Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The pomegranate fruit is cultivated worldwide for dietary consumption, but has been used therapeutically in Eastern medicine from times dating back to ancient Egypt due to its potent anti-inflammatory properties. Recent studies have attributed this well-documented immunomodulatory influence to anthocyanin and hydrolysable tannins, which are polyphenolic compounds contained in the edible part of the fruit. A commercially- standardized nutraceutical preparation of a polyphenol-rich pomegranate extract (POMx) has previously been created and shown to suppress disease activity in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis and inhibit NFkB activity in human cell lines. In the present study, our objective was to establish an animal model to longitudinally measure systemic effects of POMx on NFkB-mediated inflammation in vivo.
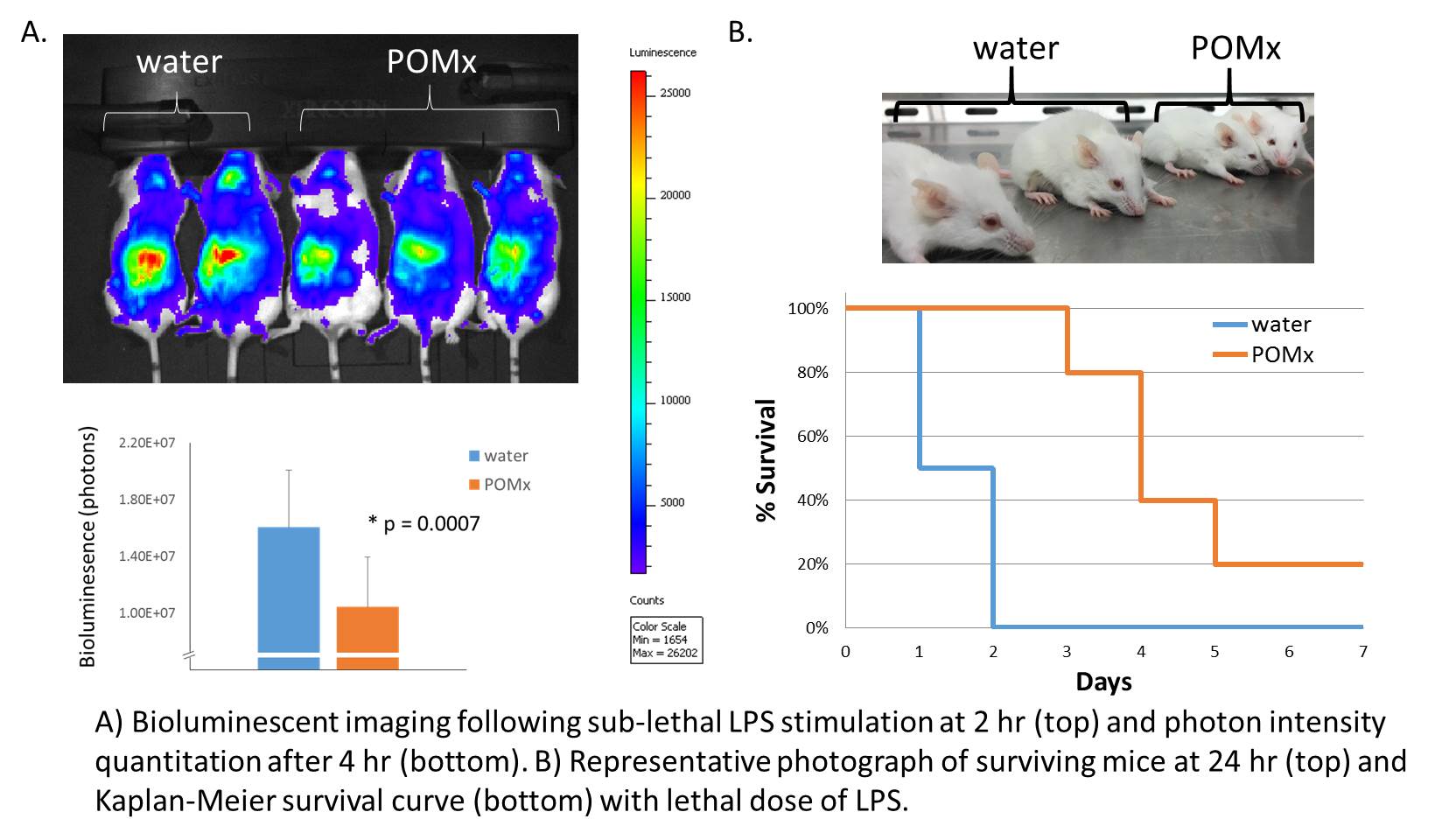
Methods: Endotoxemia was induced in BALB/C-Tg(NFkB-RE-luc)-Xen mice, which have a firefly luciferase cDNA reporter gene under the regulation of 3 kB responsive binding sites, by injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). NFkB-mediated inflammation was determined following a sub-lethal dose of LPS (2 mg/kg) by measuring whole-body bioluminescent signals using the Xenogen in vivo imaging system (IVIS 200). The emitted photons were quantified for each mouse at baseline, 2 hr, 4 hr, and 24 hr. Lethal endotoxemia was induced by LPS injection (25 mg/kg) for survival curve analysis. Prior to any LPS injection, mice were pre-treated for one week with water or POMx (34mg/kg/day) and continued daily treatment was provided in survival experiments.
Results: Relative to NFkB-RE-luc mice given water, POMx inhibited NFκB-induced luciferase activity after sub-lethal endotoxemia induction with LPS injection. Systemic inflammatory responses measured by IVIS photon quantification of NF-kB activation were significantly suppressed with POMx treatment. Lethal endotoxemia led to 50% survival of control mice receiving water after 24 hr, but POMx treatment resulted in 100% survival. Subsequently, while all controls did not survive past 48 hr, daily dosing of POMx resulted in 20% total survival after 7 days.
Conclusion: This novel application of the NF-kB-regulated luciferase mouse model establishes a system that may facilitate the future therapeutic development of POMx as an anti-inflammatory nutraceutical extract by enabling the longitudinal analysis of systemic NFkB-mediated inflammatory responses and will permit further elucidation of the mechanism of NFkB inhibition in vivo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Young NA, Mobeen M, Haqqi TM, Jarjour WN. Nutraceutical Therapy with Polyphenol-Rich Pomegranate Fruit Extract (POMx) Inhibits Systemic NFκB-Mediated Inflammation in a Murine Model of Endotoxemia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nutraceutical-therapy-with-polyphenol-rich-pomegranate-fruit-extract-pomx-inhibits-systemic-nf%ce%bab-mediated-inflammation-in-a-murine-model-of-endotoxemia/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nutraceutical-therapy-with-polyphenol-rich-pomegranate-fruit-extract-pomx-inhibits-systemic-nf%ce%bab-mediated-inflammation-in-a-murine-model-of-endotoxemia/