Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects III: Obesity and Other Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: We sought to identify biomarkers associated with erosive disease and bone loss in an inception rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cohort receiving treat-to-target combination DMARD therapy without oral corticosteroids. Markers of osteoclast activation (RANKL) and inhibition [osteoprotegerin (OPG)], osteoblast inhibition [Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1), sclerostin (SOST), osteopontin (OPN)], were serially tested. The degree of inflammation (TNFa, IL6, IL1b, ACTH); adipose tissue activity (leptin, insulin) and markers of bone turnover/damage [osteocalcin (OC), parathyroid hormone (PTH), fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23)], were also tested.
Methods: Patients with early RA (< 1 year; fulfilling ACR 1987 and/or 2010 classification criteria) received triple therapy (methotrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine) escalated to achieve DAS28 remission. Serum biomarkers were analysed using human bone panel Luminex kits in patients (n=112) at 0, 6, 12 months, and controls (n=33). Responses to treatment were analysed by mixed model regression. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on the within-individual correlations between treatment responses. Erosion and femoral neck bone density (BMD) data were available at 0, 1, 2, 3 years, and were analysed using the biomarker log(mean) as a predictor, adjusted for baseline covariates. Erosion progression was analysed using a zero inflated Poisson regression model.
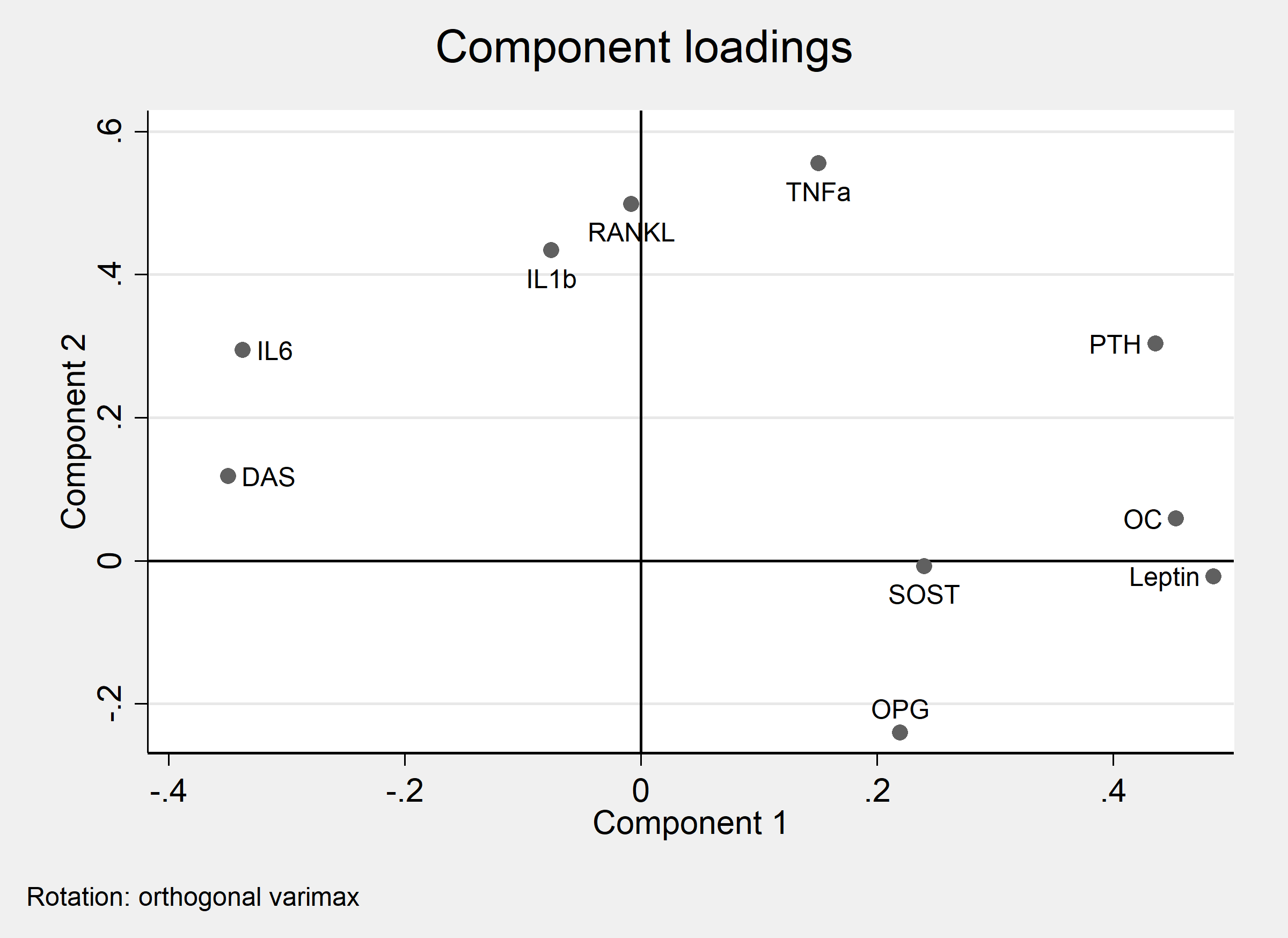
Results: 53% of the cohort were anti-CCP (cyclic-citrullinated peptide) positive; mean (SD) age was 58(14) years, DAS28 5.5(1.3), 73% females, 60% current/past smokers and 20% had erosive disease. Table 1 summarises results. Nine biomarkers changed following therapy: IL6, TNFa, IL1b, RANKL levels were decreased, whereas leptin, SOST, PTH, OC, OPG were increased. IL6 and TNFa represented two different axes of the treatment response (PCA analysis, Figure 1). Anti-CCP positivity (p = 0.009), higher disease activity (p<0.001), OPN (p<0.001), and lower leptin levels (p=0.002) were associated with higher erosion counts, and older age (p=0.001) and higher TNFa (p = 0.022) were associated with a lower probability of remaining erosion-free. Higher TNFa (p=0.003) and lower leptin (p = 0.029) levels were associated with lower BMD.
