Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: BHV-1300 is a molecular degrader of extracellular protein (MoDETM) in development for the treatment of IgG-driven autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis. MoDEs are bifunctional molecules that reduce pathogenic IgG autoantibodies and immune complexes through asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR)-mediated lysosomal degradation in the liver.
TNFα inhibitors and other biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs), the cornerstone of RA therapy, do not achieve sustained remission in a large proportion of patients. The development of neutralizing anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) can reduce the efficacy of these agents.
Unlike other IgG targeting approaches (i.e. FcRN inhibitors), BHV-1300 can be co-administered with Fc-containing bDMARDs. BHV-1300 has the potential to lower pathogenic autoantibodies, and immune complexes, and to optimize the efficacy of bDMARDs by reducing ADAs.
Methods: Studies were conducted in cynomolgus monkeys to (1) assess the PK of adalimumab when co-administered with BHV-1300 and (2) evaluate the ability of BHV-1300 to remove adalimumab ADAs and restore anti-TNFα activity.
Study 1: 6 groups of cynos (3/group, N=18) received single doses of adalimumab (3 mg/kg SC x1) at various times relative to BHV-1300 (30 mg/kg IV x1). Concentrations of BHV-1300 and adalimumab were determined by LCMS and ELISA, respectively.
Study 2: Cynos received adalimumab (10 mg/kg) in CFA followed by two QW doses of adalimumab in PBS (10 mg/kg). ADA positive cynos were randomized to Groups 1 and 2, and ADA negative cynos were placed in Group 3. Group 2 received active drug (BHV-1300 50 mg/kg IV x1) while Groups 1 and 3 received placebo. After 24 hours, all cynos received adalimumab (3 mg/kg SC x1). Readouts included adalimumab PK, adalimumab’s neutralizing activity of TNF-a, total IgG and PK of BHV-1300.
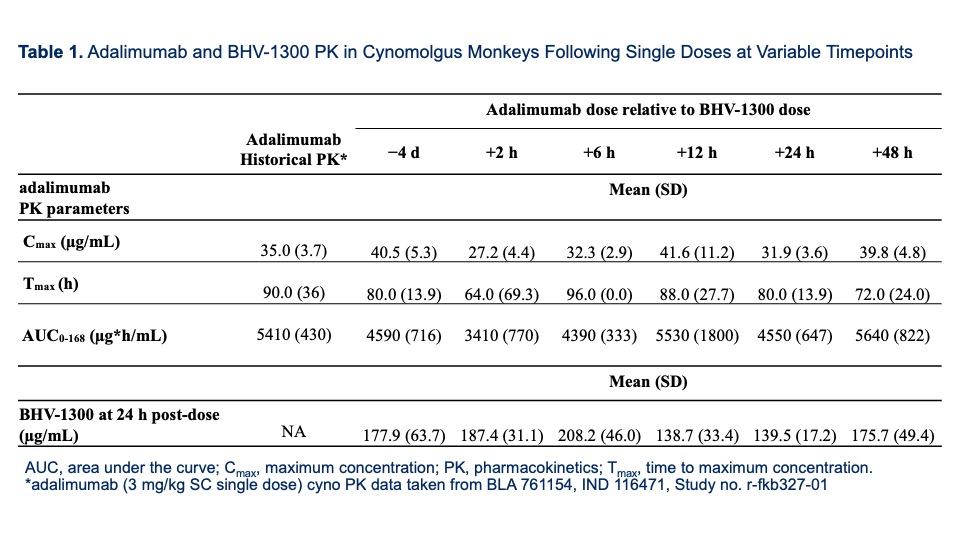
Results: In Study 1, adalimumab PK, at all timepoints from 6- to 48-hours post-dosing with BHV-1300, was within 20% of historical values. Concentrations of BHV-1300 at 24 hours post-dose showed < 1.5x difference across the 6 groups (see Table 1).
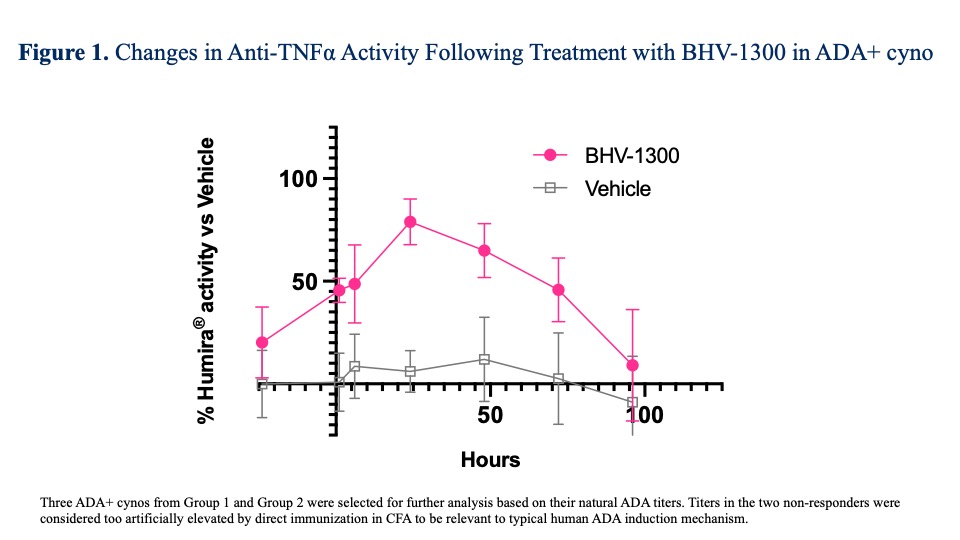
In Study 2, 3/5 cynos in Group 2 had improvement in ADA titers following treatment with BHV-1300 vs. 0/5 untreated ADA-positive cynos. There were significant improvements in adalimumab anti-TNFα activity in BHV-1300 treated ADA+ cynos vs. PBO (Group 2 BHV-1300 vs. Group 1 Vehicle, respectively, Figure 1).
Conclusion: These data demonstrate BHV-1300 does not adversely affect exposure to adalimumab and that it can reduce neutralizing ADAs. MoDE IgG degraders can be co-administered with bDMARDs in RA. Thus, MoDE degraders offer a unique combinatorial therapeutic approach for difficult to treat RA and other rheumatologic diseases, enabling removal of ADAs, pathogenic autoantibodies, and immune complexes as key differentiated features compared to other approaches.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dierks E, Bunin A, Ackerman P, Heller D, Engler F, Dubowchik G, Spiegel D, Qureshi I, Pirman D, Coric V, Car B. Novel IgG Degrader BHV-1300 Demonstrates the Ability to Remove Anti-bDMARD ADA and Allows for Co-administration with Fc-containing Biologics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-igg-degrader-bhv-1300-demonstrates-the-ability-to-remove-anti-bdmard-ada-and-allows-for-co-administration-with-fc-containing-biologics/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-igg-degrader-bhv-1300-demonstrates-the-ability-to-remove-anti-bdmard-ada-and-allows-for-co-administration-with-fc-containing-biologics/