Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Inflammation and damage to the vascular endothelium are implicated in the pathogenesis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), particularly dermatomyositis. Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) is a high density lipoprotein (HDL)- associated enzyme, which normally protects the vascular endothelium from damage due to oxidized phospholipids, which accumulate under conditions of oxidative stress. The current work evaluates PON1 activity in IIM patients compared to healthy controls.
Methods: In a cross sectional analysis of 169 patients with IIM and 112 healthy controls we measured plasma PON1 activity using the arylesterase assay (Clin Chim Acta. 402(1-2):67-74, 2009). Lipoprotein cholesterol levels, inflammatory markers, and myositis autoantibodies(ab) were assessed by standard assays, and myositis disease activity was assessed using physician global 100 mm visual analogue scales (VAS) and CPK levels.
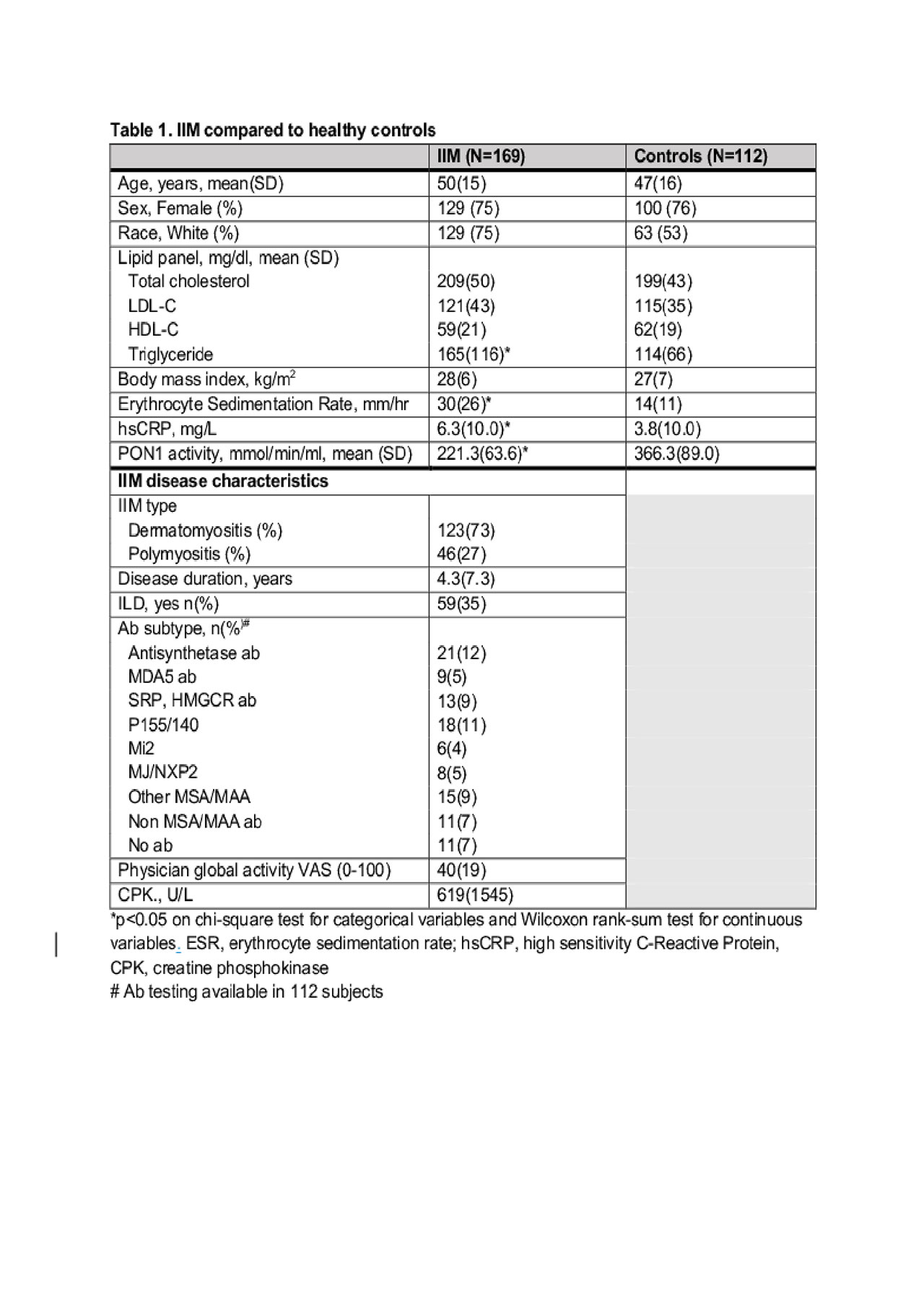
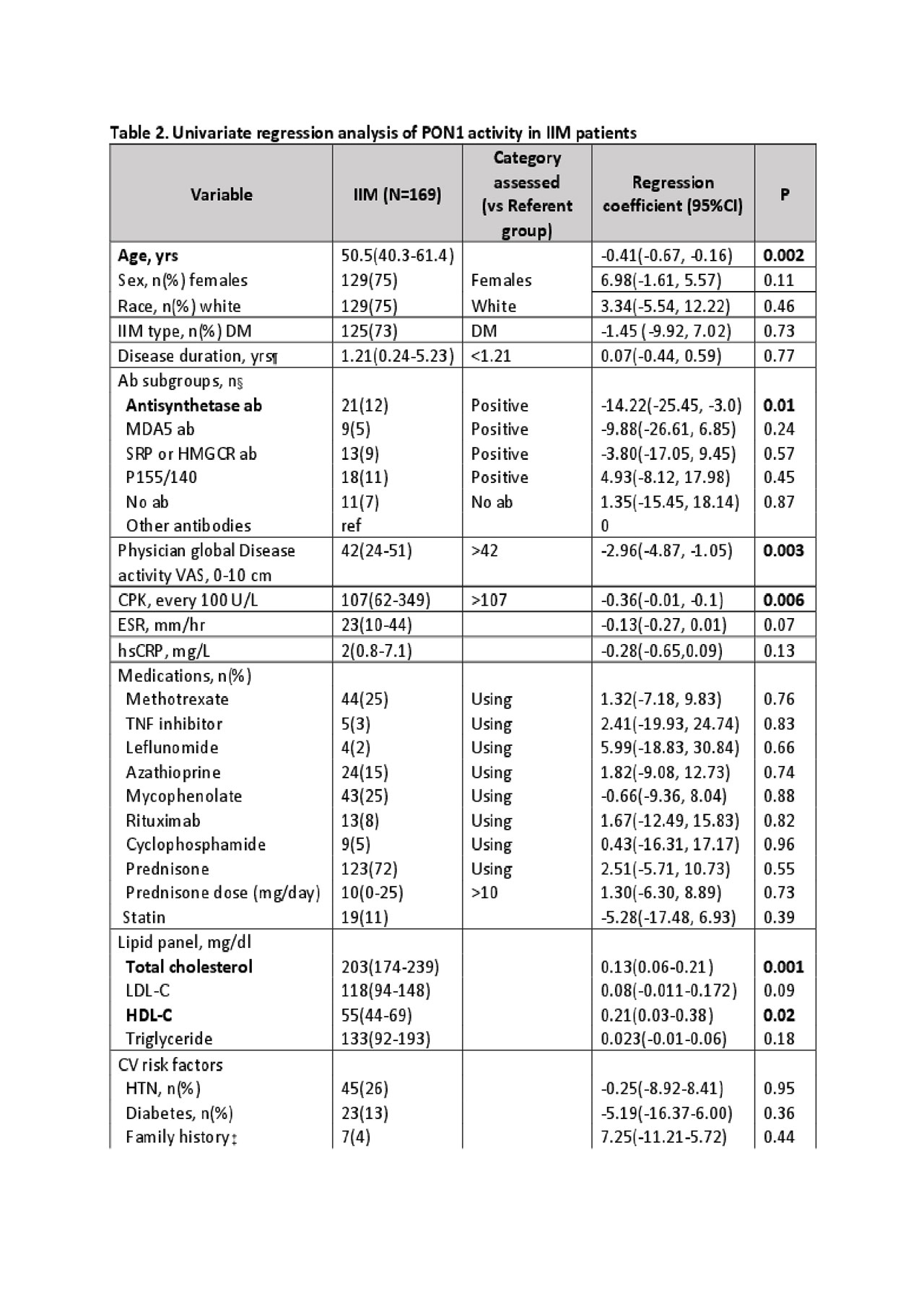
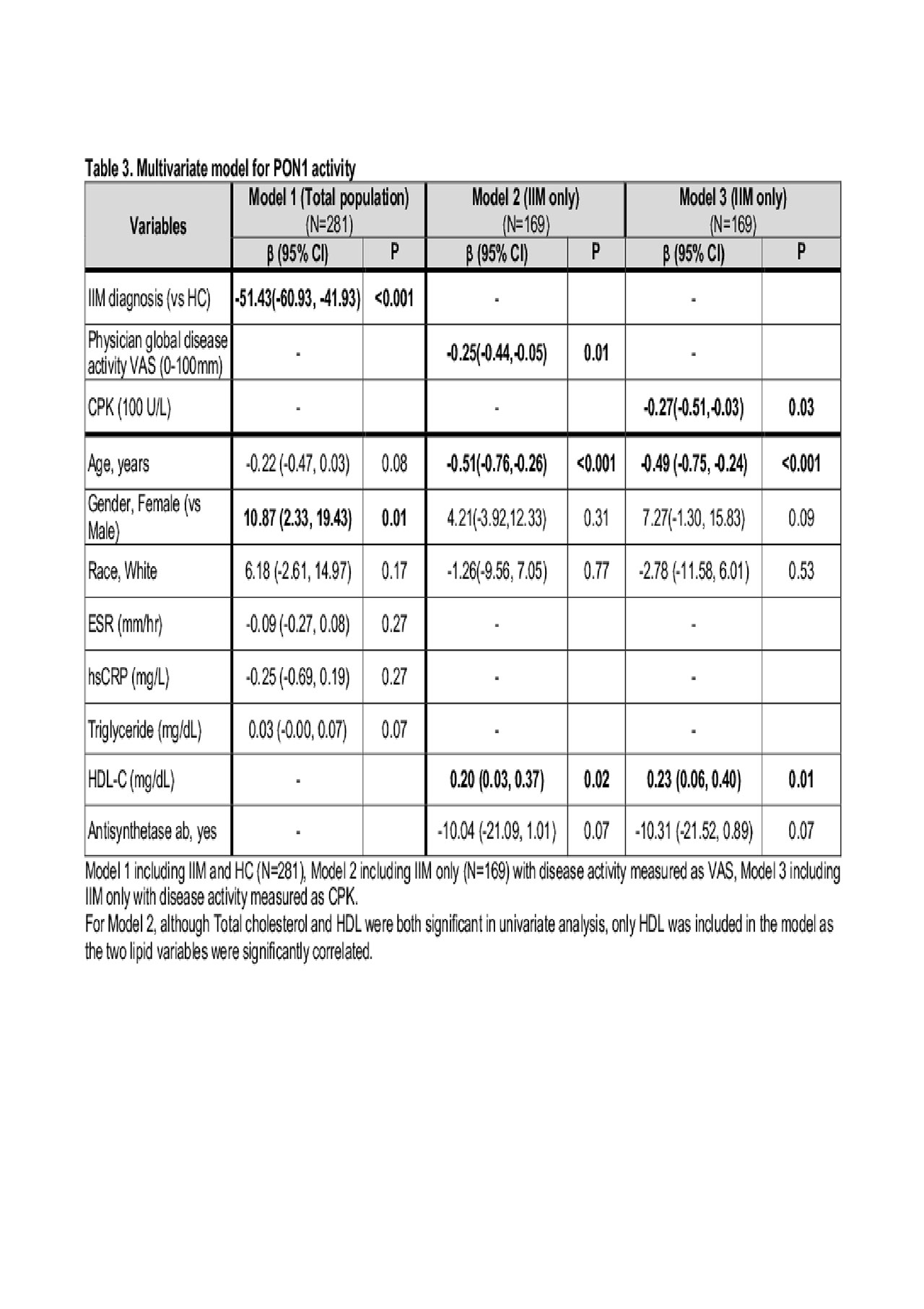
Results: Patients with IIM had significantly lower PON1 activity compared to healthy controls (Table 1). Univariate analysis of PON1 activity in IIM patients showed associations of lower PON1 activity with higher disease activity measured by VAS and CPK, as well as with the presence of antisynthetase antibodies (Table 2). PON1 activity remained strongly associated with IIM diagnosis and myositis disease activity measures after multivariate adjustment for demographic factors (age, gender, race) and factors that were significantly different in univariate analysis (Table 3).
Conclusion: In a large cross sectional cohort of IIM patients, plasma PON1 activity was significantly lower than healthy controls of similar demographics, and was associated with myositis disease activity. Low PON1 activity has been previously associated with increased vascular risk and may warrant further investigation for its role in perpetuation of vascular damage in IIM patients.
# Ab testing available in 112 subjects
# avail in 161; ¶ avail in 171; ‡ avail in 168; § avail in 112
For Model 2, although Total cholesterol and HDL were both significant in univariate analysis, only HDL was included in the model as the two lipid variables were significantly correlated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bae S, Golub I, Wang J, Shahbazian A, Reddy S, Charles-Schoeman C. Paraoxonase 1 Activity Is Abnormal in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies and Associates with Poor Disease Control [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paraoxonase-1-activity-is-abnormal-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-and-associates-with-poor-disease-control/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/paraoxonase-1-activity-is-abnormal-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-and-associates-with-poor-disease-control/