Conclusion: Biomarkers from both treatment response axes (Figure 1) are associated with erosive disease and bone loss in RA. Low leptin (Component 1) may be a new biomarker for erosive disease and bone loss in RA, and its improvement with treatment was correlated with suppression of IL-6. OPN, which was invariant to treatment, may be a novel biomarker for active erosive disease.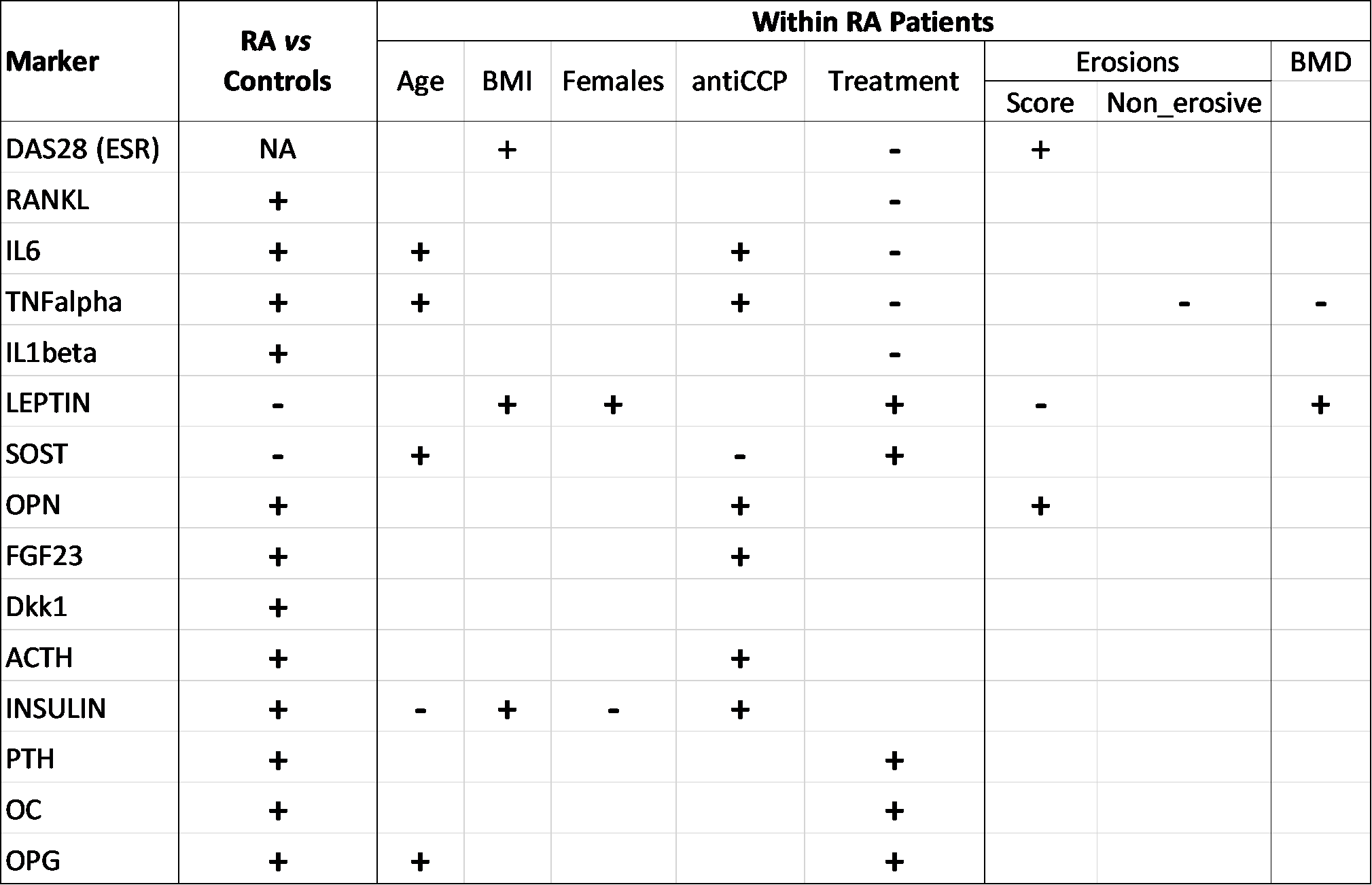
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wechalekar MD, Lester S, Nagpal S, Cole S, Peters J, Das A, Hissaria P, Crotti T, Hill C, Raghunath S, Spargo L, Walker JG, Smith MD, Proudman S. Osteopontin and Leptin Are Associated with Erosive Disease in an Inception Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated-to-Target with Combination Conventional DMARD Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/osteopontin-and-leptin-are-associated-with-erosive-disease-in-an-inception-cohort-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-to-target-with-combination-conventional-dmard-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/osteopontin-and-leptin-are-associated-with-erosive-disease-in-an-inception-cohort-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-to-target-with-combination-conventional-dmard-therapy/
