Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
1) To describe the role of MSUS, using both grey scale (GS) and Power Doppler (PD), to detect skin ulcers in SSc patients. 2) To look for initial indications that MSUS may be useful to guide therapy for SSc-ulcers.
Methods:
We examined a convenience sample of 7 SSc patients with skin ulcers by MSUS which was performed using General Electric Logic E9 scanner using a 5-16 MHz linear array transducer. PD settings: pulse repetition frequency 800 Hz, frequency 10 mHz and low wall filter. We proposed preliminary definitions of Ulcer characteristics based on normal skin reference (1). Pain and ulcer measures were obtained using 100 mm visual analogue scales (VAS).
Results:
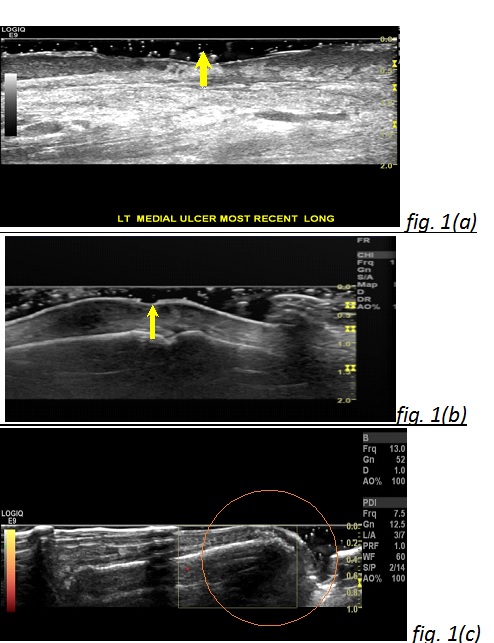
7 SSc patients met 2013 EULAR /ACR criteria for SSc. Median (range) for mRSS: 14 (9-25). 5 patients had diffuse SSc. The 7 patients had 16 clinically apparent skin ulcers. We categorized them on GS as a) skin ulcer (GS-SU); characterized by loss of skin thickness both epidermal and dermal layers, or loss of epidermal layer with irregular hyper-echoic granulation tissue below the level of the surrounding epidermis (figure 1a, b), b) Non-ulcer lesions (GS-NUL); show no loss of epidermal layer but show irregular hyper-echoic tissue at the same or above the level of epidermis (figure 1c).
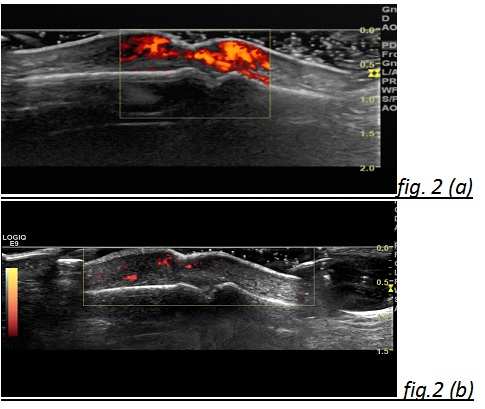
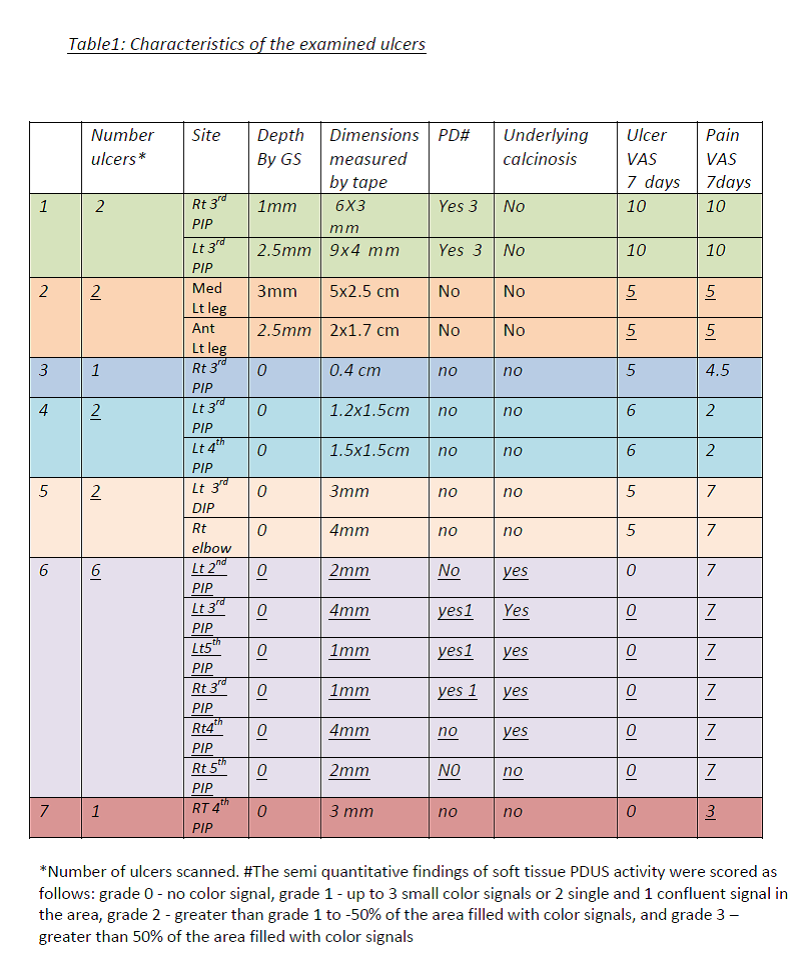
Twelve GS-SU/NUL (75%) were on the PIPs, 2 (13%) on the legs, 1 (6%) on the DIP and 1(6%) on the elbow. Two ulcers in one patient demonstrated high PD signals (presumed underlying infection). After treatment for 15 days with Ciprofloxacin, PD signal was reduced, and both pain and ulcer VASs decreased from 100 mm to 40mm (fig 2a,b). Five lesions showed underlying calcinosis (3 of 5 lesions with calcinosis had evidence of positive PD signals). Variable ulcer depths and dimensions were detected. The highest pain and ulcer VASs (100mm) were recorded in the ulcers with the highest PD signal (table 1).
Conclusion:
This is the first study to show a promising role of MSUS in evaluating skin ulcers in SSc patients. MSUS may have a role in identifying depth and underlying pathology (i.e. infection and calcinosis) of the lesion. Hence, MSUS can add clinical information and help in guiding treatment. Future studies are warranted with more SSc patients to further validate our preliminary findings.
Ref (1)Wortsman X. Sonography of Cutaneous and Ungual Lumps and Bumps Ultrasound Clin 7 (2012) 505–523
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Suliman Y, Ranganath VK, Kafaja S, Furst DE. Novel Use of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound (MSUS) to Measure Ulcers in the Skin of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Patients. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-use-of-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-msus-to-measure-ulcers-in-the-skin-of-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-use-of-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-msus-to-measure-ulcers-in-the-skin-of-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-patients/