Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by arterial, venous, or microvascular thrombosis, recurrent pregnancy morbidity, or non-thrombotic manifestations in the setting of persistent antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), namely anti-β2 glycoprotein-I antibody (aβ2GPI), anticardiolipin antibody (aCL), and lupus anticoagulant (LAC). Around one-third of the APS patients had an isolated LAC positivity lacking aβ2GPI and aCL. This study aimed to identify novel autoantibodies in APS using protein microarray technology.
Methods: Sera from APS patients, disease controls (DCs), and healthy controls (HCs) were applied to the HuProt™ Human Proteome Microarray v4.0 for the discovery of novel autoantibodies. Candidate autoantibodies were then validated using ELISA in an additional 372 sera samples, comprising 189 primary APS patients, 87 secondary APS patients, 48 SLE patients, and 48 HCs.
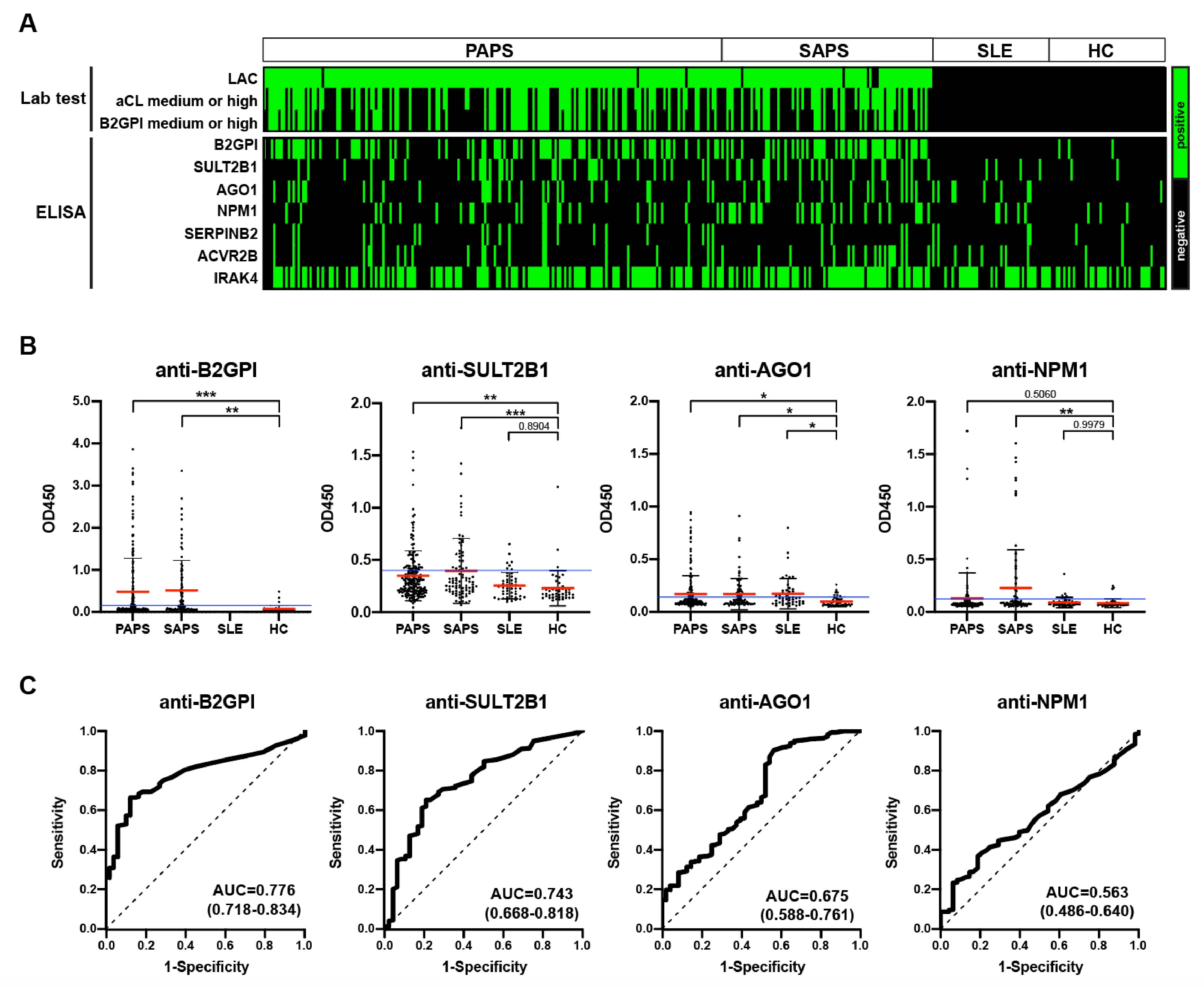
Results: During the discovery phase, HuProt microarrays were incubated with serum samples (5:1 mixture) from APS patients, DCs, and HCs to identify APS-associated autoantigens. Approximately twenty autoantigens were identified for subsequent validation. These potential autoantigens include proteins involved in or associated with ubiquitination and deubiquitination (UBE3A, ATXN3), proteasome (PSME3), microtubule (MAP9), vesicular transport (ASAP2), ribosome (NPM1, RPLP2), amino acid modification (PRMT7), DNA and RNA (RBM38, IRX2, AGO1), inflammation (WDR54, IRAK4, ACVR2B, N4BP1, MX1), metabolism (ACSBG1, SULT2B1, HK1, GLOD4), coagulation factor (SERPINB2), and others. In the validation phase, six proteins (SULT2B1, NPM1, AGO1, SERPINB2, ACVR2B, IRAK4) were selected and validated using ELISA. Anti-SULT2B1 and anti-AGO1 autoantibodies were significantly higher in primary APS patients. Anti-SULT2B1, anti-AGO1, and anti-NPM1 were also significantly higher in secondary APS patients. Anti-NPM1 positive patients exhibited a significantly higher incidence of SLE (50.9% vs 33.7%, p=0.013), cardiac valve involvement (16.3% vs 6.1%, p=0.031), and triple positivity (53.1% vs 33.5%, p=0.010) compared to anti-NPM1 negative patients. Validation of other autoantibodies is ongoing.
Conclusion: We identified novel autoantibodies targeting proteins involved in a broad range of biological processes in APS. Anti-SULT2B1, anti-AGO1, and anti-NPM1 autoantibodies were identified in APS patients, demonstrating diagnostic and clinical value. Further validation of additional autoantibodies in larger APS cohorts is ongoing.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hu S, Zhou Y, Cai M, Li M, ZHAO J. Novel Autoantibodies Identified in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-identified-in-the-antiphospholipid-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-identified-in-the-antiphospholipid-syndrome/