Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Universally acceptable clinical and imaging criteria to define axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is lacking.1 Machine learning (ML) algorithms can detect patterns from large clinical datasets and identify clusters with potential therapeutic or prognostic significance.2 This post hoc analysis of 10 pooled Phase III trials from the clinical development program of secukinumab in PsA (FUTURE 1–5)3,4, ankylosing spondylitis (AS; MEASURE 1–4)5,6, and patients (pts) with PsA with axial manifestations (MAXIMISE)1, aimed to identify clinical clusters based on pts demographics and baseline clinical indicators to support the characterization of the axial PsA phenotype within the spondyloarthritis (SpA) spectrum.
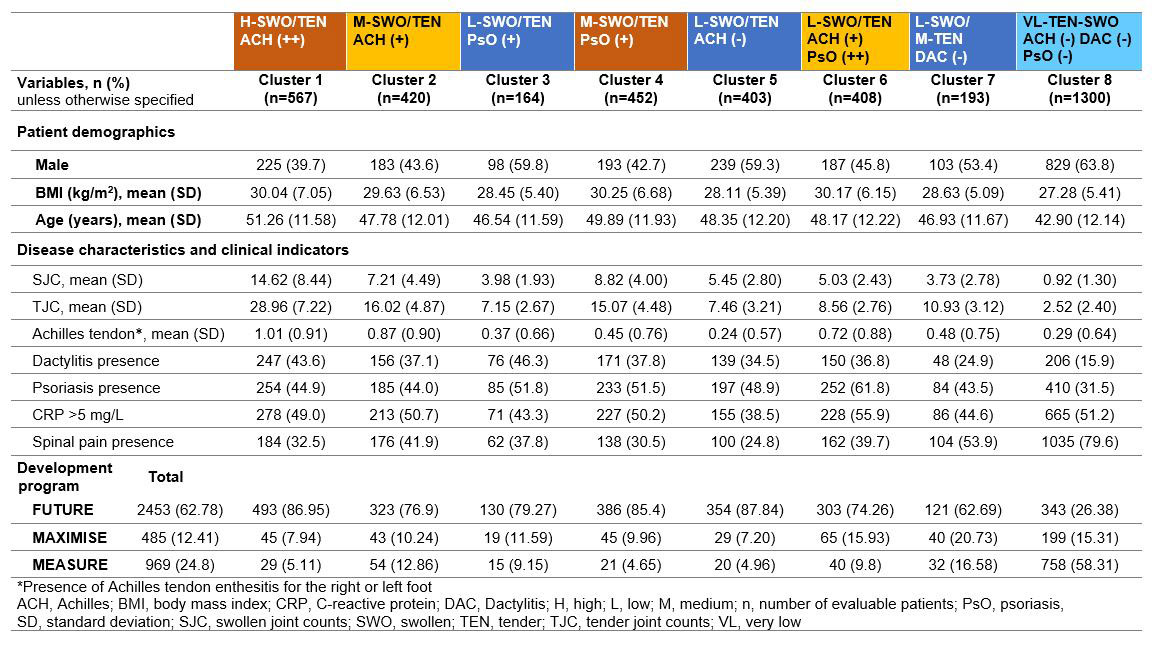
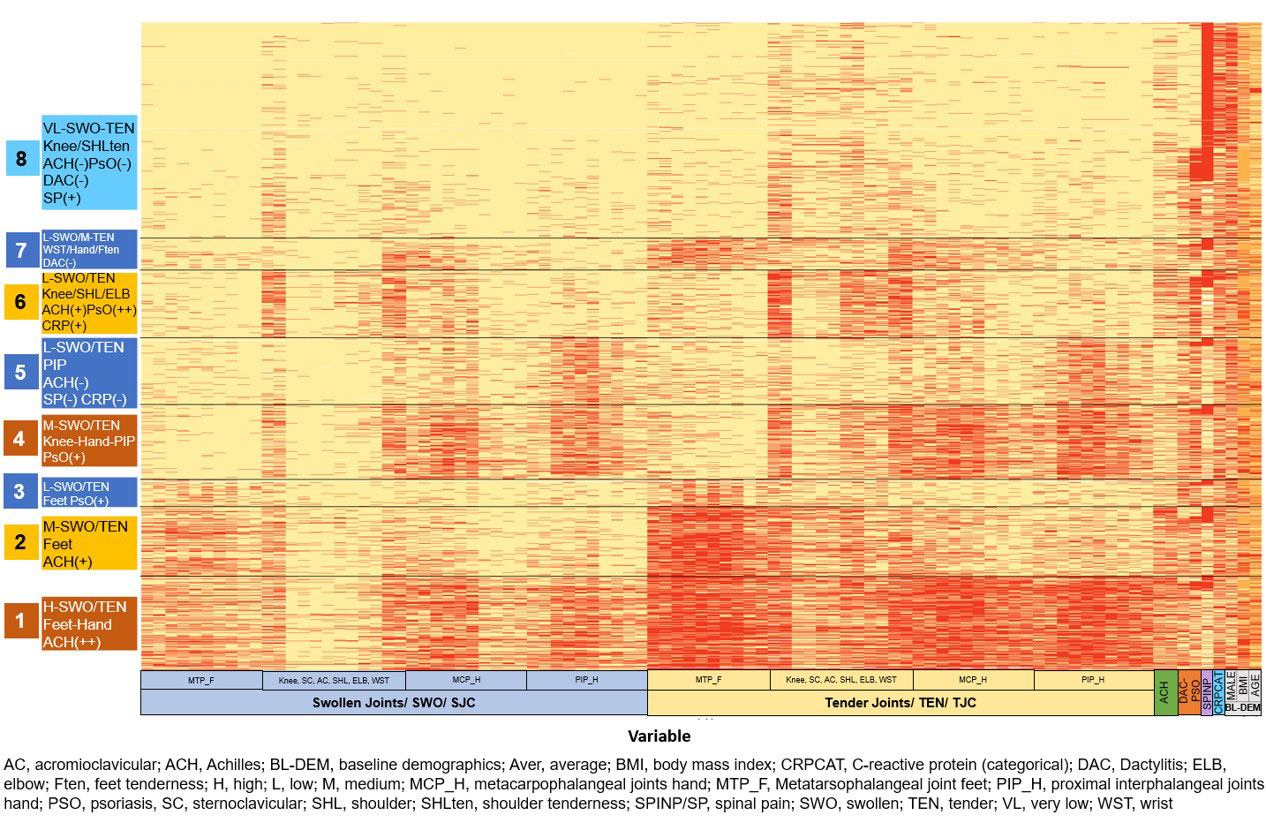
Methods: Pts demographics (sex, age, BMI) and baseline clinical indicators (swollen and tender joints, Achilles tendon enthesitis, presence of dactylitis, psoriasis [PsO], spinal pain at baseline) were analyzed to identify pts clusters by ML. Finite mixture model methodology was applied to the pooled clinical data of secukinumab-treated pts from 10 clinical trials (FUTURE 1–5, MEASURE 1–4, and MAXIMISE).1, 3-6 This approach assumed multinomial mixture distributions on categorical variables, appropriate for application to a dataset of binary variables. The clustering algorithm was applied repeatedly on different subsamples of the pts to assess clustering robustness and stability.
Results: Overall, 3907 pts were grouped into 8 distinct clusters based on pts demographics and baseline clinical characteristics. PsA pts with axial manifestations from the MAXIMISE trial were overrepresented in clusters 6–8. Pts in cluster 8 were predominantly AS pts, mostly males (63.8%), younger (mean age of 