Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: IIMs associate with significant lifelong disability due to progressive loss of muscle function and lack of curative interventions; little is known about the relative contribution of different pain patterns in IIMs. Although not commonly associated with inflammatory myositis, myalgia is a sine qua non component of central pain states and is frequently perceived by patients as a sign of “inflammation”. Our objective is to evaluate the prevalence of central pain in different types of IIM (dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), immune-mediated necrotizing myositis (IMNM), overlap myositis (OM), anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS) and inclusion body myositis (IBM)) and how it relates to objective disease activity measures and patient-reported quality of life measures.
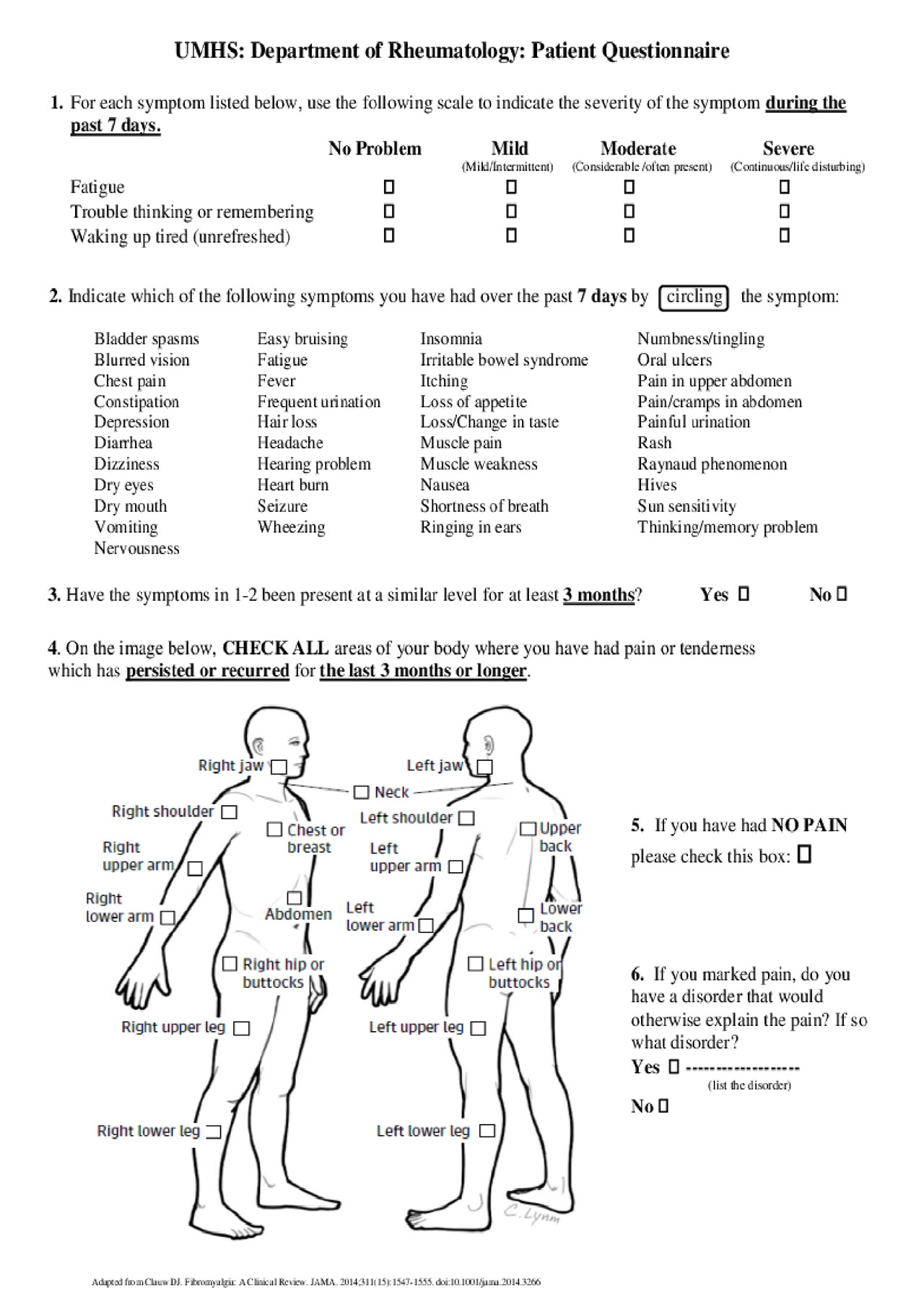
Methods: In a single Myositis Center we collected demographic and clinical information in a cross-sectional manner in 51 consecutive IIM patients (2018-present): age, gender, race, type of IIM, disease duration (from diagnosis to clinic visit), anti-nuclear antibody pattern and titer, myositis specific antibodies, presence/absence of gastrointestinal (GI) and pulmonary (interstitial lung disease, ILD) comorbidities, serum muscle enzymes (creatine kinase (CK), aldolase