Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II (1364–1390)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Our understanding of the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis (SSc) continues to evolve. Oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathophysiology of disease, but minimal work has investigated specific markers and mechanisms for oxidative stress in SSc. Paraoxonase-1 is a major HDL-associated protein, which metabolizes pro-inflammatory, oxidized lipids. In the current work, we evaluated the paraoxonase (PON), lactonase (LAC), and arylesterase (ARES) activities of PON1 in both a murine model of SSc and human samples, assessing their correlation with the extent of SSc manifestations and severity.
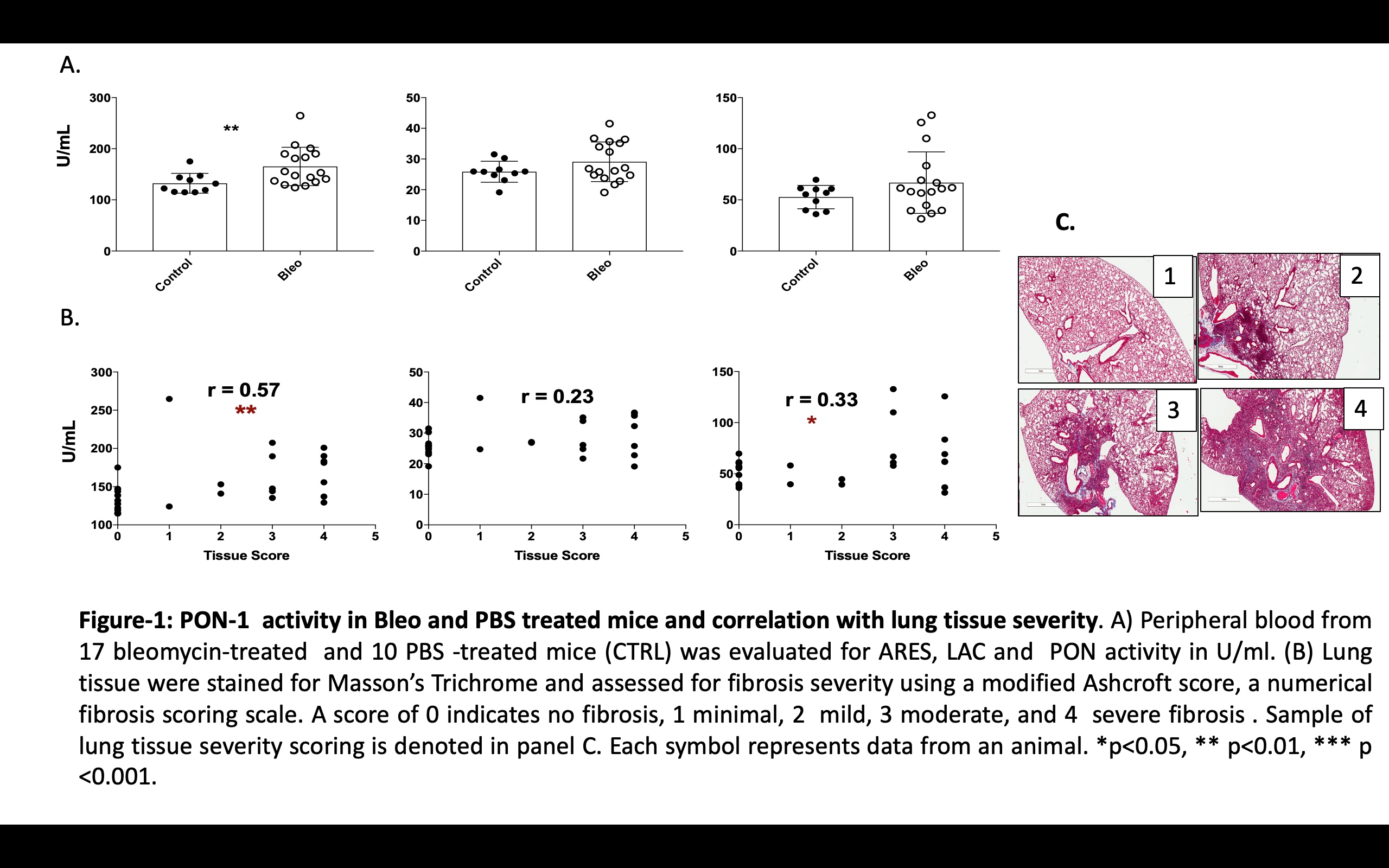
Methods: We assessed PON, ARES and LAC activities in the murine model of SSc using Black 6 (B6) mice. To induce fibrosis, mice age 8-10 weeks were anesthetized with intraperitoneal ketamine (then treated via oropharyngeal installation with bleomycin (Bleo) or PBS. We assessed Masson’s trichrome-stained lung sections using a modified Ashcroft score, a numerical fibrosis scoring scale. A score of 0 indicates no fibrosis, 1 minimal, 2 mild, 3 moderate, and 4 severe fibrosis. PON1 activities were also evaluated in serum samples from 72 SSc patients (pts) meeting the ACR/EULAR 2013 SSc criteria and 50 healthy controls (CTRL). We assessed associations of PON, ARES and LAC activities with disease manifestations including interstitial lung disease (ILD), in both humans and mice (histopathological), vascular disease (pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) as well as skin severity (modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS). PON1 activities were measured in mouse and human serum samples as described previously using paraoxon (PON), phenylacetate (ARES), and dihydrocoumarin (LAC) as substrates.
