Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – ePoster I: Basic Science, Biomarkers, & Sclerodermic Fever
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Activated T cells are involved in the pathogenesis of the synovitis in oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (o-JIA). T cell activation is counter-balanced via co-inhibitory receptors (co-IRs) such as CTLA-4, PD-1, LAG-3, and TIM-3. Here we identify the role of co-IRs in the pathogenesis of o-JIA.
Methods: Paired synovial fluid (SF) and plasma, PBMCs and SFMCs, were obtained from o-JIA patients together with clinical data (n=14). Plasma from healthy controls (HC, n=14) and paired SF and plasma from 5 children requiring arthroscopy for non-inflammatory orthopaedic problems (OC, n=5) served as controls. Soluble levels of co-IRs were measured by ELISA and their cellular expression by flow cytometry. Spontaneously differentiated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) from SFMCs were co-cultured with autologous PBMCs/SFMCs and used as an ex-vivo disease models. Functional effects of co-IRs were evaluated via blocking them with checkpoint inhibitors in these ex-vivo disease models.
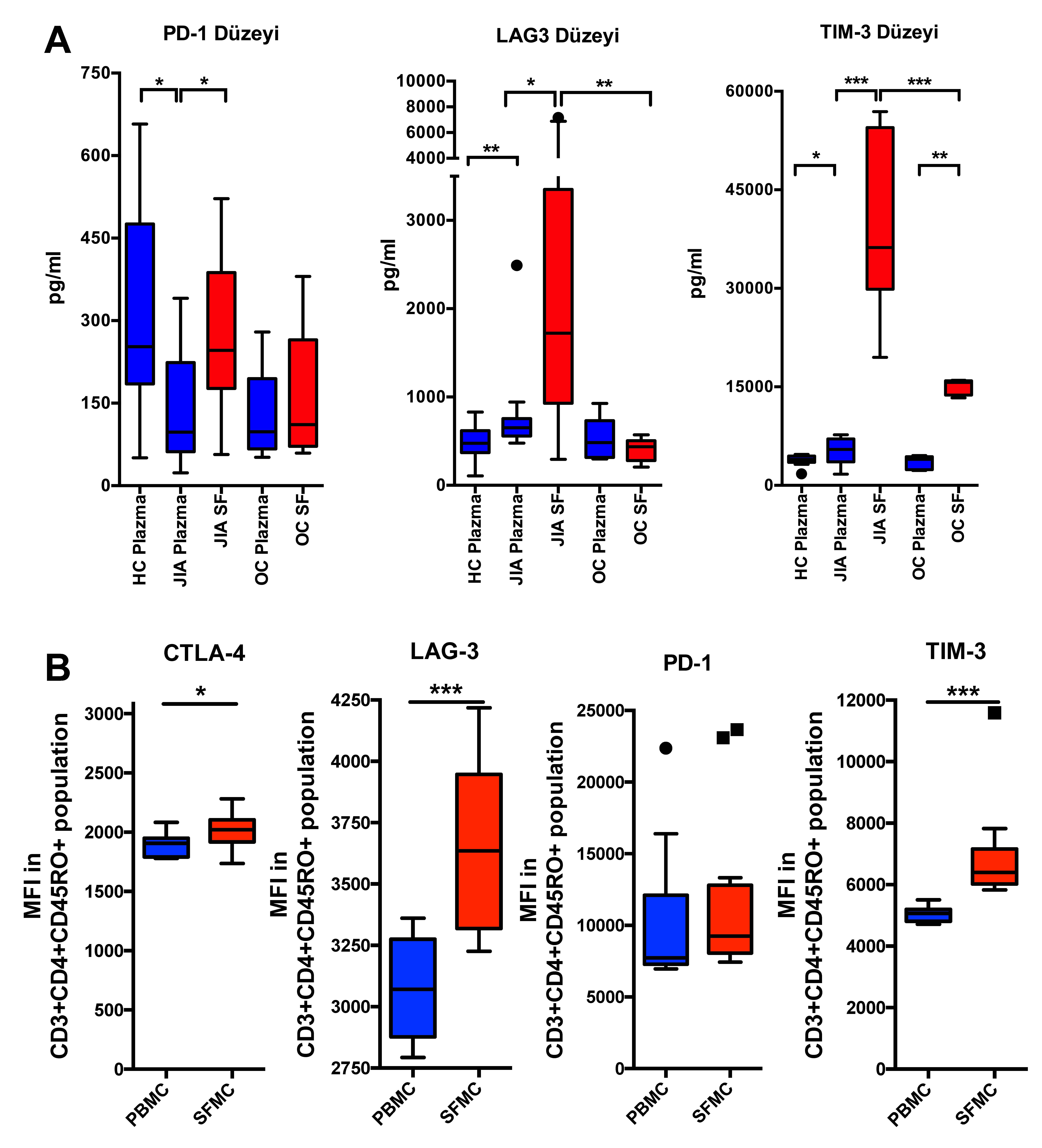
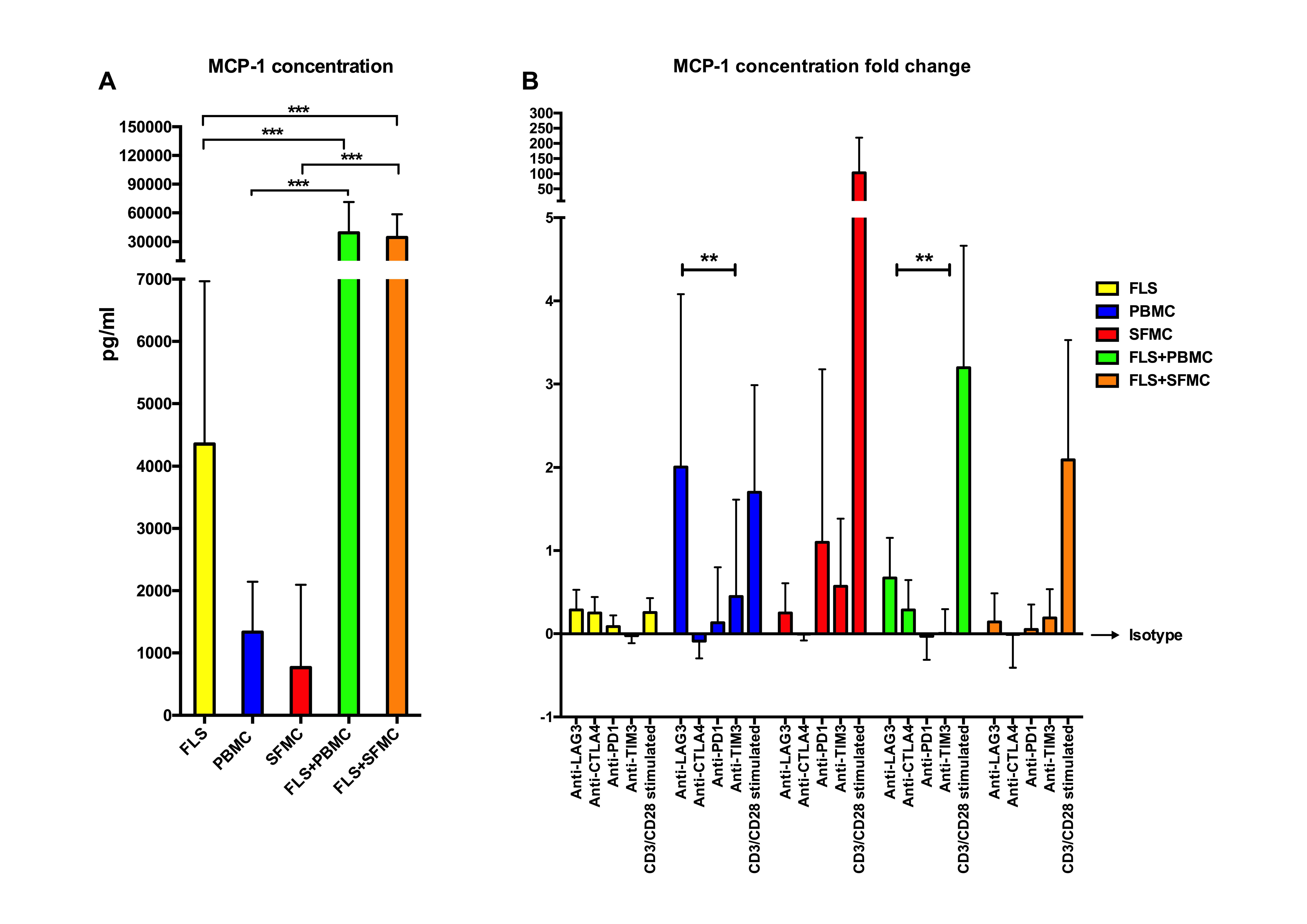
Results: o-JIA patients had increased soluble levels (Figure 1A) and CD3+CD4+CD45RO+ T cell surface expressions of sPD-1, sLAG-3, sTIM-3, but not sCTLA-4 in SF compared with plasma (Figure 1B). Plasma and SF levels of sLAG-3 and TIM-3, but not sPD-1 levels were higher in o-JIA patients compared with controls. (Figure 1A) None of the soluble co-IR