Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Immunosuppression attenuates immune response to vaccination. A 2-week interruption in low-dose weekly methotrexate immediately after COVID-19 booster improved antibody response to vaccination. There is limited evidence on whether the number of days between previous methotrexate dose and vaccination could affect the antibody response. Our objectives were to explore whether the antibody response to COVID-19 booster was affected by the number of days between previous methotrexate administration and vaccination in those that interrupted or did not interrupt methotrexate treatment for 2-weeks immediately after vaccination against COVID-19.
Methods: Data from the VROOM study were used. VROOM study was a multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised, superiority trial conducted in rheumatology and dermatology clinics in the UK. Adults (aged ≥18 years) with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases taking methotrexate (≤25 mg/week) for ≥3 months, who had received two COVID-19 vaccine doses were randomly assigned (1:1), to temporarily suspend methotrexate treatment for 2 weeks immediately after COVID-19 booster vaccination or continue treatment as usual. S1-RBD antibody titres were measured 4 and 12 weeks after COVID-19 booster vaccination.
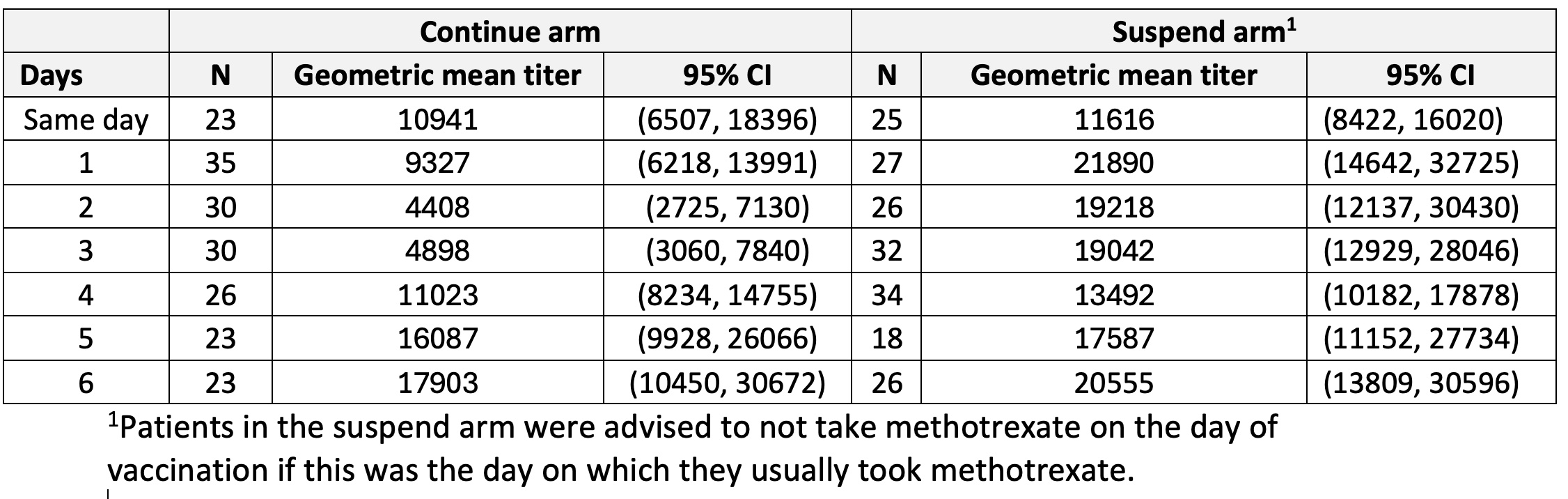
Data from all randomly assigned patients with results for S1-RBD antibody titres, and self-reported information about day on which they usually took methotrexate were included. Geometric mean titre (GMT) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of S1-RBD antibody at weeks 4 and 12 were stratified by number of days since last methotrexate administration and trial arm.
Results: Data from 378 of the 383 patients enrolled into the VROOM study were included. Among them 190 were randomised to continue and 188 were randomised to suspend methotrexate for 2-weeks immediately after COVID-19 booster vaccination. In the continue methotrexate arm at 4-weeks, the S1-RBD antibody GMT (95% CI) was 5497 (3815, 7921) and 6448 (4210, 9877) in those that took their previous methotrexate dose 3 and 2 days before vaccination respectively, compared to 24702 (14858, 41068) and 19705 (12669, 30649) in those that took their previous methotrexate dose 6 and 5 days before vaccination respectively (Table 1). In the continue methotrexate arm at 12-weeks, the S1-RBD antibody GMT (95% CI) was 4898 (3060, 7840) and 4408 (2725, 7130) in those that took their previous methotrexate dose 3 and 2 days before vaccination respectively, compared to 17903 (10450, 30672) and 16087 (9928, 26066) in those that took their previous methotrexate dose 6 days and 5 days before vaccination respectively (Table 2). In the suspend methotrexate arm at 4- and 12-weeks, the GMT of the S1-RBD antibody varied according to the number days between previous methotrexate dose and the day of vaccination against COVID-19 with overlapping 95% CIs (Tables 1, 2).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that vaccination against COVID-19 should be avoided on day 2 and day 3 after low-dose weekly methotrexate administration in those that are unable to suspend low-dose weekly methotrexate treatment for 2-weeks after vaccination against COVID-19. Further confirmatory randomized controlled trials are needed to address this question definitively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abhishek A, Peckham N, Cook J. Number of Days Between Prior Low-dose Weekly Methotrexate Administration and S1-RBD Antibody Response in Adults with Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Vaccinated Against COVID-19: Secondary Analysis of the Vaccine Response On-Off Methotrexate (VROOM) Study Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/number-of-days-between-prior-low-dose-weekly-methotrexate-administration-and-s1-rbd-antibody-response-in-adults-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-vaccinated-against-covid-19-secondary-analys/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/number-of-days-between-prior-low-dose-weekly-methotrexate-administration-and-s1-rbd-antibody-response-in-adults-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-vaccinated-against-covid-19-secondary-analys/