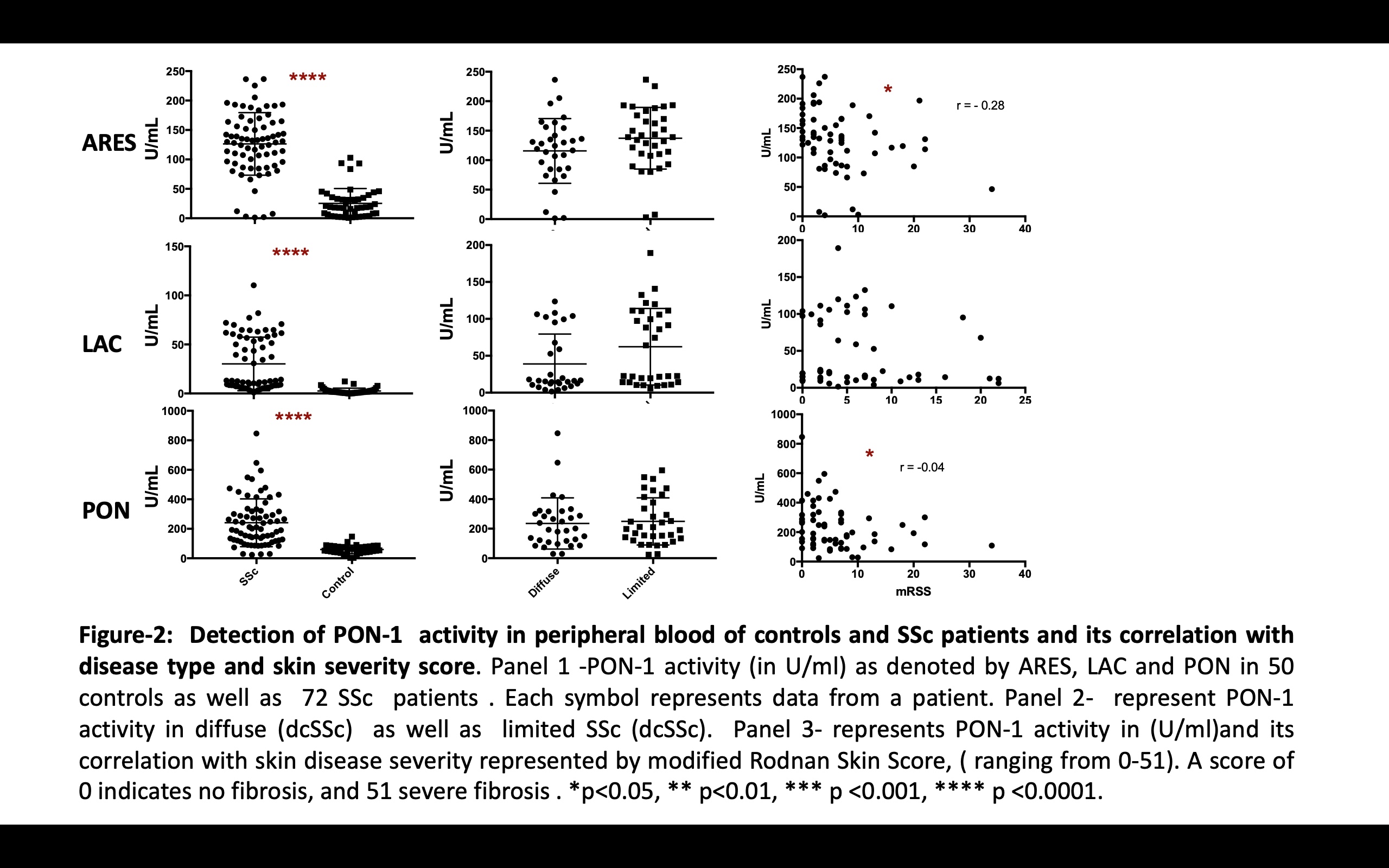
Results: Clinical patient characteristics include: 32 (44%) with diffuse SSc (dcSSc) , age (mean , range in years) ( 56 , 20-85 ) SSc and (48, 18-65) CTRL; gender,19.4% male (SSc) 18% male (CTRL); active skin ulcers 17 (25.7%); interstitial lung disease (ILD) 40 (55%) pts; (PAH) 23 (31%) pts.
