Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 8, 2017
Title: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies II: Mechanisms of Crystal Inflammation and Metabolism
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Intra-articular basic calcium phosphate (BCP) crystals are associated with advanced osteoarthritis (OA) andsynovitis. OA-associated synovium exhibits increased numbers of macrophages compared with non-OA joints. Total joint replacements (TJR) are performed for advanced OA but periprosthetic osteolysis remains a complication. The local generation of prosthesis-associated wear particles (WP) over time leads to an inflammatory cascade which culminates in implant loosening. Studies suggest that WP-activated macrophages assume a classically activated M1 inflammatory phenotype that overcomes the M2 macrophage-associated activities required for healing. This in turn contributes to the initiation and progression of peri-implant inflammation. Modulating macrophage cytokine production could be a treatment option for periprosthetic inflammation and also OA synovitis.However,the effect of BCP crystals and hydroxyapatite (a component of BCP crystals and commonly used biomaterial) on macrophage polarization has not been previously reported.
We sought to examine 1)macrophage polarization in response to BCP crystals and 2) the signalling pathways involved in BCP crystal, hydroxyapatite (HA) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cement-induced macrophage polarization in primary human macrophages and to determine whether pharmacological blockade of these pathways can impact on M1 macrophage phenotype and inflammatory gene induction.
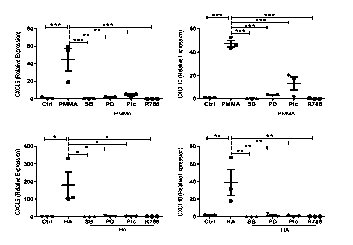
Methods: Primary human macrophages were stimulated with PMMA (500 µg/ml) or hydroxyapatite particles(250 μg/ml) over the course of 30 minutes. Activated Syk, p38 and ERK were detected by immunoblotting using phospho-specific antibodies. mRNA expression levels of M1 and M2 macrophage markers were analysed by q-PCR 24 hrs post-stimulation while cytokine production was measured by ELISA. Statistical analysis was performed by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey post-test where applicable or studentÕs t test when comparing only two observations.
Results: We demonstrate that BCP crystals as well as PMMA and HA particles promote macrophage polarization and pro-inflammatory cytokine production via activation of the membrane proximal kinase, Syk, and members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family of signaling molecules.Pre-treatment of macrophages with Syk or MAPK inhibitors, not only prevents macrophage polarization, but also attenuates production of key pro-inflammatory mediatorsimplicated in periprosthetic osteolysis (Fig) as well as OA
Conclusion: Both BCP crystal and WP-induced macrophage polarization and cytokine production is dependent onactivationof specific intracellular signalling molecules. Improved understanding of the biological cascades activated by microparticles could lead to new treatments to modulate OA synovitis as well as aseptic implant loosening.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McCarthy GM, Mahon O, O'Hanlon S, Kelly D, Dunne A. Osteoarthritis-Associated Calcium-Containing Crystals and Biomaterial Microparticles Both Drive M1 Macrophage Polarization in a Syk and MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/osteoarthritis-associated-calcium-containing-crystals-and-biomaterial-microparticles-both-drive-m1-macrophage-polarization-in-a-syk-and-map-kinase-dependent-manner/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/osteoarthritis-associated-calcium-containing-crystals-and-biomaterial-microparticles-both-drive-m1-macrophage-polarization-in-a-syk-and-map-kinase-dependent-manner/