Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Oncostatin M receptor (OSMR), that binding to oncostatin M (OSM) cytokine are associated with inflammation and cell’s growth and differentiation. OSM uses the OSMR to powerfully induce RANKL production and osteoclast formation and downregulate the expression of Wnt signalling antagonists such as sclerostin in osteocytes, suggesting these cytokines mediate the enhanced bone formation. Our hypothesis is that OSMR are implicated on physiopathology of syndesmophytes formation in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. The objective of this study was to evaluate the OSMR levels in AS patients compared to health controls and correlate with disease activity and treatment.
Methods: Seventy two adults patients with AS and 32 healthy age and sex-matched healthy controls were enrolled. The disease activity was calculated by both Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS/CRP). Cytokines in serum samples were quantified by human sandwich ELISA (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, USA and eBioscience, San Diego, CA). The lower limits of detection according to our standard curves were 156.25 – 20000 pg/mL for OSMR.
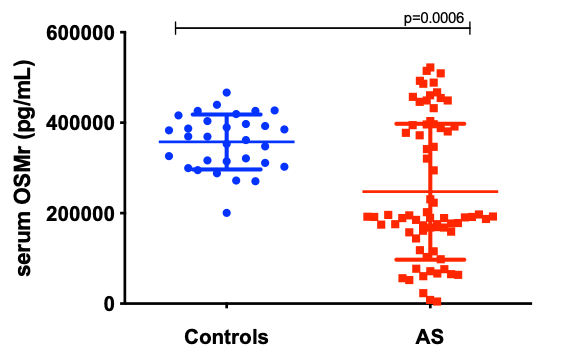
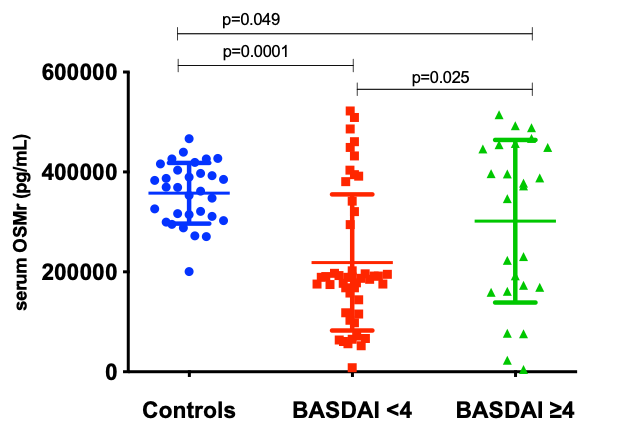
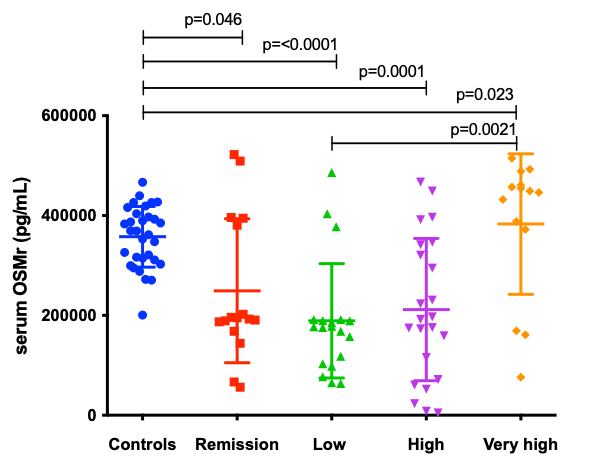
Results: Among the 72 patients with AS, the majority were male (71.2%; n=52), with a mean age 46.6 (10.5), of the diagnostic time of 8.7 (9.8) years. The mean of BASDAI was 3.18 (2.19) and ASDAS/PCR was 2.32 (1.33). Serum OSMR levels were significantly lower in AS patients than in controls (Figure 1). When the AS group was stratified by disease activity, a statistically significant difference was observed between OSMR levels in patients with low (BASDAI < 4) and high disease activity (BASDAI³ 4) when compared to controls (p=0.001 and 0.049, respectively). Statistical difference was also observed among and patients with low and high disease activity (p=0.025) (Figure 2). These results were similar when we used ASDAS cutoff points to assess disease activity (Figure 3). When patients were stratified by treatment, OSMR levels were similar in those that had not yet been treated and in those using anti-TNF alone (p=0.999). Patients who used only SSZ or NSAID had higher OSMR levels at levels similar to controls.
Conclusion: OMSR expression is reduced in patients with AS compared to healthy controls, and these levels are lower in patients who are either on low disease activity or treated with anti-TNF. These results suggest that despite the control of clinical activity, the OSMR mediates the enhanced bone formation in the form of syndesmophytes in an independent way and may eventually become a potential therapeutic target in ankylosing spondylitis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Correia M, Marques C, Almeida A, Silva V, Cavalcanti N, Rego M, Duarte A, Pitta M. Oncostatin M Receptor (OSMR) Underexpression in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oncostatin-m-receptor-osmr-underexpression-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oncostatin-m-receptor-osmr-underexpression-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/