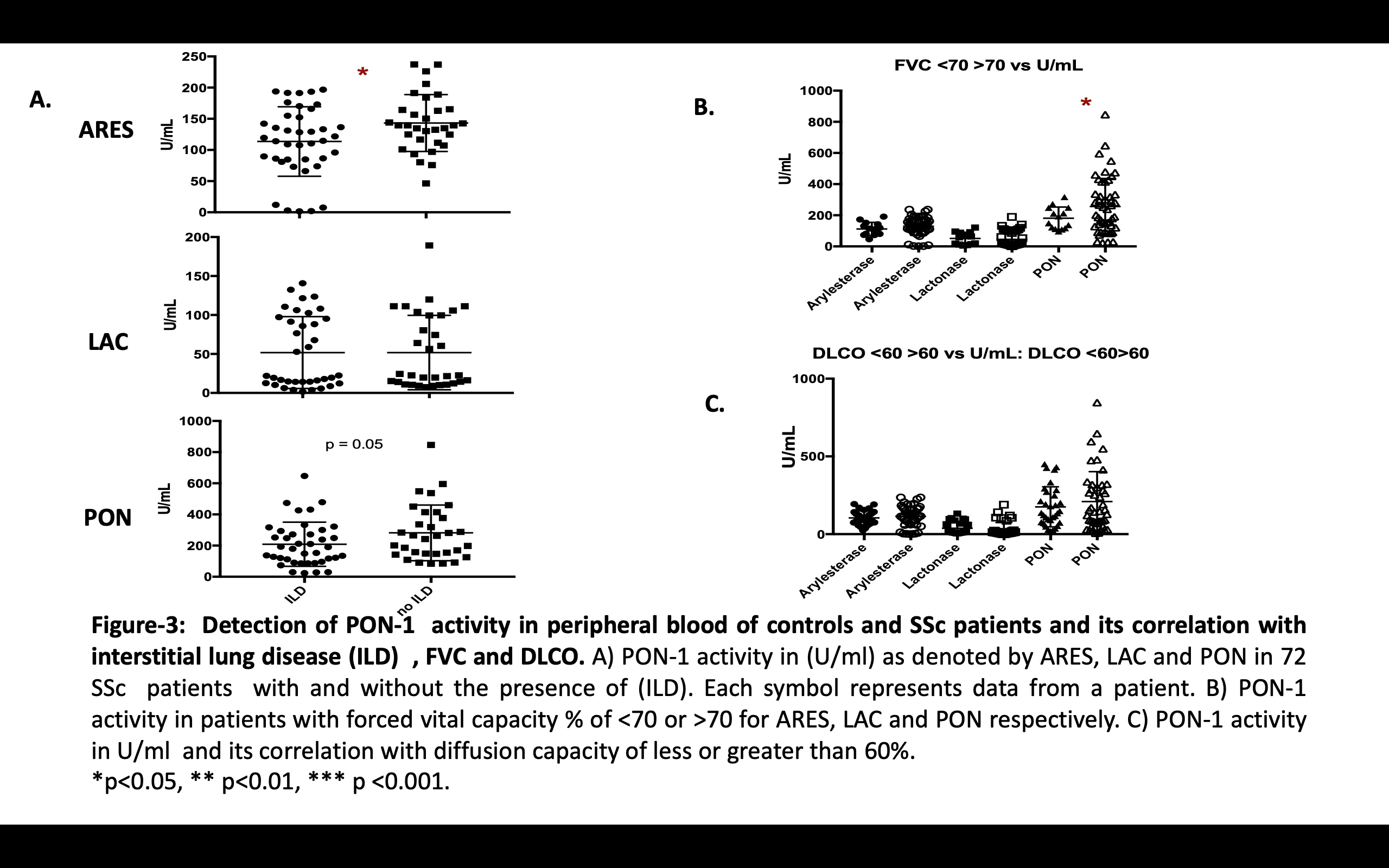
In the murine model of SSc, serum PON1 activities were greater in bleo-treated mice when compared to PBS. Higher ARES , PON and LAC activities correlated with greater tissue severity scores (with r2 of 0.57 (p< 0.001), 0.33 (p < 0.05) and 0.23 (p =ns ) respectively) (Figure 1). In human data, mean ARES and LAC activities were higher in SSc compared to CTRL (66.43 ± 3.29 SSc patients vs 13.31 ± 1.91 CTRL) p < 0.0001. ARES and LAC activities were lower in patients with dcSSc compared to limited (lcSSc). No significant differences were noted in PON activity between dcSSc and lcSSc pts. Moreover, lower levels of ARES and PON significantly correlated with higher skin scores: mRSS correlations: ARES (r2= 0.08, p < 0.05) and PON (r2= 0.06, p < 0.04), (Figure2. Interestingly, lower activities of ARES, LAC, and PON were noted in patients with ILD, (figure 3).
Conclusion: Markers of oxidative stress measured by PON1 activities associate with disease severity in both SSc patients and a murine model of SSc. Further work is warranted and ongoing to examine the role of PON1 as a disease marker and mechanism in the pathogenesis of SSc and SSc-associated ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kafaja S, Valera I, Suliman Y, Alemam M, Mamita R, Wang J, Shahbazian A, Clements P, Charles-Schoeman C. Paraoxonase-1: Potential Novel Marker of Disease Extent and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paraoxonase-1-potential-novel-marker-of-disease-extent-and-activity-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paraoxonase-1-potential-novel-marker-of-disease-extent-and-activity-in-systemic-sclerosis/