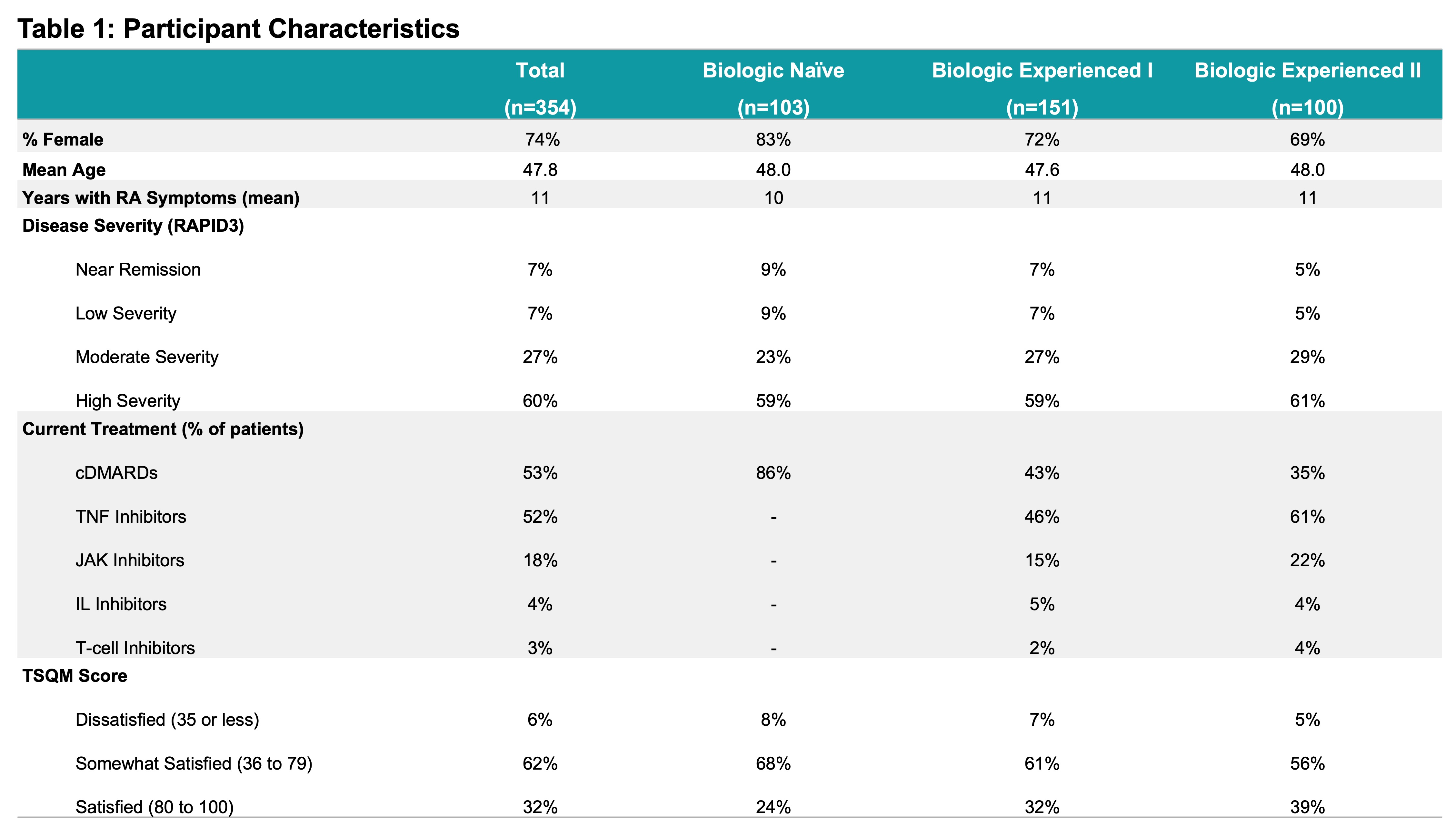
Results: 354 completed surveys were included in the analysis. Participants were stratified into three subgroups, Biologic Naïve (n=103); Biologic Experienced I, those on their first biologic (n=151); and Biologic Experienced II, those who had a history of multiple biologics (n=100). Disease severity, as measured by RAPID3, indicated 27% had ‘Moderate Disease Activity’ (RAPID3 > 6, ≤12) and 60% with ‘High Disease Activity’ (RAPID3 > 12). Based on the TSQM, only 32% were satisfied with their RA treatment; dissatisfaction increased with exposure to a greater number of biologics or JAKs (Table 1). The initial impression of implantable device-based treatment option was regarded as “Positive” or “Extremely Positive” by 45%. Patient preferences were modeled for biologic-experienced patients with moderate to high disease severity who were dissatisfied or only somewhat satisfied with their current RA treatment. Neuroimmune modulation therapy was preferred over trying another drug treatment options for both Biologic Experienced I and II groups (Figure 1). Key drivers of treatment preference included out-of-pocket treatment cost, proportion of improvement in symptoms, level of physical function and fatigue, and effectiveness in protection from irreversible joint damage (Table 2).
Conclusion: These results indicate that RA patients are accepting of a novel neuroimmune modulation approach using a surgically implanted device. Preference for neuroimmune modulation device over another biologic or JAK was particularly high for those who had previous exposure to, and dissatisfaction with, currently available advanced RA therapies. These results underscore the importance of discussing patients’ personal preferences, their experiences with prior therapies and the attributes of treatment that are most important to them in making future treatment selections.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Baker J, Venkatachalam S, Danese S, Ulloa J, Shah A. Patient Preferences for Treatments of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Discrete Choice Experiment Evaluating Preference for Advanced Drug Therapies and Neuroimmune Modulation Device [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-preferences-for-treatments-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-discrete-choice-experiment-evaluating-preference-for-advanced-drug-therapies-and-neuroimmune-modulation-device/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-preferences-for-treatments-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-discrete-choice-experiment-evaluating-preference-for-advanced-drug-therapies-and-neuroimmune-modulation-device/

.jpg)
.jpg)