and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)) and manual muscle testing 8 (MMT8). In addition, each patient completed the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), which includes the pain visual analogue scale (pain VAS), the patient global activity scale (PGA) and the 2010 American College of Rheumatology self-reported Fibromyalgia (FMS) diagnostic criteria, including the symptom severity index (SSI) and widespread pain index (WPI) (Fig. 1). A single assessor (ES) performed the physician global activity (MDGA) and the investigators global assessment of skin involvement (IGA: 0=no involvement, 1= minimal-, 2= mild-, 3= moderate- and 4= severe skin erythema). Descriptive statistics and comparisons on demographic and disease variables between those with or without fibromyalgia using non-parametric statistics (Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney) are presented.
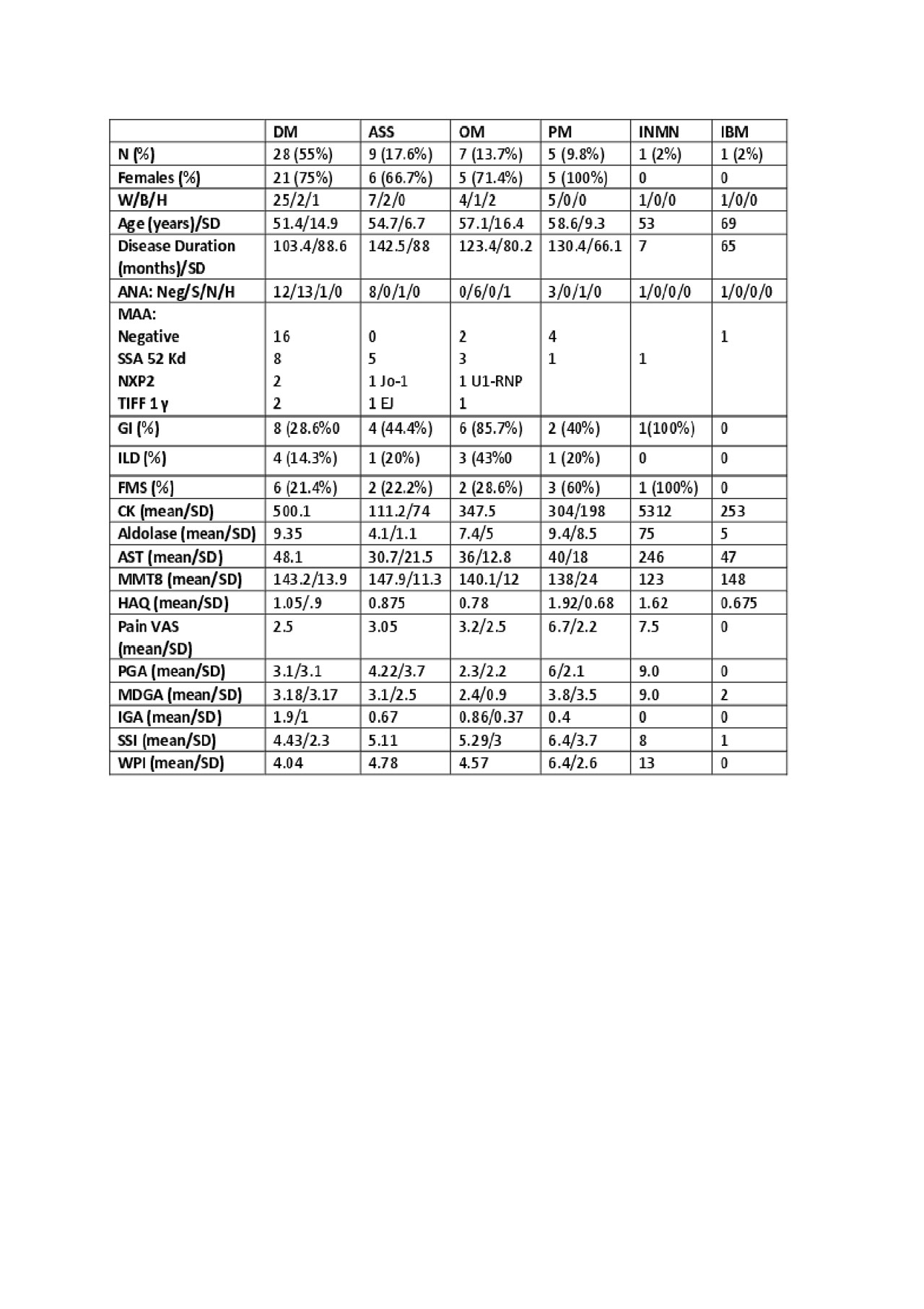
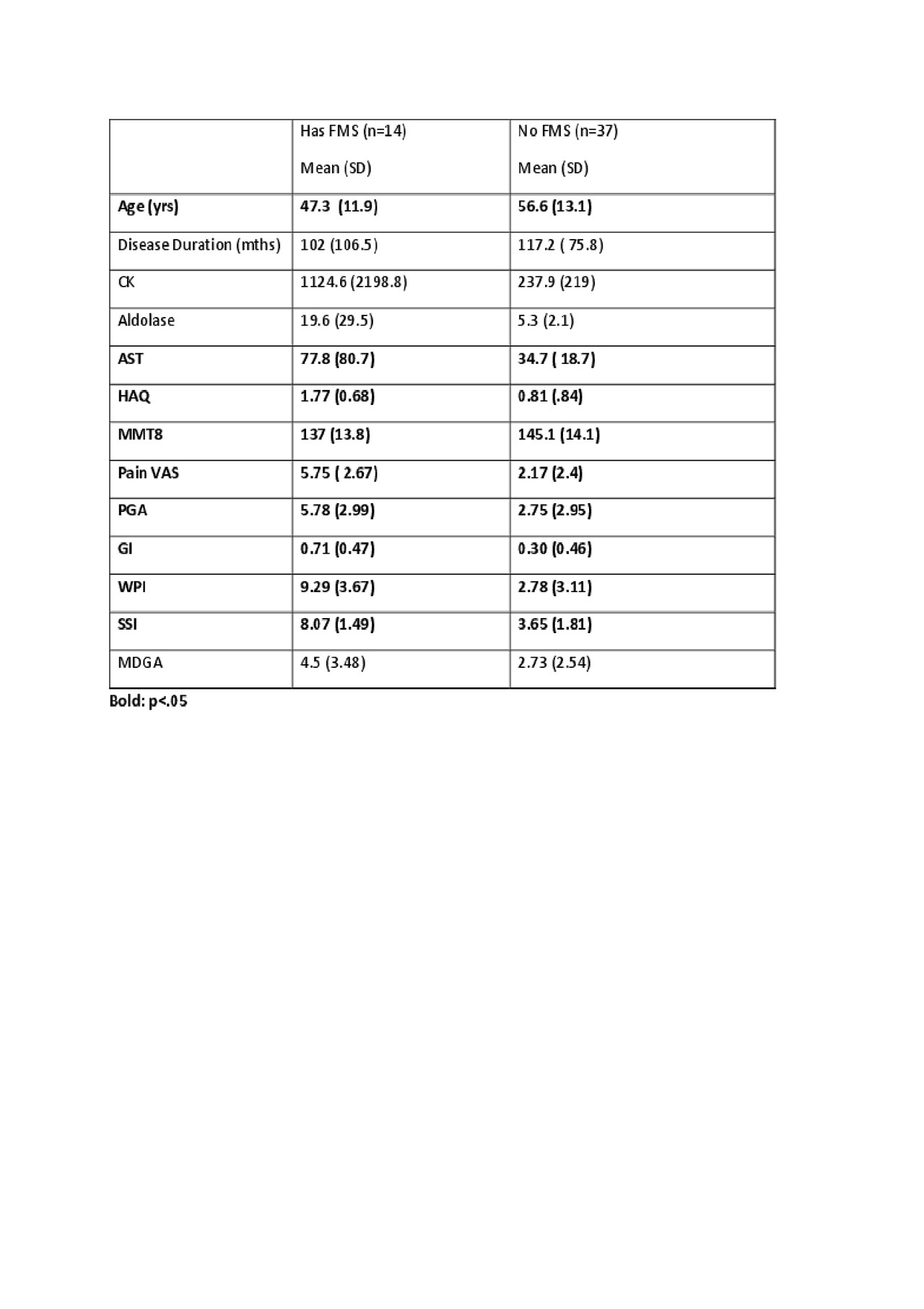
Results: Mean age/SD at the time of analysis was 54/13.3yrs, and the mean/SD disease duration from diagnosis was 113/84 months; most of our cohort had DM (54.9%) and AAS (17.6%), were female (72.5%), white (84.3%), 30 (58/8%) had GI involvement and 17 (33.3%) had ILD. Differences among different IIMs are presented in Table 1. Twelve (23.5%) of the 51 IIM patients met the classification criteria for central pain syndrome (FMS-ness) and the parallels between the groups with and without FMS are presented in Table 2.