42.9 years), with a mean BMI of 27.3 kg/m2, oligoarthritis and high prevalence of spinal pain. Pts in cluster 6 were commonly female (54%), older (mean age of 48 years), overweight, with notable presence of PsO, and higher articular burden of the knees, shoulders, elbows, and wrists. In comparison, pts in cluster 7 were mostly male (53%), younger (mean age of 47 years) and less overweight with low polyarticular burden and notable tenderness of the joints of the feet, wrists, and hands (Table and Figure). Cluster 1 was predominantly a PsA cluster of older female pts, having high BMI, with polyarticular burden and Achilles tendon enthesitis.
Conclusion: PsA clusters obtained by ML in the pooled dataset of the FUTURE, MEASURE and MAXIMISE trials indicate phenotypical heterogeneity of pts with PsA with axial manifestations and overlapping features across the SpA spectrum. Further studies are needed to explore differences in response to therapy and validate further these clusters to determine phenotypes of pts with SpA.
References
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Pournara E, Gladman D, Mease P, Jahandideh S, Coates L. Patient Clusters Identified by Machine Learning from a Pooled Analysis of the Clinical Development Program of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and Psoriatic Arthritis with Axial Manifestations [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-clusters-identified-by-machine-learning-from-a-pooled-analysis-of-the-clinical-development-program-of-secukinumab-in-psoriatic-arthritis-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-with-ax/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-clusters-identified-by-machine-learning-from-a-pooled-analysis-of-the-clinical-development-program-of-secukinumab-in-psoriatic-arthritis-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-with-ax/