levels correlated with disease activity. As CD4 T cell exhaustion is an outcome of continued antigen presentation, we examined if MHC-class II expression was present on these FLS. FLS expressed nearly no MHC-class II molecules in monocultures, but this was readily detected when co-cultured with PBMCs and SFMCs together with an increased Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) production. (Figure 2A) Only anti-LAG3 antibodies significantly increased the MCP-1 production in PBMC monocultures and FLS+PBMC co-cultures. (Figure 2B) PBMCs and SFMCs produced significantly higher levels of IFN-ɣ after CD3/CD28 activation (p< 0.001), but they were not affected by the addition of antibody towards the other checkpoint inhibitors. Conclusion: This is the first report studying the effects of different co-IRs in o-JIA. Both the soluble levels and the surface expressions of co-IRs were higher at the site of inflammation in o-JIA. SFMCs and PBMCs of o-JIA patients are not exhausted, based on their ability to respond to CD3/CD28 activation. This is opposite to what has been shown in adult inflammatory arthritis. Co-cultures of autologous FLSs and PBMCs/SFMCs may serve as an ex-vivo arthritis model to perform functional analysis. LAG-3 might play a role in o-JIA pathogenesis and maybe a potential therapeutic option.
A. Soluble Levels of Co-inhibitor Receptors In Oligoarticular JIA -n=14-, Non-inflammatory Juvenile Orthopaedic Controls -n=5- And Healthy Controls -n=14- In Plasma and SF
B. Surface expressions of Co-inhibitor Receptors In JIA PBMC and SFMCs -n=12-
-HC: Healthy Control, OC: Non-Inflammatory Juvenile Orthopedic Controls, JIA: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, SF: synovial fluid, PBMC: Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells; SFMC: Synovial Fluid Mononuclear Cells, MFI: Median Fluorescence Intensity, sPD-1: soluble Programmed Death-1, sLAG-3: soluble Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3, sTIM-3: soluble T cell Immunoglobulin Mucin 3, CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte associated Antigen 4; Boxes indicate median and IQR, whiskers indicate 10th–90th percentiles*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001-
-FLS: Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes PBMC: Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells; SFMC: Synovial Fluid Mononuclear Cell; MCP-1: Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Cells CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte associated Antigen 4, PD-1: Programmed Death-1, LAG-3: Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3, TIM-3: T cell Immunoglobulin Mucin 3-
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sag E, Demir S, Nielsen M, Hvid M, Turhan E, Bilginer Y, Ozen S, Deleuran B. Oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Displayed Increased Expression of Co-Inhibitory Receptors Without Signs of T-Cell Exhaustion [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-displayed-increased-expression-of-co-inhibitory-receptors-without-signs-of-t-cell-exhaustion/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-displayed-increased-expression-of-co-inhibitory-receptors-without-signs-of-t-cell-exhaustion/