Conclusion: A large proportion of patients with IIM met classification criteria for FMS, and when compared to patients without FMS, they were almost a decade younger, weaker, had significantly higher AST (but not aldolase or CK), were more likely to have PM or INMN, and had significantly lower levels of function (∆HAQ almost 1.0). Myalgia is not specific or included in the IIM diagnostic criteria, but it could interfere with rehabilitative exercise. Careful phenotyping of pain patterns in IIMs could help functionality by customizing treatment approaches.
N = number, DM= dermatomyositis, ASS = anti-synthetase syndrome, PM = polymyositis, INMN = necrotizing myositis, IBM = inclusion body myositis, W/B/H = white/black/Hispanic, SD = standard deviation, ANA = anti-nuclear antibody, Neg/S/N/H = negative/speckled/nucleolar/homogeneous, MAA = myositis associated antibodies, GI = gastrointestinal, ILD = interstitial lung disease, FMS = fibromyalgia syndrome, CK = creatine kinase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, MMT8 = manual muscle testing 8, HAQ = health assessment questionnaire, VAS= visual analogue scale, PGA = patient global activity scale, MDGA = physician global activity, IGA = investigators global assessment of skin involvement, SSI = symptom severity index, WPI = widespread pain index.
n = number, GI = gastrointestinal, FMS = fibromyalgia syndrome, CK = creatine kinase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, MMT8 = manual muscle testing 8, HAQ = health assessment questionnaire, VAS= visual analogue scale, PGA = patient global activity scale, MDGA = physician global activity, IGA = investigators global assessment of skin involvement, SSI = symptom severity index, WPI = widespread pain index.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schiopu E, Farshad S, Abdulaziz N, Anderson S, Impens A. Pain Patterns in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy (IIM): Associations with Disease Activity Measures (Muscle Enzymes, Manual Muscle Testing 8), Patient-Reported Quality of Life (HAQ) and Pain Scales (Widespread Pain Index (WPI), Symptom Severity Index (SSI) and Visual Analogue Scale) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-patterns-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-iim-associations-with-disease-activity-measures-muscle-enzymes-manual-muscle-testing-8-patient-reported-quality-of-life-haq-and-pain-scales/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-patterns-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-iim-associations-with-disease-activity-measures-muscle-enzymes-manual-muscle-testing-8-patient-reported-quality-of-life-haq-and-pain-scales/